|
Billing and coding for Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression (MILD) procedures is a complex process requiring detailed understanding of procedural codes, diagnosis codes, documentation requirements, and adherence to clinical guidelines. This comprehensive guide will cover these aspects in depth, ensuring a clear understanding of the entire process. Introduction to MILD Procedures Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression (MILD) is a surgical technique used to treat lumbar spinal stenosis. This condition involves the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can compress nerves and lead to pain, numbness, or weakness in the lower back and legs. The MILD procedure aims to relieve this pressure with minimal tissue disruption, making it a preferred option for many patients. Billing and Coding for MILD Procedures CPT Codes for MILD Procedures The Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes are essential for accurately billing medical procedures. For MILD procedures, the primary CPT code is:
ICD-10 Codes for Diagnoses In addition to procedural codes, International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) codes must be used to identify the patient’s diagnosis. Common ICD-10 codes for conditions treated with MILD procedures include:
Documentation Requirements for MILD Procedure Accurate and thorough documentation is critical for successful billing and reimbursement. The documentation should provide a clear and comprehensive picture of the patient’s condition, the necessity of the procedure, and the details of the procedure itself. Key Components of Documentation
Clinical Guidelines and Resources Adhering to clinical guidelines is essential to ensure that the MILD procedure is medically necessary and performed according to best practices. Here are some relevant guidelines and resources: Medicare Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs) Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs) are policies developed by Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) that provide guidance on the coverage of specific procedures. These policies can vary by region, so it’s important to refer to the LCDs applicable to the provider’s location. LCDs typically include information on covered indications, documentation requirements, and billing guidelines for the MILD procedure. National Coverage Determinations (NCDs) National Coverage Determinations (NCDs) provide national policy on whether Medicare will pay for an item or service. Although there may not be a specific NCD for the MILD procedure, general guidelines for spine surgery can be helpful. For instance, the NCD for Lumbar Spinal Fusion Surgery provides criteria that can be relevant for determining the medical necessity of procedures addressing spinal stenosis.
The ASIPP provides guidelines for interventional pain procedures, including those for lumbar spinal stenosis. These guidelines offer evidence-based recommendations on patient selection, procedural techniques, and post-procedure care. Clinical Guidelines on the Management of Lumbar Spinal Stenosis Clinical guidelines on the management of lumbar spinal stenosis offer comprehensive information on the diagnosis and treatment options for this condition. These guidelines are often developed by professional organizations and can be accessed through medical journals or databases like PubMed. Medicare and CMS Guidelines Compliance with Medicare and CMS guidelines is crucial for accurate billing and reimbursement. Providers should familiarize themselves with the following resources: CMS Manual SystemThe CMS Manual System includes the Medicare Claims Processing Manual and the Medicare Program Integrity Manual. These manuals provide detailed information on billing and coding practices, including specific instructions for surgical procedures like the MILD procedure.
The NCCI edits are designed to promote correct coding methodologies and prevent improper coding that leads to inappropriate payment. Providers should ensure that they are in compliance with these edits to avoid claim denials. Detailed Explanation of the MILD Procedure Understanding the clinical aspects of the MILD procedure helps in accurate documentation and justification of its medical necessity. Indications for MILD Procedure The primary indication for the MILD procedure is lumbar spinal stenosis causing neurogenic claudication. Patients typically present with symptoms such as:
A thorough preoperative evaluation is essential to confirm the diagnosis and assess the suitability of the patient for the MILD procedure. This includes:
The MILD procedure is performed using specialized instruments to remove small portions of bone and ligament through a tiny incision, relieving pressure on the spinal nerves. The key steps include:
Postoperative care involves monitoring the patient for complications, managing pain, and providing instructions for activity modification. Follow-up appointments are essential to assess the patient’s recovery and address any concerns. Importance of Compliance and Accurate Coding Compliance with billing and coding guidelines is not only crucial for reimbursement but also for avoiding legal and financial repercussions. Accurate coding ensures that the healthcare provider is appropriately compensated for the services rendered, while also preventing issues such as:
Challenge 1: Staying Updated with Coding ChangesCoding guidelines and reimbursement policies are subject to frequent changes. Keeping up with these changes can be challenging but is essential for compliance. Solution: Regularly subscribe to updates from professional organizations, CMS newsletters, and coding resources. Attend workshops and webinars to stay informed about the latest changes in billing and coding practices. Challenge 2: Ensuring Thorough DocumentationIncomplete or inaccurate documentation can lead to claim denials and compliance issues. Solution: Implement standardized documentation templates that include all necessary components such as patient history, imaging studies, procedural details, and post-operative care. Regular training sessions for staff on documentation best practices can also help. Challenge 3: Proper Use of CPT and ICD-10 CodesSelecting the correct CPT and ICD-10 codes for the MILD procedure and associated diagnoses is crucial for accurate billing. Solution: Use coding software and tools that assist in selecting the appropriate codes based on the documented procedure and diagnosis. Regularly review coding guidelines and ensure that coders are certified and well-trained. Challenge 4: Meeting Medical Necessity RequirementsProving medical necessity is essential for reimbursement. Insufficient evidence can result in denied claims. Solution: Ensure that the documentation includes detailed information about the patient’s condition, previous treatments, and why the MILD procedure is necessary. Adhere to clinical guidelines and payer policies when determining medical necessity. Best Practices for Successful Billing and Coding Following best practices can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of billing and coding for MILD procedures. 1. Use Detailed and Clear Documentation Comprehensive documentation should include the following:
Continuous education and training for coding staff, physicians, and administrative personnel are crucial. This includes:
Utilize technology to streamline the billing and coding process:
Establish a compliance program to monitor and enforce adherence to coding and billing guidelines. This includes:
Medicare and CMS Resources Medicare and CMS offer various resources that can assist in the billing and coding process for MILD procedures. CMS Manual System The CMS Manual System includes several manuals that provide detailed information on billing and coding practices. These manuals are essential for understanding Medicare policies and ensuring compliance.
NCCI edits are designed to promote correct coding methodologies and prevent improper coding that leads to inappropriate payment. Providers should ensure compliance with these edits to avoid claim denials.
American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians (ASIPP) GuidelinesThe ASIPP provides evidence-based guidelines for interventional pain procedures, including those for lumbar spinal stenosis. These guidelines offer recommendations on patient selection, procedural techniques, and post-procedure care.
These guidelines provide comprehensive information on the diagnosis and treatment options for lumbar spinal stenosis. They are often developed by professional organizations and can be accessed through medical journals or databases like PubMed.
0 Comments
Orthopedic spinal fusion is a surgical procedure used to join two or more vertebrae in the spine. This process can help stabilize the spine, reduce pain, and correct deformities. Accurate coding and billing for these procedures are essential for proper reimbursement and compliance with healthcare regulations. This guide will explain the key terminology, procedures, techniques, and CPT® codes associated with orthopedic spinal fusion. Spinal Fusion Techniques and Procedures Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF): Procedure Description: In a PLIF procedure, the surgeon makes a midline incision in the back to access the lumbar spine. The affected disc is removed, and bone graft material is placed between the vertebrae to facilitate fusion. This technique helps alleviate pain caused by conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, or spinal instability.
Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF): Procedure Description: Similar to PLIF, TLIF involves a posterior approach but accesses the vertebral body at an angle. The surgeon makes an incision on the side of the spine, removes the affected disc, and inserts bone graft material to promote fusion. This technique minimizes disruption to the spinal muscles and may reduce recovery time.
Procedure Description: In an ALIF procedure, the surgeon makes an incision in the abdomen to access the spine. The affected disc is removed, and bone graft material is placed in the intervertebral space to promote fusion. This approach avoids the posterior muscles and nerves, potentially reducing postoperative pain.
Procedure Description: The surgeon makes an incision on the patient's side to access the intervertebral space anteriorly. This technique minimizes disruption to muscles and nerves, providing a clear path to the interbody space. Bone graft material is placed between the vertebrae to facilitate fusion.
Procedure Description: In an OLIF procedure, the surgeon makes an oblique incision to access the interbody space, avoiding the psoas muscle and minimizing the risk of nerve damage. Bone graft material is inserted to promote fusion.
Instrumentation for Spinal Fusion Posterior Instrumentation: Instrumentation provides stability to the spine and supports the fusion process. Different types of posterior instrumentation include non-segmental and segmental fixation methods.
Anterior instrumentation is used to stabilize the spine through an anterior approach. These procedures often involve inserting rods, screws, and other hardware from the front of the spine to provide support and promote fusion.
Spinal prosthetic devices are crucial in maintaining disc space and providing spinal stability, particularly when natural disc material is removed. These devices, such as synthetic cages and meshes, help maintain the proper alignment of the spine and can promote bone growth.
Bone Grafting: Bone grafting is an essential part of spinal fusion procedures, as it facilitates the growth of new bone tissue to achieve a successful fusion. Different types of bone grafts include autografts, allografts, and synthetic grafts.
Billing and Coding tips: Prosthetic Devices: CPT Code 22853: Insertion of interbody biomechanical device(s) (e.g., synthetic cage, mesh) with integral anterior instrumentation for device anchoring (e.g., screws, flanges), when performed, to intervertebral disc space in conjunction with interbody arthrodesis, each interspace (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure). Breakdown of CPT Code 22853Components of the Procedure:
Diagnosis: Severe lumbar disc degeneration and spondylolisthesis at L4-L5 causing chronic back pain and radiculopathy. Procedure: Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF) at L4-L5 with insertion of a synthetic cage and anterior instrumentation. Coding and Billing:
Example Clinical Cases with Instrumentation, Billing & Coding, Place of Service, Technical and Professional Fees, Modifiers, Global Period, ICD-10 Codes, Clinical Policies, and Local Coverage Determination 1. Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (PLIF) Clinical Case:
Clinical Policies and Local Coverage Determination:
2. Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF) Clinical Case:
Clinical Policies and Local Coverage Determination:
3. Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF) Clinical Case:
Clinical Policies and Local Coverage Determination:
4. Direct Lateral Interbody Fusion (DLIF) Clinical Case:
Clinical Policies and Local Coverage Determination:
5. Oblique Lateral Interbody Fusion (OLIF) Clinical Case:
Clinical Policies and Local Coverage Determination:
Reporting Co-surgeries for Spinal Fusion Procedures Source: CPT® Assistant July 1996 page 7 Coding Tip Reporting Cosurgeries "We receive many questions concerning how to report surgeries performed by more than one physician. To help you understand the proper coding we present the following information." The General Question "I am a general surgeon who sometimes performs surgeries with other surgeons (cosurgeries), such as orthopedic or neurosurgeons. I open the surgical site, the other surgeon does the definitive portion of the procedure, and then I close. What CPT codes should I report for my services? I have heard from some sources that I should bill for a thoracotomy and wound repair. But other sources have told me to report the same CPT codes as the other surgeon. Which is correct? CPT® ASSISTANT'S REPLY: Here's How to Code: "For situations in which one surgeon performs the opening and closing of a surgery and another physician performs the definitive portion of the procedure, both physicians should report the same CPT codes, and appropriately append either modifier -62 or modifier -66." Illustration A patient's surgery includes arthrodesis of two interspaces of the thoracic spine by anterior interbody technique, with anterior instrumentation of three vertebral segments. Physician "A" performs a thoracotomy at the start of the surgical session, and Physician "B" performs the arthrodesis and spinal instrumentation. Upon completion of the arthrodesis and spinal instrumentation, Physician A closes the operative site. Coding the Illustration (The physicians in the illustration would report the codes indicated below.) Physician A 22556-62 Physician B 22556-62 22558-62 22558-62 22845-62 22845-62 When performing these cosurgeries, it is important to communicate with the other surgeon's office to be certain that you submit the claims properly Important Billing and Coding Tips for Lumbar Spinal Fusion Procedures
Best Practices and Compliance for Lumbar Spinal Fusion Billing and Coding
Citations and Sources:
Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions for Prior Authorization services? Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions?
Below is a comprehensive guide to the most common Medicare denial codes, their meanings, prevention strategies, and steps on how to fix them if encountered.
Detailed Overview of Medicare Denial Codes with Prevention and Fixes (Continued)
COMPREHENSIVE GUIDE TO AVOIDING MEDICARE CLAIM DENIALS: UNDERSTANDING DENIAL CODES AND BEST PRACTICES Detailed Overview of Medicare Denial Codes with Prevention and Fixes (Continued)
Strategies to Prevent Medicare Claim DenialsAccurate and Complete Documentation
While understanding and preventing Medicare claim denials is crucial, it is equally important to know how to effectively respond to them when they do occur. Here are some detailed strategies for managing and appealing denied claims: Steps to Respond to Claim Denials
Summary Recap:
Advanced Strategies for Denial ManagementIn addition to the foundational strategies outlined previously, employing advanced techniques can further enhance your ability to prevent and manage Medicare claim denials. These advanced strategies involve leveraging technology, refining workflows, and adopting best practices in documentation and coding. Leveraging Technology for Denial Management
Looking for Prior Authorization Services for Pain Management? Here’s What You Need to Know7/19/2024 Navigating the complexities of prior authorization (PA) services in pain management can be challenging. Whether you're a healthcare provider or a patient, understanding the intricacies of prior authorization can streamline the process and ensure timely access to necessary treatments. In this article, we'll delve into what prior authorization entails, why it's essential for pain management, and how specialized services can make a significant difference. The Importance of Prior Authorization in Pain Management
Prior authorization is a critical component of pain management, ensuring that patients receive necessary and effective treatments while controlling costs. By leveraging professional prior authorization services, healthcare providers can navigate this complex process more efficiently, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes. If you are looking for reliable prior authorization services for pain management, ensure they have the experience, efficiency, and support needed to streamline the approval process. Common Pain Management Procedures Requiring Prior Authorization Several pain management procedures typically require prior authorization due to their complexity and cost. Here are some examples along with their corresponding Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes:
Case Study: Successful Prior Authorization in Pain ManagementConsider a pain management clinic that integrated a professional prior authorization service to handle their high volume of procedures. The clinic experienced significant improvements in efficiency and patient satisfaction. Approval times were reduced by 50%, and the clinic saw a 30% increase in successful authorizations. Patients received timely treatments, leading to better pain management outcomes and overall satisfaction. What to Look for in a Prior Authorization Service Provider for Pain Management What to Look for in a Prior Authorization Service Provider for Pain Management: Choosing the right prior authorization service provider for pain management is crucial for ensuring timely and effective treatment for patients. Here are key factors to consider when selecting a service provider: 1. Experience and ExpertiseSpecialization in Pain Management: Ensure the provider has extensive experience specifically in pain management. Familiarity with the unique requirements and challenges of pain management procedures can lead to more efficient and accurate authorizations. Track Record: Look for a provider with a proven track record of successful prior authorizations. High success rates and positive client testimonials can indicate reliability and competence. Knowledge of CPT Codes: The provider should have in-depth knowledge of the relevant CPT codes used in pain management procedures. This ensures accurate and efficient processing of prior authorization requests. 2. Efficiency and Turnaround TimeQuick Processing: Time is critical in pain management. Choose a provider known for fast turnaround times. Efficient processing helps avoid delays in patient care, which is essential for managing chronic pain effectively. Streamlined Processes: The provider should use streamlined processes to handle prior authorization requests, reducing the administrative burden on your staff and speeding up approvals. 3. Technology IntegrationAdvanced Technology: Modern prior authorization services should utilize advanced technology for tracking and managing authorizations. Look for providers that offer real-time updates, electronic submissions, and automated workflows. Interoperability: Ensure that the provider’s technology integrates seamlessly with your existing electronic health record (EHR) systems and practice management software. This integration can streamline the authorization process and improve efficiency. 4. Comprehensive SupportEnd-to-End Service: Choose a provider that offers comprehensive support throughout the entire prior authorization process, from initial request to final approval. This includes handling denials and appeals if necessary. Dedicated Account Management: A dedicated account manager can provide personalized support, addressing any issues promptly and ensuring smooth communication between your practice and the prior authorization service. 5. Transparency and CommunicationClear Communication: Effective communication is key. The provider should keep you informed at every stage of the prior authorization process, providing regular updates and immediate notifications of any issues or delays. Transparency in Pricing: Ensure that the provider offers transparent pricing with no hidden fees. Understand the cost structure and what services are included to avoid unexpected charges. 6. Compliance and Regulatory KnowledgeUp-to-Date Knowledge: The provider should stay current with all relevant regulations and insurance policies. This ensures compliance and reduces the risk of denied authorizations due to outdated information. Credentialing and Certifications: Check if the provider and their staff have relevant certifications and credentials, such as those from the Healthcare Financial Management Association (HFMA) or the American Health Information Management Association (AHIMA). 7. Customization and FlexibilityTailored Solutions: Choose a provider that offers customized solutions tailored to the specific needs of your pain management practice. Flexibility in their services can better align with your workflow and patient population. Scalability: Ensure the provider can scale their services to match the growth of your practice. This is particularly important if you plan to expand your services or patient base in the future. 8. Positive Client Feedback and Case StudiesClient Testimonials: Look for positive client testimonials and case studies that highlight the provider’s success in prior authorization for pain management. Real-world examples of improved efficiency and patient outcomes can give you confidence in their capabilities. References: Don’t hesitate to ask for references from other pain management practices that have used the provider’s services. Speaking directly with current or past clients can provide valuable insights. ConclusionSelecting the right prior authorization service provider for pain management involves careful consideration of their experience, efficiency, technology integration, support, communication, compliance, customization, and client feedback. By focusing on these key factors, you can find a provider that will streamline your prior authorization process, enhance patient care, and improve overall practice efficiency. Achieving Success with the Right Prior Authorization Team for Pain Management Achieving Success with the Right Prior Authorization Team for Pain Management: Having the right team in place is crucial for success in managing prior authorizations for pain management. Here’s how to maximize the effectiveness of your team to achieve outstanding results: 1. Expertise and Continuous TrainingHire Skilled Professionals: Ensure your team includes individuals with strong backgrounds in healthcare administration, particularly in pain management. Look for certifications in revenue cycle management, healthcare compliance, and clinical operations. Ongoing Education: The healthcare landscape and insurance requirements are constantly evolving. Invest in continuous training for your team to keep them updated on the latest regulations, best practices, and technologies in prior authorization. Cross-Functional Knowledge: Encourage your team to understand various aspects of the pain management process, from clinical procedures to insurance protocols. This comprehensive knowledge helps in accurately assessing and processing prior authorization requests. 2. Efficient Workflow ManagementDefine Clear Processes: Establish clear, standardized workflows for handling prior authorizations. This includes defining roles, responsibilities, and steps for submitting and following up on requests. Utilize Technology: Implement advanced technology solutions to streamline the prior authorization process. Use software that allows for electronic submissions, real-time tracking, and automated notifications to enhance efficiency. Regular Audits and Improvements: Conduct regular audits of your processes to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Use data analytics to track performance metrics and adjust workflows accordingly. 3. Strong Communication and CollaborationFoster Team Collaboration: Encourage open communication and collaboration within your team. Regular meetings and updates ensure everyone is aligned and can address issues proactively. Effective External Communication: Develop strong relationships with insurance companies, healthcare providers, and patients. Clear and prompt communication helps in resolving issues quickly and maintaining smooth workflows. Patient Advocacy: Train your team to be strong advocates for patients. Ensuring that patients receive timely and necessary treatments should be a top priority, and this can be achieved through effective communication and persistence in follow-ups. 4. Comprehensive Documentation and Follow-UpAccurate Documentation: Ensure that all prior authorization requests are thoroughly documented with accurate and complete patient information. This reduces the likelihood of denials and delays. Persistent Follow-Up: Implement a system for regular follow-ups on pending authorizations. Timely follow-ups can significantly reduce approval times and ensure that no requests fall through the cracks. Appeal Management: Equip your team with the skills and knowledge to handle denied requests effectively. Having a robust appeal process in place ensures that legitimate requests are eventually approved. 5. Data-Driven Decision MakingTrack Key Metrics: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as approval rates, turnaround times, and denial rates. Use this data to identify trends and areas for improvement. Benchmarking: Compare your team’s performance against industry standards and benchmarks. This helps in setting realistic goals and striving for continuous improvement. Feedback Loop: Create a feedback loop where team members can share insights and suggestions based on data findings. This collaborative approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement. 6. Building a Positive Team CultureRecognize and Reward Excellence: Celebrate the successes and hard work of your team. Recognizing and rewarding excellence boosts morale and motivates team members to maintain high performance. Professional Growth Opportunities: Provide opportunities for career advancement and professional growth. Encourage team members to pursue further education and certifications that enhance their skills and value to the organization. Work-Life Balance: Promote a healthy work-life balance to prevent burnout and ensure long-term productivity. A supportive work environment contributes to higher job satisfaction and better performance. 7. Leveraging Expertise of a Professional Service ProviderOutsourcing: If managing prior authorizations in-house becomes overwhelming, consider partnering with a professional service provider. They bring specialized expertise and can handle complex cases more efficiently. Collaborative Approach: Work closely with your service provider to ensure seamless integration with your practice. Regular communication and feedback help in maintaining alignment and achieving shared goals. ConclusionSuccess in managing prior authorizations for pain management hinges on having the right team and utilizing their expertise effectively. By focusing on continuous training, efficient workflow management, strong communication, accurate documentation, data-driven decision-making, a positive team culture, and potentially partnering with a professional service provider, you can streamline the prior authorization process, enhance patient care, and improve overall practice efficiency. For more information on building a successful prior authorization team or partnering with a professional service provider, contact us today. What are the best skills of Prior Authorization Experts? Prior authorization experts play a crucial role in ensuring that patients receive timely and necessary medical treatments while navigating the complexities of insurance approvals. Here are the top skills that make a prior authorization expert effective and successful: 1. In-Depth Knowledge of Medical Procedures and TerminologyUnderstanding of Medical Procedures: A thorough understanding of medical procedures, especially in specialized fields like pain management, is essential. This includes familiarity with various treatments, diagnostic tests, and their clinical indications. Medical Terminology: Proficiency in medical terminology ensures accurate communication with healthcare providers and insurance companies. This knowledge helps in correctly interpreting and documenting medical information. 2. Familiarity with Insurance Policies and RegulationsInsurance Protocols: Experts must be well-versed in the protocols and requirements of different insurance companies. This includes knowledge of coverage criteria, documentation requirements, and submission processes. Regulatory Compliance: Keeping up-to-date with healthcare regulations and payer policies is crucial to ensure compliance and reduce the risk of denials. 3. Attention to DetailAccurate Documentation: Attention to detail is critical for accurately completing prior authorization requests. This includes gathering and verifying all necessary patient information, medical records, and supporting documentation. Error-Free Submissions: Minimizing errors in submissions reduces the likelihood of delays and denials, ensuring smoother and faster approval processes. 4. Strong Communication SkillsInterpersonal Communication: Effective communication with healthcare providers, insurance representatives, and patients is key. This involves clearly explaining the authorization process, requirements, and status updates. Negotiation Skills: The ability to negotiate with insurance companies can help in resolving issues and obtaining approvals for necessary treatments. 5. Analytical and Critical ThinkingProblem-Solving: Prior authorization experts must be able to analyze complex cases, identify potential issues, and develop solutions. This includes understanding why a request might be denied and how to address it. Data Analysis: Analyzing data and trends related to prior authorization requests helps in identifying patterns, improving processes, and increasing approval rates. 6. Organizational and Time Management SkillsEfficient Workflow Management: Managing multiple prior authorization requests simultaneously requires excellent organizational skills. Experts must prioritize tasks effectively to meet deadlines and ensure timely approvals. Time Management: Efficiently handling the administrative workload and follow-up activities is essential to keep the authorization process moving smoothly. 7. Technical ProficiencyUse of Technology: Familiarity with electronic health records (EHR) systems, prior authorization software, and other relevant technology is important. This includes proficiency in data entry, tracking, and reporting tools. Adaptability to New Tools: As technology evolves, experts should be able to quickly learn and adapt to new tools and systems that can enhance efficiency. 8. Persistence and PatienceFollow-Up: Persistence in following up on pending requests and addressing any issues that arise is crucial. This involves regularly checking the status of requests and communicating with insurance companies. Patience: Navigating the complexities of prior authorization can be challenging. Patience is needed to handle lengthy processes and potential frustrations. 9. Customer Service OrientationPatient Advocacy: Prior authorization experts should prioritize patient care and act as advocates, ensuring that patients receive the necessary treatments without undue delays. Empathy and Support: Providing empathetic support to patients and their families during the authorization process helps in building trust and maintaining a positive experience. 10. Continuous LearningStaying Informed: The healthcare landscape and insurance policies are constantly changing. Continuous learning and staying informed about the latest developments are essential for maintaining expertise. Professional Development: Pursuing additional certifications, attending relevant workshops, and participating in professional organizations can enhance skills and knowledge. ConclusionThe best prior authorization experts possess a combination of medical knowledge, attention to detail, strong communication, analytical thinking, organizational skills, technical proficiency, persistence, customer service orientation, and a commitment to continuous learning. These skills enable them to navigate the complexities of the prior authorization process effectively, ensuring timely and accurate approvals that benefit both healthcare providers and patients. For more information on enhancing the skills of your prior authorization team or partnering with expert services, contact us today. Mastery of Clinical Insurance Policies, Guidelines, and Reimbursement by Prior Authorization Experts Prior authorization experts must have a deep understanding of clinical insurance policies, guidelines, and reimbursement processes to effectively secure approvals and ensure that patients receive necessary treatments. Here’s how their mastery in these areas contributes to their success: 1. Comprehensive Knowledge of Insurance PoliciesUnderstanding Payer Requirements: Prior authorization experts must be familiar with the specific requirements and protocols of various insurance payers. This includes knowing the criteria for coverage, necessary documentation, and the step-by-step process for submitting requests. Policy Variations: Different insurance companies have unique policies, and even within a single insurer, policies can vary by plan. Experts must stay updated on these variations to ensure compliance and avoid denials. Coverage Limitations: Being aware of what treatments and services are covered under different insurance plans helps in determining the likelihood of approval and preparing the necessary documentation to support the request. 2. Proficiency in Clinical GuidelinesMedical Necessity Criteria: Insurance companies require proof that a procedure or treatment is medically necessary. Prior authorization experts must understand clinical guidelines and how to align the patient's medical condition with these criteria. Evidence-Based Practices: Experts should be knowledgeable about the latest evidence-based practices and clinical guidelines to justify the necessity of treatments. This involves staying current with medical literature and professional guidelines from organizations like the American Medical Association (AMA) or specialty-specific bodies. Procedure-Specific Guidelines: Each medical procedure or treatment has specific guidelines that must be met for authorization. Understanding these detailed requirements ensures that the submission includes all necessary information, reducing the chances of denial. 3. Expertise in Reimbursement ProcessesCoding Proficiency: Accurate coding is critical for successful reimbursement. Experts must be proficient in Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) codes, International Classification of Diseases (ICD) codes, and Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS) codes relevant to pain management. Documentation Standards: Insufficient or incorrect documentation is a common reason for denial. Prior authorization experts ensure that all required clinical documentation, including patient history, diagnostic results, and treatment plans, are thoroughly and accurately recorded. Claim Submission: Mastery of the claim submission process, including electronic submission systems, ensures that requests are processed efficiently. Experts must know how to use these systems to submit claims correctly and follow up as needed. 4. Handling Denials and AppealsDenial Management: When a prior authorization request is denied, experts must analyze the reasons for denial and address them effectively. This requires a deep understanding of both clinical guidelines and insurance policies. Appeal Process: Experts should be adept at navigating the appeals process, including preparing and submitting appeal documentation, providing additional clinical information, and communicating effectively with insurance representatives to overturn denials. Persistence and Advocacy: Advocating for the patient’s needs and persisting through multiple levels of appeal if necessary demonstrates the expert’s commitment to securing necessary treatments. 5. Interpreting and Applying GuidelinesPolicy Updates: Insurance policies and clinical guidelines are frequently updated. Prior authorization experts must continuously monitor for changes and quickly interpret how these changes impact the prior authorization process. Training and Education: Experts often provide training to other staff members to ensure that everyone involved in the authorization process understands the latest guidelines and policies. Collaboration with Providers: Working closely with healthcare providers to ensure that clinical documentation supports the insurance guidelines and policies is crucial. This collaboration ensures that requests are robust and justified from a clinical perspective. 6. Technology UtilizationElectronic Health Records (EHR): Proficiency in EHR systems is essential for accessing patient information and submitting prior authorization requests. Experts must know how to navigate these systems to retrieve and document necessary data efficiently. Authorization Software: Many prior authorization processes are managed through specialized software. Experts must be adept at using these tools to track requests, manage documentation, and communicate with payers. Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics to track trends, identify common reasons for denials, and develop strategies for improvement helps in refining the authorization process and increasing approval rates. ConclusionMastery of clinical insurance policies, guidelines, and reimbursement processes is a cornerstone of the expertise required for successful prior authorization specialists. Their deep understanding of payer requirements, clinical guidelines, coding standards, and the reimbursement landscape ensures that prior authorization requests are accurate, compliant, and effective in securing necessary treatments for patients. This proficiency not only improves approval rates but also enhances the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the healthcare provider’s practice. For more insights on leveraging expert prior authorization services to enhance your practice, contact us today. Key Insurance Payer Portals for Prior Authorization Experts Mastering the use of insurance payer portals is essential for prior authorization experts to streamline the authorization process, reduce delays, and ensure efficient communication with payers. Here are some of the key insurance payer portals that prior authorization experts should be proficient in: 1. AvailityOverview: Availity is a widely-used healthcare clearinghouse that provides access to multiple payers' portals through a single platform. Key Features:
2. NavinetOverview: NaviNet is a multi-payer platform that offers comprehensive tools for interacting with various health plans. Key Features:
3. Optum360Overview: Optum360 is a healthcare information technology platform that offers services for revenue cycle management, including prior authorizations. Key Features:
4. Availity EssentialsOverview: This portal provides access to Anthem Blue Cross Blue Shield and other payers for managing prior authorizations and other administrative tasks. Key Features:
5. Cigna for Health Care ProfessionalsOverview: Cigna's dedicated portal for healthcare providers to manage various administrative tasks, including prior authorizations. Key Features:
6. Aetna Provider PortalOverview: Aetna’s provider portal offers tools for managing patient care and administrative tasks. Key Features:
7. Humana’s Availity PortalOverview: Humana partners with Availity to provide a comprehensive portal for prior authorizations and other services. Key Features:
8. UnitedHealthcare Provider PortalOverview: UnitedHealthcare’s dedicated portal for managing patient care and administrative tasks. Key Features:
9. Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) PortalsOverview: Various MACs provide portals for managing Medicare prior authorizations and other administrative tasks. Key Features:
10. Medicaid State PortalsOverview: Each state has its own Medicaid portal for managing prior authorizations and other services. Key Features:
ConclusionMastering the use of these key insurance payer portals is crucial for prior authorization experts. These portals facilitate efficient submission, tracking, and management of prior authorization requests, ensuring timely patient care and optimized administrative workflows. Familiarity with each portal’s features and payer-specific requirements will enhance the effectiveness and success rates of prior authorization processes. For more detailed guidance on mastering these portals or integrating them into your practice, contact us today. Mastering Key Insurance Payer Portals: Carelon, Cohere, RADMD, and eviCore In addition to the widely-used payer portals previously mentioned, it's crucial for prior authorization experts to also be proficient in specialized portals such as Carelon, Cohere, RADMD, and eviCore. These portals are integral for managing prior authorizations for various procedures, especially in specialized fields like pain management, radiology, and other complex treatments. Here’s an overview of each: 1. Carelon (formerly AIM Specialty Health)Overview: Carelon, previously known as AIM Specialty Health, provides clinical solutions and services for managing specialty care. This portal is widely used for prior authorizations related to advanced imaging, cardiac care, oncology, and musculoskeletal care. Key Features:
2. Cohere HealthOverview: Cohere Health focuses on transforming prior authorization through its collaborative utilization management platform. It is designed to streamline the prior authorization process for a variety of medical services, enhancing care coordination. Key Features:
3. RADMD (NIA Magellan)Overview: RADMD, managed by National Imaging Associates (NIA) under Magellan Health, specializes in managing authorizations for radiology services. This portal is essential for handling prior authorizations for advanced imaging procedures. Key Features:
4. eviCore HealthcareOverview: eviCore Healthcare provides utilization management services across several specialties, including radiology, cardiology, oncology, and musculoskeletal care. This portal is critical for managing complex prior authorizations efficiently. Key Features:
ConclusionPrior authorization experts need to be proficient in using specialized payer portals like Carelon, Cohere, RADMD, and eviCore. These portals are essential for managing authorizations in specialized areas such as advanced imaging, cardiology, oncology, and musculoskeletal care. Mastery of these platforms enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of the prior authorization process, ensuring timely and appropriate patient care. UNDERSTANDING OUTSOURCED PRIOR AUTHORIZATION FOR MEDICAL DEVICE MANUFACTURING COMPANY: PROCESSES, PITFALLS, AND BEST PRACTICES Table of Contents
1. Introduction In the realm of medical device manufacturing, obtaining prior authorization for products and procedures is a critical component of the reimbursement process. This authorization ensures that healthcare providers receive approval from payers before delivering specific medical services or utilizing particular devices. However, navigating the complex landscape of prior authorization can be daunting for manufacturers, often requiring significant time, resources, and expertise. As a result, many companies opt to outsource this process to specialized third-party entities. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of outsourced prior authorization in the context of medical device manufacturing, elucidating its workings, benefits, challenges, and best practices. 2. The Importance of Prior Authorization in Medical Device Manufacturing Prior authorization serves as a pivotal checkpoint in the healthcare ecosystem, facilitating cost control, quality assurance, and regulatory compliance. For medical device manufacturers, securing prior authorization ensures that their innovative products are accessible to patients who need them while also guaranteeing reimbursement from insurance providers. Without proper authorization, manufacturers risk financial losses, delayed market access, and regulatory non-compliance, impeding the adoption and utilization of their devices. 3. Outsourcing Prior Authorization: Overview and Benefits Outsourcing prior authorization involves delegating the responsibility of navigating the authorization process to specialized third-party organizations. These entities, often referred to as prior authorization services or medical billing companies, possess the expertise and infrastructure necessary to streamline the authorization process, alleviate administrative burdens, and optimize reimbursement outcomes for manufacturers. By outsourcing this function, medical device companies can focus on core competencies such as research, development, and innovation while entrusting authorization-related tasks to dedicated professionals. 4. How Outsourced Prior Authorization Works Outsourced prior authorization typically follows a structured workflow encompassing several key steps: Step 1: Initial Assessment and Planning Upon engagement, the outsourcing partner conducts a comprehensive assessment of the manufacturer's products, procedures, and reimbursement requirements. This involves understanding the intricacies of each device, its indications for use, and the corresponding billing and coding protocols. Based on this assessment, a tailored authorization strategy is developed, outlining timelines, responsibilities, and performance metrics. Step 2: Gathering Necessary Documentation The outsourced provider collaborates with the manufacturer to compile all requisite documentation essential for the authorization process. This includes clinical evidence, patient records, procedural documentation, insurance information, and any other relevant paperwork mandated by payers. Attention to detail and adherence to regulatory guidelines are paramount during this phase to ensure smooth processing and approval. Step 3: Submission and Follow-Up Once the documentation is compiled, the outsourcing partner submits the authorization requests to the relevant insurance providers on behalf of the manufacturer. Timely follow-up and communication are maintained to track the progress of each request, address any queries or discrepancies, and expedite approval whenever possible. Close coordination between the outsourcing partner and the manufacturer is essential to navigate any obstacles encountered during this phase effectively. Step 4: Appeals Process In the event of a denial or partial approval, the outsourcing partner initiates the appeals process on behalf of the manufacturer. This involves meticulous review of the denial rationale, identification of potential discrepancies or errors, and preparation of compelling arguments to overturn the decision. The outsourcing partner leverages its expertise in navigating payer requirements, coding guidelines, and regulatory frameworks to strengthen the manufacturer's appeal and maximize the chances of a favorable outcome. Continuous monitoring and escalation of the appeal process ensure timely resolution and mitigation of reimbursement delays. 5. Common Challenges in Outsourced Prior Authorization While outsourcing prior authorization offers numerous advantages, it also presents inherent challenges that can impact efficiency and effectiveness. Some of the common challenges include:
6. Strategies to Mitigate Risks and Improve Efficiency To address the challenges associated with outsourced prior authorization and enhance overall efficiency, manufacturers can implement the following strategies:
UNDERSTANDING OUTSOURCED PRIOR AUTHORIZATION IN MEDICAL DEVICE MANUFACTURING: PROCESSES, PITFALLS, AND BEST PRACTICES Expanding on Common Challenges:
Expanding on Engaging in Collaborative Partnerships:
Incorporating Nurses in Outsourced Prior Authorization:
References:
PRIOR AUTHORIZATION FOR ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY BILLING Obtaining prior authorization is an essential component in the billing process for orthopedic surgery. This procedure involves healthcare providers obtaining approval from a patient’s insurance company before they can proceed with specific surgeries or treatments. This step is critical in orthopedic surgery due to the high cost associated with procedures such as joint replacements, spinal surgeries, and other surgical interventions. Prior authorization ensures these procedures are deemed medically necessary and are covered under the patient's insurance plan. Additionally, this process is mandatory for diagnostic imaging studies like MRI or CT scans, crucial for diagnosing orthopedic conditions. Detailed Steps for Obtaining Prior Authorization in Orthopedic Surgery BillingTo navigate the process of obtaining prior authorization for orthopedic surgery efficiently, follow these detailed, instructional steps:
Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Choosing GoHealthcare Practice Solutions for your orthopedic surgery prior authorization needs means choosing a partner dedicated to your success and the well-being of your patients. Our specialized focus, combined with our commitment to efficiency and a high approval rate, makes us an unparalleled asset in the healthcare industry. By outsourcing to us, healthcare providers can reduce administrative burdens, focus more on patient care, and enjoy peace of mind knowing that their prior authorization needs are in expert hands. In a healthcare landscape where prior authorization can often be a bottleneck to timely and necessary care, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions stands out as a beacon of efficiency, expertise, and success. Our unique services ensure that your patients receive the care they need without unnecessary delays, reinforcing your commitment to excellence in patient care. READ TESTIMONIALS HERE: https://www.gohealthcarellc.com/testimonials.html Overturning Medical Prior Authorization Denials. How to Appeal Successfully for Interventional Pain Management and Orthopedic Surgeries.
Understanding Prior AuthorizationPrior authorization is a precautionary measure employed by insurance companies to verify the necessity and appropriateness of specific healthcare services, procedures, or medications before they are executed or prescribed. This process is essentially a pre-approval mechanism where healthcare providers must obtain permission from the insurance provider to proceed with a proposed treatment plan. The primary rationale behind this system is to ensure that the proposed medical interventions are medically necessary, cost-effective, and aligned with accepted clinical guidelines and practices. The utilization of prior authorization serves multiple purposes: it aims to prevent unnecessary procedures that may expose patients to undue risk, ensures the optimal use of healthcare resources, and controls healthcare spending by avoiding costly and potentially ineffective treatments. By requiring a thorough review of the medical necessity and appropriateness of certain services before they are delivered, insurance companies can manage costs more effectively while striving to maintain a high standard of care. In the context of interventional pain management and orthopedic services, prior authorization plays a crucial role. These medical specialties often involve complex, high-cost procedures and treatments, ranging from advanced diagnostic imaging like MRIs to surgical interventions and long-term pain management therapies. Given the complexity and potential risks associated with these services, insurance providers scrutinize requests for prior authorization with particular diligence to ensure that each proposed treatment is the best course of action for the patient's specific condition. For interventional pain management, this could mean a thorough review of the patient's medical history, previous treatments or therapies attempted, and the current level of pain and its impact on the patient's quality of life. The insurance company may require detailed information, including diagnostic reports, pain scale assessments, and documentation of conservative treatments tried, such as physical therapy or medication, before approving more invasive procedures. Similarly, in orthopedic services, prior authorization helps ensure that surgeries or other interventions are indeed necessary and that all conservative treatment options have been explored. For instance, before approving a knee replacement surgery, the insurance company might need evidence of the patient's attempts at physical therapy, weight loss, and pain management, along with imaging studies that confirm the extent of joint damage. The rigorous nature of the prior authorization process in these specialties underscores the need for healthcare providers to submit comprehensive, well-documented requests that clearly demonstrate the medical necessity of the proposed interventions. Failure to provide adequate documentation or justification can lead to prior authorization denials, delaying critical treatments and adversely affecting patient outcomes. Therefore, understanding the intricacies of the prior authorization process and the specific requirements of insurance providers is essential for healthcare professionals working in interventional pain management and orthopedic services. This knowledge enables them to navigate the process more effectively, ensuring that patients receive the timely and appropriate care they need. Common Reasons for DenialsDenials of prior authorization in interventional pain management and orthopedic services can stem from various reasons, often related to the rigorous requirements set forth by insurance companies to ensure medical necessity and adherence to clinical policies and guidelines. Understanding these common reasons for denials is crucial for healthcare providers to navigate and address the challenges effectively.
Preparing for a Successful AppealReceiving a prior authorization denial can be a significant setback for both patients awaiting crucial medical interventions and healthcare providers striving to deliver optimal care. However, an initial denial is not the end of the road but rather the beginning of an appeal process that requires careful preparation and detailed documentation. The key to overturning such denials lies in understanding the appeal process and meticulously preparing your case to address the reasons for the denial. Immediate Steps Post-DenialThe moment a denial is received, it's imperative to act swiftly and methodically. The first step is to thoroughly review the denial letter to understand the specific reasons cited by the insurance company. This critical review will guide the preparation of your appeal, as it highlights the areas that need to be addressed comprehensively in your submission. Gathering Necessary DocumentationThe cornerstone of a successful appeal is the compilation of robust and relevant documentation that substantiates the medical necessity of the denied service or procedure. This documentation should paint a comprehensive picture of the patient's medical history, current condition, and the clinical rationale behind the recommended intervention. Key documents to gather include:
Medical Necessity and Clinical GuidelinesArticulating the medical necessity for a requested service or procedure is the linchpin in overturning a prior authorization denial. This requires a nuanced understanding of the patient's condition, the proposed intervention, and how the intervention is expected to improve the patient's health outcomes. The appeal must convincingly demonstrate that the requested service is not only appropriate but also essential for the patient's well-being. Articulating Medical Necessity The argument for medical necessity should be grounded in clinical evidence and patient-specific information. This includes a detailed explanation of the patient's diagnosis, the severity and duration of their condition, and how the condition impacts their daily life and overall health. It's essential to detail the expected benefits of the proposed treatment, including how it will alleviate symptoms, improve functionality, or prevent the progression of the condition. A compelling narrative should be crafted, one that connects the patient's clinical presentation with the proposed intervention, showing a clear line of reasoning based on established medical standards and practices. This narrative should also address any specific points of contention raised in the denial, directly refuting them with clinical evidence and expert opinion. Reviewing and Aligning with Clinical Policy and Guidelines Insurance companies rely heavily on their clinical policies and guidelines to make coverage decisions. Therefore, it's crucial to review these documents carefully to understand the criteria used to evaluate medical necessity and align your appeal with these standards. This review can help identify any areas where the insurance company's assessment may have deviated from accepted medical guidelines or overlooked key aspects of the patient's condition. Incorporating references to widely accepted clinical guidelines, such as those from reputable medical societies or organizations related to interventional pain management or orthopedics, can strengthen the appeal. These references can serve as authoritative evidence supporting the appropriateness and necessity of the proposed treatment. Utilization of Guidelines to Strengthen the Appeal Case Utilizing the insurance payers' clinical policies and reimbursement guidelines in the appeal serves multiple purposes. Firstly, it establishes that the requested intervention is consistent with current medical practice and is recognized as effective for the patient's condition. Secondly, it demonstrates a commitment to evidence-based medicine, underscoring that the treatment plan is not experimental or outside the standard of care. When referencing guidelines, it's important to be specific. Cite relevant sections or recommendations that directly support the necessity of the proposed treatment. If the guidelines outline specific criteria for treatment eligibility, ensure that the appeal documentation clearly demonstrates how the patient meets these criteria. In cases where the patient's situation does not fit neatly within established guidelines, it's essential to provide a detailed justification for the proposed approach. This might include highlighting unique aspects of the patient's condition or explaining why standard treatments are contraindicated or have been ineffective. In summary, effectively articulating medical necessity and aligning the appeal with clinical policy and guidelines are critical strategies in overturning prior authorization denials. By grounding the appeal in solid clinical evidence, patient-specific details, and authoritative guidelines, healthcare providers can significantly enhance their chances of a successful outcome. This not only supports the immediate goal of securing coverage for the necessary treatment but also reinforces the broader commitment to patient-centered, evidence-based care. Highlighting Conservative Treatments and Patient EvaluationWhen appealing a prior authorization denial, it's essential to emphasize the conservative treatments that have been attempted and to provide a detailed evaluation of the patient's condition. This approach not only demonstrates the thoroughness of the patient's care plan but also aligns with most insurance providers' requirements that less invasive options be explored before approving more advanced interventions. Documenting these aspects meticulously can significantly strengthen your appeal. Documenting Conservative Treatments and OutcomesConservative treatments refer to non-invasive interventions aimed at managing a patient's condition without immediate recourse to surgery or other high-level procedures. Documenting these treatments involves detailing the types of conservative care provided, such as physical therapy, medications, injections, or lifestyle modifications, along with their respective durations and outcomes. For each treatment, include the following information:
Diagnostic Reports: The Backbone of Your AppealDiagnostic reports, particularly those from imaging studies like X-rays and MRIs, serve as a foundational element in the appeal process for overturning medical prior authorization denials. These reports offer concrete, objective evidence that can substantiate the medical necessity of a requested service or procedure. Their role in the appeal process cannot be overstated, as they provide the visual and technical data needed to support the clinical assessments and treatment recommendations made by healthcare providers. The Critical Role of Diagnostic ReportsDiagnostic imaging reports are invaluable because they offer a visual confirmation of the clinical findings noted during physical examinations and patient evaluations. For conditions that require interventional pain management or orthopedic services, such as structural abnormalities, degenerative changes, or specific injuries, these reports can vividly demonstrate the medical issues at hand. They provide a level of detail that cannot be conveyed through clinical notes alone, making them critical for justifying the necessity of certain treatments. Presenting Diagnostic Findings EffectivelyWhen including diagnostic reports in an appeal, it's crucial to present them in a manner that highlights their relevance to the case. Here are some strategies for effectively arguing the findings of these reports in your appeal:
How to Avoid Peer-to-Peer ReviewsPeer-to-peer reviews, a process where a healthcare provider discusses a patient's case directly with a medical reviewer from the insurance company, are often seen as a last resort in the prior authorization process. While they offer an opportunity to advocate for a patient's needs, they can also be time-consuming and stressful. Minimizing the need for these reviews through comprehensive and well-documented prior authorization requests is preferable. Here are strategies to reduce the likelihood of peer-to-peer reviews and tips for preparation if they become unavoidable. Strategies for Comprehensive Prior Authorization Requests
Writing a Compelling Appeal LetterCrafting a compelling appeal letter is a critical step in the process of overturning a medical prior authorization denial. This letter is not just a formality; it's an opportunity to present a well-argued, evidence-based case that demonstrates the medical necessity of the requested service or procedure. A successful appeal letter should be clear, concise, and comprehensive, incorporating key components that address the specific reasons for the denial while highlighting the clinical evidence and guidelines that support your case. Key Components of an Effective Appeal Letter
The Appeal Process: Step by StepNavigating the appeal process for overturning a medical prior authorization denial is a structured yet intricate journey that requires a clear understanding of each step, meticulous preparation, and timely action. This step-by-step guide aims to demystify the process, from the initial submission of the appeal to its final resolution, providing insights into the timelines and expectations at each stage. 1. Review the Denial Notice The first step in the appeal process is to thoroughly review the denial notice received from the insurance company. This notice should detail the reasons for the denial, reference specific policy guidelines, and outline the steps for filing an appeal. Understanding the grounds for denial is crucial for crafting a targeted and effective appeal. 2. Understand Your Appeal Rights Familiarize yourself with your appeal rights, which are often outlined in the denial notice and the patient’s insurance policy. This includes understanding the types of appeals available (e.g., internal, external), the number of appeal levels, and any specific deadlines for submitting an appeal. 3. Gather Supporting Documentation Compile all necessary documentation to support your appeal. This includes medical records, clinical notes, diagnostic reports, evidence of conservative treatments tried, pain assessments, ADL evaluations, and any relevant clinical guidelines or literature supporting the medical necessity of the treatment. 4. Write the Appeal Letter Craft a comprehensive appeal letter that includes:
Submit the appeal package, including the appeal letter and all supporting documentation, to the insurance company via the required method (often mail or fax). Ensure you adhere to any submission deadlines. It’s advisable to send the package with tracking or delivery confirmation for your records. 6. Confirmation and Follow-Up After submission, you should receive confirmation from the insurance company that they have received your appeal. If not, follow up to ensure it has been received and is being processed. Keep a record of all communications. 7. Peer-to-Peer Review (If Applicable) In some cases, a peer-to-peer review may be requested by the insurance company as part of the appeal process. This is an opportunity for the treating provider to discuss the case directly with a clinician from the insurance company. If a peer-to-peer review is scheduled:
The insurance company will review the appeal and make a decision within a specified timeframe, which can vary depending on the urgency of the treatment and the specific regulations governing the appeal process. This timeframe should be communicated in the denial notice or the insurance policy. 9. Review the Appeal Decision Upon receiving the decision, review it carefully. If the appeal is successful, the denial will be overturned, and the treatment will be authorized. If the appeal is denied, the decision letter should provide the reasons for the denial and information about further appeal options, such as an external review. 10. Consider Further Appeals or External Review If the internal appeal is unsuccessful, and the situation warrants, consider pursuing further appeals or an external review process. An external review involves an independent third party reviewing the decision, which can be an option in certain jurisdictions or under specific insurance policies. Navigating the appeal process requires patience, attention to detail, and a thorough understanding of both medical and insurance protocols. By following these steps and preparing a well-documented and persuasive appeal, healthcare providers can advocate effectively for their patients' needs and potentially overturn prior authorization denials. Case Studies: Overturning Denials SuccessfullyExamining real-life examples of successful appeals in the realms of interventional pain management and orthopedic prior authorization cases provides invaluable insights and best practices for healthcare providers navigating similar challenges. These case studies not only highlight effective strategies but also underscore the importance of thorough preparation, detailed documentation, and a deep understanding of the appeals process. Case Study 1: Interventional Pain Management Success Background: A patient with chronic lower back pain, unresponsive to conservative treatments like physical therapy and medication management, was recommended for a spinal cord stimulator by their pain management specialist. The initial prior authorization request was denied by the insurance company on the grounds of insufficient evidence of medical necessity. Appeal Strategy: The healthcare provider meticulously compiled a comprehensive appeal package, including detailed clinical notes that chronicled the patient's long history of conservative treatments and their outcomes. Pain scales and ADL assessments were used to quantify the patient's suffering and functional impairment. The appeal also included a thorough review of recent diagnostic reports, such as MRI scans showing significant spinal abnormalities unresponsive to non-invasive treatments. The provider referenced current clinical guidelines supporting the use of spinal cord stimulators in similar cases. Outcome: The detailed appeal, bolstered by objective evidence and guideline-based recommendations, led to the overturning of the initial denial. The patient was approved for the spinal cord stimulator, resulting in significant pain relief and improved quality of life. Case Study 2: Orthopedic Prior Authorization Victory Background: An orthopedic surgeon submitted a prior authorization request for a knee replacement surgery for a patient with severe osteoarthritis. The request was denied due to alleged lack of evidence that all conservative measures had been exhausted. Appeal Strategy: In response, the surgeon prepared an appeal that included a comprehensive history of conservative treatments undertaken over several years, including medications, physical therapy, and less invasive procedures, all documented with dates and outcomes. Pain scores and ADL assessments were provided to illustrate the impact of the condition on the patient's daily life. The surgeon also included recent X-ray and MRI images showing the advanced stage of osteoarthritis, alongside guidelines recommending knee replacement for such cases. Outcome: The appeal successfully demonstrated the patient's need for surgery, leading to the authorization being granted. The surgery proceeded, ultimately enhancing the patient's mobility and significantly reducing pain. Lessons Learned and Best Practices Thorough Documentation: Both cases underscore the critical importance of maintaining comprehensive and detailed patient records. Documenting every step of the treatment process, from conservative measures to diagnostic findings, is crucial. Evidence-Based Guidelines: Leveraging current clinical guidelines to support the medical necessity of a procedure can greatly strengthen an appeal. These guidelines provide an authoritative basis for the recommended treatments. Patient-Centered Approach: Appeals that effectively communicate the impact of a condition on a patient's quality of life, through pain scales and ADL assessments, can be more compelling. Personalizing the appeal to showcase the patient's unique situation helps to humanize the case. Visual Evidence: Including diagnostic images as part of the appeal can provide a powerful visual argument for the necessity of the intervention, making it harder for reviewers to deny the request on the basis of insufficient evidence. These case studies reveal that successful appeals often hinge on a combination of detailed, patient-specific documentation, adherence to evidence-based clinical guidelines, and a clear demonstration of the impact of the condition on the patient's life. By following these best practices, healthcare providers can enhance their ability to overturn prior authorization denials and secure the necessary treatments for their patients. Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions for your Prior Authorization for Interventional Pain Management and Orthopedic Surgeries? Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice SolutionsOutsourcing your prior authorization needs for interventional pain management and orthopedic surgeries to GoHealthcare Practice Solutions offers a multitude of benefits that can significantly enhance the efficiency and success rate of obtaining necessary approvals for patient care. As the only company specializing in these specific services, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions brings a unique blend of expertise, precision, and dedication to the complex process of prior authorization, setting a new standard in healthcare support. Specialized Expertise GoHealthcare Practice Solutions stands out in the healthcare industry by focusing exclusively on prior authorizations for interventional pain management and orthopedic surgeries. This specialization means that our team is not just familiar with the general process of prior authorization; we have a deep understanding of the specific requirements, challenges, and nuances associated with these particular medical fields. Our experts stay abreast of the latest clinical guidelines, insurance policies, and procedural updates, ensuring that every authorization request is as strong and compliant as possible. Faster Turnaround Time In the world of healthcare, time is of the essence. Delays in obtaining prior authorization can lead to postponed treatments, prolonged patient suffering, and increased administrative burdens. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions addresses this critical issue with a streamlined process that ensures faster turnaround times for prior authorization requests. Our efficient workflow and dedicated team work tirelessly to expedite each case, understanding the urgency behind every request and working diligently to minimize wait times for both patients and providers. Exceptional Approval Rates Perhaps most compelling is GoHealthcare Practice Solutions' remarkable track record of achieving a 98% prior authorization approval rate. This exceptional success rate is a testament to our meticulous approach to each case, our thorough understanding of insurance requirements, and our ability to effectively articulate the medical necessity of proposed treatments. By entrusting your prior authorization needs to us, you significantly increase the likelihood of obtaining timely approvals, thereby facilitating uninterrupted patient care and optimizing treatment outcomes. Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions Choosing GoHealthcare Practice Solutions for your interventional pain management and orthopedic surgery prior authorization needs means choosing a partner dedicated to your success and the well-being of your patients. Our specialized focus, combined with our commitment to efficiency and a high approval rate, makes us an unparalleled asset in the healthcare industry. By outsourcing to us, healthcare providers can reduce administrative burdens, focus more on patient care, and enjoy peace of mind knowing that their prior authorization needs are in expert hands. In a healthcare landscape where prior authorization can often be a bottleneck to timely and necessary care, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions stands out as a beacon of efficiency, expertise, and success. Our unique services ensure that your patients receive the care they need without unnecessary delays, reinforcing your commitment to excellence in patient care. In the rapidly evolving field of healthcare, the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has promised enhancements in efficiency, accuracy, and patient care. However, when it comes to the nuanced and intricate world of interventional pain management and orthopedic surgeries, the reliance on human expertise becomes irreplaceable, particularly in the prior authorization process. This process, essential for ensuring the medical necessity and appropriateness of treatments, involves a detailed review of clinical policies, guidelines, and individual patient assessments that AI, in its current state, cannot fully comprehend or execute. The Human Touch in Interventional Pain Management: Why AI Can't Navigate Prior Authorization Complexities The Essence of Human Expertise in Prior Authorization Understanding Prior AuthorizationPrior authorization is a fundamental process in the healthcare system, serving as a checkpoint before certain medications, treatments, or procedures are approved for coverage by a patient's insurance provider. This process is designed to ensure that the proposed medical services are medically necessary, appropriate for the patient's condition, and in line with the insurer's coverage policies and guidelines. The goal is to optimize patient care while managing costs and preventing unnecessary or ineffective treatments. The Human Touch in Interventional Pain Management: (Hard Truth) - Why AI Can't Navigate Prior Authorization Complexities Definition and Importance in HealthcarePrior authorization is a form of cost-control and quality assurance mechanism that requires healthcare providers to obtain approval from an insurance company before a specific service is delivered to the patient. This preemptive verification aims to ensure that the proposed treatment is clinically justified and aligns with the insurer's criteria for "medical necessity." It plays a critical role in the healthcare system by:
Role in Interventional Pain Management and OrthopedicIn the context of interventional pain management—a specialty focused on diagnosing and treating pain with techniques such as injections, nerve blocks, and minimally invasive surgeries—prior authorization plays a pivotal role. Given the complexity and variety of treatments within this field, the process ensures that:
Outsourcing the prior authorization process to specialized firms like GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, known for their expertise in interventional pain management procedures and orthopedic spinal surgeries, offers numerous benefits that can significantly enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and success rates of obtaining necessary authorizations for complex medical treatments. Here are some compelling reasons why leveraging their professional services can be advantageous: Expertise in Specialized Medical Fields:
The Human Element in HealthcareThe human element in healthcare, particularly in areas requiring complex decision-making such as interventional pain management and orthopedic spinal surgeries, is irreplaceable. This element encompasses the nuanced clinical judgment and decision-making capabilities of healthcare professionals, alongside their ability to conduct personalized patient assessments and foster meaningful interactions. These human facets play a crucial role in delivering high-quality, compassionate, and effective care. Clinical Judgment and Decision-Making: Clinical judgment refers to the ability of healthcare professionals to integrate their knowledge, experience, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills to make decisions regarding patient care. This is especially vital in fields like interventional pain management and orthopedic surgeries, where:
Personalized Patient Assessments and InteractionsPersonalized patient assessments and interactions are at the heart of patient-centered care. They involve:
Limitations of AI (Artificial Intelligence) in HealthcareCurrent Capabilities of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has made significant inroads into the healthcare sector, offering remarkable capabilities in data processing, analytics, and pattern recognition. These technological advancements have enhanced various aspects of healthcare, from diagnostic imaging to patient data management and predictive analytics. However, despite these advancements, AI faces notable limitations, particularly when it comes to understanding context, nuance, and the complex, multifaceted nature of human health. Current Capabilities of AI systems, especially those based on machine learning and deep learning algorithms, excel at processing vast amounts of data at speeds and scales unattainable by humans. In healthcare, this capability translates into several practical applications:
Limitations in Understanding Context and Nuance Despite its strengths, AI's ability to understand the broader context and nuances of individual patient cases remains limited. This limitation arises from several inherent challenges:
Shortcomings in Complex Decision-Making The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in healthcare has shown promise in various applications, from diagnostic support to patient data management. However, when it comes to complex decision-making, particularly in contexts that require nuanced interpretation of clinical guidelines and personalized assessment of medical necessity, AI faces significant challenges. Inability to Interpret Complex Clinical Guidelines Clinical guidelines in healthcare are often intricate, with recommendations that are contingent upon a myriad of factors including the patient's medical history, the progression of their condition, comorbidities, and even social or psychological aspects that might influence treatment outcomes. These guidelines are not always straightforward or binary; they require a level of interpretation that considers the subtleties of human health and the art of medicine.
Challenges in Assessing Medical Necessity and Individual Cases Patient Needs Determining the medical necessity involves evaluating whether a particular medical procedure or treatment is essential for diagnosing or treating a patient's condition in accordance with accepted standards of medical practice. This determination is inherently complex and highly individualized, presenting several challenges for AI:
Complexities of Prior Authorization in Pain ManagementInterventional pain management is a specialized field that employs a range of procedures to diagnose and treat pain. These procedures can vary significantly in terms of their invasiveness, the technology used, and the specific conditions they aim to address. The field is particularly known for its application in managing spinal pain and orthopedic conditions, where precise, targeted interventions are often required to alleviate pain and improve patient function. Variety and Specificity of Pain Management Treatments The range of treatments in interventional pain management is extensive, encompassing various injections (like epidurals and facet joint injections), nerve blocks, minimally invasive spinal procedures, and more advanced techniques such as spinal cord stimulation. Each of these treatments is designed for specific types of pain conditions, often related to the spine, nerves, or musculoskeletal system. In the context of spinal pain and orthopedic surgeries, interventions may include:
The decision to employ a particular interventional technique is highly individualized, taking into account the patient's specific condition, medical history, previous treatment responses, and overall health status. This personalized approach is crucial because:
Importance of Diagnostic Imaging
An essential part of navigating interventional procedures is patient education. Patients should be informed about the potential benefits, risks, and alternatives of the proposed interventions. Informed consent is particularly crucial in spinal and orthopedic surgeries, where the procedures can have significant implications on the patient's life. A well-informed patient is better prepared to participate in their care, set realistic expectations, and engage in post-treatment rehabilitation, contributing to better outcomes. Importance of Conservative Treatment Trials Conservative treatments play a critical role in the management of pain, particularly for spinal and orthopedic conditions. These non-invasive options serve several purposes:
A comprehensive review of the patient's medical history and responses to previous treatments is crucial for several reasons:
Diagnostic imaging and reports are invaluable in the field of interventional pain management, especially for conditions related to the spine and musculoskeletal system. Tools such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans provide detailed insights into the anatomical structures and potential sources of pain, guiding the selection and planning of interventions. Importance of Accurate Diagnosis The accurate diagnosis of the source of pain is paramount in interventional pain management for several reasons:
Outsourcing pain management and orthopedic surgeries prior authorization to specialized services like GoHealthcare Practice Solutions can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of obtaining necessary approvals for treatments. This approach offers several key advantages for healthcare providers and their patients, particularly in the complex field of pain management. Expertise in Pain Management Prior Authorization GoHealthcare Practice Solutions possesses specialized knowledge and expertise in navigating the intricacies of prior authorization for pain management procedures. This expertise is critical because:
Outsourcing to GoHealthcare Practice Solutions allows for the streamlining of the prior authorization process, which can be highly beneficial for practices handling a high volume of cases, including spinal and orthopedic surgeries. Streamlined processes lead to:
With their focus on pain management and related procedures, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions brings a level of precision to the prior authorization process that can improve the success rate of authorization requests. This is due to:
Outsourcing prior authorization tasks to GoHealthcare Practice Solutions can lead to improved financial and operational efficiency for healthcare practices. This is achieved through:
Ultimately, by outsourcing pain management prior authorization to GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, healthcare providers can redirect their focus and resources towards direct patient care. This enhanced focus can lead to better patient outcomes, higher patient satisfaction, and a more efficient healthcare practice overall. In conclusion, outsourcing pain management prior authorization to specialized services like GoHealthcare Practice Solutions offers a strategic advantage for healthcare providers. It ensures that the complex and time-consuming process of obtaining prior authorizations is handled efficiently, accurately, and with a high degree of expertise, benefiting both providers and patients in the realm of pain management. The Role of Human Judgment in Medical and Surgical Prior Authorization The process of obtaining prior authorization for medical and surgical interventions, particularly in specialized fields like pain management and orthopedics, is inherently complex and nuanced. At the heart of this process lies the indispensable role of human judgment, which is critical in interpreting clinical policies and guidelines, delivering patient-centered care, and navigating the ethical and empirical aspects of medical decision-making. Clinical Policy and Guidelines The Intricate Nature of Medical Guidelines Medical guidelines are designed to provide healthcare professionals with evidence-based recommendations for the treatment of various conditions. However, these guidelines are often intricate, encompassing a wide range of potential patient scenarios and treatment modalities. Human judgment is crucial in:
Each patient presents a unique set of clinical challenges, necessitating a personalized approach to treatment. Human judgment plays a key role in:
In the realm of prior authorization, especially for interventions that can significantly impact a patient's quality of life, a patient-centered approach is paramount. This approach relies heavily on human judgment in several aspects: Considering Patient-Reported Outcomes, ADL, and Pain Scores Human judgment is essential in interpreting patient-reported outcomes, activities of daily living (ADL) assessments, and pain scores. These subjective measures provide insight into the patient's experience and are critical in:
The customization of treatment plans to address the unique needs of each patient is a complex process that requires:
Medical and surgical prior authorization processes are also fraught with ethical and empirical considerations that require nuanced human judgment. Ethical Implications of Treatment DecisionsTreatment decisions, especially those requiring prior authorization, often carry significant ethical implications. Clinicians must navigate issues related to:
While Artificial Intelligence (AI) has made significant advancements in healthcare, there are inherent limitations that prevent it from fully replicating the nuanced and multifaceted role of human judgment in medical and surgical prior authorization processes. These limitations stem from the current capabilities of AI systems and their inability to fully grasp and navigate the complexities inherent in healthcare decision-making. Understanding Context and Nuance AI systems, including the most advanced machine learning models, primarily operate by recognizing patterns in data. However, the subtleties of clinical decision-making often involve understanding context, nuance, and the unique circumstances of individual patients—areas where AI currently falls short. For example:
AI systems are not equipped to navigate the ethical considerations inherent in medical decision-making. Decisions about patient care often involve ethical judgments about patient autonomy, equity, and the best interests of the patient—areas that rely on human values and empathy. Additionally, the empirical nature of medical decision-making, which blends scientific evidence with clinical intuition and experience, is something that AI cannot replicate. Human clinicians draw on a wealth of experience and tacit knowledge that AI cannot access. Adaptability and Flexibility The medical field is characterized by continuous evolution, with new research, treatments, and guidelines emerging regularly. Human clinicians are capable of adapting to these changes, integrating new knowledge into their practice in a way that AI systems cannot easily replicate. AI requires retraining and updating to incorporate new information, a process that can be time-consuming and may lag behind the pace of medical advancements. Communication and Empathy A significant component of the prior authorization process involves communication with patients, families, and insurance representatives. Human clinicians can provide explanations, offer reassurance, and discuss the rationale behind treatment decisions in a way that is empathetic and responsive to the concerns and emotional states of patients and their families. AI lacks the ability to engage in this level of empathetic communication and to make judgments that consider the emotional and psychological aspects of patient care. Dealing with Uncertainty and Complexity Medical decision-making often involves navigating uncertainty and making judgments in situations where there is no clear "right" answer. Human clinicians can consider a wide range of factors, including potential risks, benefits, and the preferences and values of the patient, to make decisions in these complex situations. AI, on the other hand, may struggle in the face of ambiguity and complexity, particularly when decisions require a balance of competing considerations that are not easily quantifiable. In summary, while AI can support certain aspects of healthcare, the full scope of medical and surgical prior authorization requires human judgment, empathy, ethical reasoning, and the ability to navigate complex, nuanced, and evolving scenarios. These are inherently human capabilities that AI, in its current state, cannot replicate or replace. Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions for Prior Authorization Services for Interventional Pain Management and Orthopedic Surgeries? For all the healthcare providers and groups facilities navigating the complexities of the prior authorization process for interventional pain management and orthopedic surgeries, partnering with a seasoned expert like GoHealthcare Practice Solutions can be a game-changer. With over 20 years of dedicated experience in this specialty, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions stands out as a unique provider of prior authorization services, unmatched in its depth of knowledge, expertise, and specialized focus. Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions for Prior Authorization Services for Interventional Pain Management and Orthopedic Surgeries? Unparalleled Expertise With two decades of experience, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions brings a level of expertise to the table that is unparalleled in the industry. This extensive experience means they have encountered and successfully navigated virtually every possible scenario in the realm of interventional pain management and orthopedic surgeries. Their team of experts understands the nuances and intricacies of these specialties, ensuring that prior authorization processes are handled with the utmost precision and professionalism. Comprehensive Coverage GoHealthcare Practice Solutions is adept at managing a broad spectrum of cases, including those involving both in-network and out-of-network insurance payers. They are also highly skilled in handling injury cases resulting from motor vehicle accidents and workers' compensation claims. This comprehensive coverage ensures that no matter the complexity or nature of the case, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions has the expertise to manage it effectively. HIPAA Compliance and Adherence to Regulations In today's healthcare environment, compliance with HIPAA and government regulations is not just important—it's imperative. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions prides itself on its stringent compliance measures, ensuring that all patient information is handled with the highest level of confidentiality and security. Providers can have peace of mind knowing that their prior authorization processes are not only efficient but also fully compliant with all regulatory standards. Customized Support Tailored to Your Needs Understanding that each provider and patient case is unique, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions offers personalized solutions tailored to meet specific needs. Their approach is not one-size-fits-all; it's a customized strategy designed to optimize the prior authorization process for your particular practice and patient population. Making the Right Choice Choosing GoHealthcare Practice Solutions means opting for a partner that brings an unmatched level of expertise and dedication to the table. Their 20+ years in the field specifically focused on interventional pain management and orthopedic surgeries make them a standout provider in an area where specialized knowledge is crucial. For healthcare providers looking to streamline their prior authorization processes, reduce administrative burdens, and ensure the highest standard of patient care, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions is the ideal choice. Their commitment to excellence, compliance, and personalized service makes them not just a service provider, but a partner in your practice's success. Take the Next StepIf you're ready to enhance your practice's efficiency and focus more on patient care rather than administrative tasks, contact GoHealthcare Practice Solutions today. Experience the difference that expertise, specialization, and a commitment to compliance can make in your prior authorization processes. Join the numerous satisfied providers who have transformed their practices with the help of GoHealthcare Practice Solutions. Don't let the complexities of prior authorization hold your practice back—let GoHealthcare Practice Solutions pave the way for smoother, more efficient operations and the highest level of patient care. Insurance Payers websites:
To find prior authorization details for a specific insurer:
It's essential to note that prior authorization requirements and processes can vary within the same insurance company based on the specific plan, region, or state regulations. So, always ensure that you're referencing the correct resources for your particular scenario. For a comprehensive list tailored to your needs or for other insurance companies not mentioned here, it would be best to consult a directory or directly visit the website of the insurance payer in question. Third-party entities play a vital role in the prior authorization process for various insurance companies. Let's explore some of these entities, including Cohere, NIA (National Imaging Associates), and Carelone.
These entities offer tools and platforms to streamline the process of prior authorization, ensuring that patients receive timely, evidence-based care. Their collaborative frameworks often bridge the gap between healthcare providers and insurance payers, making the care journey smoother for all involved. Discover the Future of Prior Authorization with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions In the rapidly evolving realm of healthcare, finding a reliable partner for your prior authorization needs is paramount. Amid the myriad of options available, one company emerges as a trusted leader: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions. Orthopedic Procedures that require Prior Authorization:
Pain Management Procedures that may require Prior Authorization:
Pain Management Procedures:
Spinal Procedures:
We understand that the prior authorization process can be challenging and may sometimes feel like an administrative hurdle. However, it's important to remember that behind every authorization request is a patient seeking relief from pain, a chance for improved mobility, or a path to better health. Your dedication to this process directly impacts their lives, providing hope and healing. Let's remember that the prior authorization process is a critical link between exceptional patient care and the success of our practice as a business. Your dedication to this important task ensures that our patients receive the care they need, and our practice thrives. Thank you for your commitment and hard work in making a positive impact on both our patients' lives and our practice's future." The importance of prior authorization services in orthopedic, pain management, and hospital care settings cannot be overstated. As healthcare professionals and staff, your dedication to this process is a testament to your commitment to patient well-being and the success of our practice as a business. Remember that behind each authorization request lies a patient's hope for relief and a brighter future. By efficiently navigating this complex landscape, you ensure that our patients receive the care they need while safeguarding the financial health of our practice. Together, let's continue to streamline processes, leverage technology, and maintain open communication to make the prior. The prior authorization process stands as a cornerstone of your commitment to exceptional patient care and the profitability of your practice. Every prior authorization request represents an opportunity to enhance the lives of your patients, delivering them the relief and care they rightfully deserve. Moreover, it's a chance to ensure the financial well-being and continued growth of your practice as a business. As your endeavor to excel in both realms, we invite you to consider the exceptional support and expertise of GoHealthcare Practice Solutions. With an astounding track record boasting a remarkable 98% approval rate, they have consistently demonstrated their exceptional ability to assist your practice with prior authorization, resulting in significant time and financial savings. Their proficiency extends to eliminating the need for peer-to-peer consultations through meticulous review of medical necessity, aligned with utilization guidelines. Their extensive knowledge of clinical guidelines and policies, including frequency considerations, is unparalleled. By partnering with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, you open doors to a future where patients receive timely, necessary care without the hassle and uncertainty of prior authorization delays. It's an opportunity to streamline your operations, reduce administrative burdens, and focus on what you do best—providing exceptional care. Discover how GoHealthcare Practice Solutions can empower your practice's journey toward excellence. Explore their invaluable services and learn more about how they can transform the way you care for your patients and run your practice efficiently. Your choice to partner with them isn't just a decision; it's a commitment to a brighter, patient-centric future. Together, we can elevate your practice to new heights and ensure that every patient's path to healing is clear and uncompromised. Embrace the future of healthcare with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions. Learn more at https://www.gohealthcarellc.com Thank you for your unwavering dedication and the positive impact you make on both your patients' lives and your practice's future." Searched keywords: Human expertise prior authorization process in interventional pain management, Limitations of AI in healthcare, Complexities of prior authorization in pain management, Navigating interventional pain management procedures, The role of human judgment in medical and surgical prior authorization, Prior Authorization Outsourcing Company for Interventional Pain Management and Orthopedic Surgeries. Outsourcing Prior Authorization for Oncologic Surgery | Navigating Complexities for Improved Patient Care In the fast-paced and evolving realm of oncologic surgery, ensuring timely and effective treatments is paramount. With cancer cases rising globally, the demand for specialized surgeries has increased manifold. An essential, albeit often cumbersome, step in this process is acquiring prior authorization (PA) from insurance companies. In response, many healthcare providers are outsourcing PA, particularly for oncologic surgery. This article will explore the motivations, advantages, and challenges of this move. Understanding the Complexity: Oncologic Surgery and Its Nuances: Oncologic surgery involves the surgical treatment of cancer and is often complemented by chemotherapy, radiation, and other treatments. With advancements in technology and techniques, new and specialized surgical procedures are constantly emerging. Each procedure has its protocols, requirements, and cost structures, which can vary significantly. Prior Authorization Challenges: For oncologic surgeries, obtaining PA can be particularly daunting. The high costs associated with these procedures, combined with their urgency, means any delay can have severe repercussions. Errors or delays in PA can lead to deferred surgeries, leading to compromised patient care. The Allure of Outsourcing: Expertise on Demand: By outsourcing PA for oncologic surgery, healthcare providers can tap into a dedicated team of experts who are updated with the latest in insurance policies, procedure codes, and medical advancements. This expertise can streamline the approval process significantly. Efficiency and Speed: Dedicated PA outsourcing firms often have automated systems and standardized processes that can reduce turnaround times. For time-sensitive oncologic surgeries, this can make a substantial difference in patient outcomes. Cost-Effectiveness: Maintaining an in-house team for PA, especially for specialized fields like oncologic surgery, can be expensive. Training, infrastructure, and continual updates can drain resources. Outsourcing can provide a scalable solution, allowing providers to pay for services as needed. Focus on Patient Care: With the administrative burden of PA taken care of, healthcare providers, particularly surgeons, can focus on what they do best – delivering exceptional patient care. Potential Pitfalls and Overcoming Them: Loss of Personal Touch: One argument against outsourcing is the potential loss of a personal touch. In-house teams might have a better understanding of individual patient histories and nuances. However, with efficient communication channels and robust data-sharing protocols, this gap can be bridged. Data Privacy Concerns: Sharing patient data with third-party vendors can raise valid concerns about data security and privacy. It's crucial to choose outsourcing partners who comply with global standards like HIPAA and have stringent data protection measures in place. Dependence on External Entities: Over-reliance on external vendors can sometimes lead to complacency within the organization. It's essential to have contingency plans and regular audits to ensure that the outsourcing partner's performance remains optimal. The Way Forward: Outsourcing prior authorization in oncologic surgery represents a strategic move to enhance administrative efficiency without compromising patient care. As with any significant change, there are challenges, but with the right approach, they can be navigated. For healthcare providers, the goal remains unwavering: to ensure patients receive timely and effective treatments. If outsourcing PA can aid in this endeavor, it's a path worth considering. This article provides a comprehensive look at the subject, but it's essential for healthcare providers to conduct their due diligence and research when considering outsourcing prior authorization for oncologic surgery or any other medical field. Medical Necessity: The Cornerstone of Prior Authorization in Oncologic Surgery In the world of healthcare, especially within the realm of oncologic surgery, medical necessity is the linchpin that guides decisions, treatments, and patient pathways. It's the critical intersection where the physician's clinical expertise meets the patient's unique health requirements. And when we talk about outsourcing prior authorization, understanding and championing medical necessity becomes even more vital. Medical Necessity Defined: At its core, medical necessity refers to a decision that a treatment, test, or procedure is necessary for a patient's health or to treat a diagnosed medical problem. In oncologic surgery, this can mean the difference between life and death, between arresting the progress of a malignancy or letting it advance. Prior Authorization's Role: Prior authorization is designed as a checkpoint to ensure that treatments are not only needed but are also the most efficient and effective means of addressing a health issue. While the intent behind PA is to manage healthcare costs and ensure the judicious use of resources, it should never compromise the tenet of medical necessity. Outsourcing Prior Authorization Challenges and Solutions: Championing Medical Necessity: Companies specializing in PA for oncologic surgery must have a deep-rooted understanding of the principle of medical necessity. They must be equipped not only with administrative know-how but also with a clinical understanding, enabling them to interpret and champion the physician's recommendations effectively. Streamlined Processes: One major challenge in the PA process is the potential for delays, which can be detrimental in cases of oncologic surgery. With an appreciation of medical necessity, companies can streamline their processes to prioritize urgent cases and expedite approvals, ensuring that the patient's health is never compromised. Bridging the Knowledge Gap: A company's team must be trained to understand the nuances of oncologic conditions, treatments, and surgical interventions. This ensures that when a physician cites medical necessity, the team can validate and support that claim effectively with insurance providers. Feedback Loops: Constructive feedback loops between the healthcare provider and the PA company are vital. Regular feedback ensures that the company is aligned with the medical necessity's evolving definitions and the dynamic landscape of oncologic treatments. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve and the demand for specialized treatments like oncologic surgery grows, the role of prior authorization becomes even more critical. Outsourcing this responsibility to specialized companies can be advantageous, but only if these companies uphold the sacrosanct principle of medical necessity. By doing so, they can ensure that the patient's best interests are always prioritized, and the pivotal physician-patient relationship remains at the heart of every decision. Building Collaborative Frameworks for Success: Integration with Clinical Pathways: Understanding medical necessity isn't just about comprehending a surgeon's note or a physician's recommendation. It's about integrating the PA process within established clinical pathways. Oncologic surgery, often being complex and multifaceted, relies on structured clinical pathways to ensure optimal patient outcomes. Companies that excel in providing outsourced PA services actively seek to understand and align with these pathways. This ensures that their decisions not only uphold medical necessity but also sync seamlessly with the treatment journey that a patient is on. Strengthening Physician Collaboration: For a successful outsourced PA process, the relationship between the PA company and the physician should be more than transactional. It should be collaborative. Regular interactions, case discussions, and knowledge-sharing sessions can significantly enhance the understanding of medical necessity. This collaborative approach ensures that, over time, the PA company becomes an extension of the healthcare provider, aligning closely with the core values and patient-centric ethos of the physician. Utilizing Data Effectively: While individual cases are unique, patterns often emerge when one looks at oncologic surgery requests at a macro level. Effective PA companies use data analytics to identify these patterns. By doing so, they can preempt common challenges, understand where medical necessity is frequently cited, and streamline their processes to address these recurring themes. This proactive approach ensures faster response times and more accurate PA evaluations. Patient Advocacy: Ultimately, every stakeholder in the healthcare system, from the physician to the PA specialist, is working towards the same goal: the well-being of the patient. Companies specializing in PA must also view themselves as patient advocates. By championing medical necessity, they play a pivotal role in ensuring that patients get the care they require without undue administrative delays or barriers. The Road Ahead: The dynamic nature of healthcare, especially in areas as critical and rapidly evolving as oncologic surgery, means that systems and processes will continuously need to adapt. As more healthcare providers lean towards outsourcing PA, the mandate for these specialized companies becomes clear. They must prioritize medical necessity, foster collaboration, and utilize data effectively. By doing so, they will not only provide an essential service but also become invaluable allies in the collective mission to deliver the best patient care. Leveraging Insurance Payers' Clinical Guidelines and Medical Policies: Central to the optimization of the prior authorization process, especially in the realm of oncologic surgery, is the intricate understanding and application of insurance payers' clinical guidelines and medical policies. These guidelines, often meticulously detailed, lay down the criteria that treatments and procedures must meet to be deemed medically necessary and, consequently, be approved for coverage. Deep Diving into Clinical Guidelines: Clinical guidelines provided by insurance payers are an amalgamation of evidence-based medicine, payer-specific policies, and often, cost-management strategies. For a company specializing in PA, it's not enough to be passively aware of these guidelines. Instead, an in-depth understanding is crucial. This ensures that every PA request is framed in a manner that aligns with these guidelines, thereby improving the chances of swift and accurate approvals. Staying Updated with Dynamic Medical Policies: Medical policies of insurance payers are not static. They evolve based on emerging medical research, cost considerations, and feedback from healthcare providers. An effective PA company constantly monitors these changes, ensuring that their processes and recommendations stay current. This proactive approach not only enhances the efficiency of the PA process but also minimizes the chances of denials based on outdated information. Facilitating Continuous Education: Given the dynamic nature of clinical guidelines and medical policies, continuous education becomes imperative for PA teams. Regular training sessions, workshops, and interactions with insurance payers can ensure that the team is always equipped with the latest knowledge, ready to make informed decisions that uphold the principle of medical necessity. Bridging the Gap with Physicians: Physicians, while experts in their clinical domain, might not always be abreast of the frequent changes in insurance clinical guidelines. Here, the PA company can play a crucial role, acting as a bridge. By effectively communicating these guidelines to physicians, they can ensure that treatment plans are formulated keeping in mind both the patient's best interests and the likelihood of swift insurance approvals. Prior authorization, especially in fields as critical as oncologic surgery, is not a mere administrative task. It's a collaborative effort that necessitates understanding, championing, and communicating medical necessity. By effectively leveraging insurance payers' clinical guidelines and medical policies, PA companies can ensure they're playing their part efficiently in the larger healthcare ecosystem, ensuring patients receive the timely care they critically need. Streamlining Prior Authorization: Bypassing Peer-to-Peer Reviews through Mastery of Insurance Medical Policies and Patient Coverage Understanding to Eliminate Redundancy: One of the primary reasons for a peer-to-peer review is a discrepancy or lack of clarity between the proposed medical treatment and the payer's policies or the patient's specific coverage. However, if a PA company has an intrinsic understanding of these facets, they can preemptively address potential issues, making the peer-to-peer process redundant. Tailored Approaches: Every patient's insurance coverage is unique. By understanding the specifics of a patient's plan, a PA company can tailor their authorization request to match the coverage's nuances. This precision ensures that there's minimal room for contention or confusion, reducing the need for further verification through peer-to-peer processes. Real-time Benefits: The key advantage of bypassing peer-to-peer reviews is the time saved. Especially in critical domains like oncologic surgery, where every moment counts, streamlining the PA process can have tangible benefits on patient outcomes. A swift PA process ensures timely surgeries, potentially reducing complications and improving prognosis. Cost-Effectiveness: The peer-to-peer process, while designed to ensure the appropriateness of medical procedures, has an associated cost – both in terms of time and monetary resources. By optimizing the PA process, healthcare providers can make significant cost savings. This not only makes economic sense but also allows resources to be diverted to more pressing patient care needs. In the intricate dance of medical care, insurance coverages, and administrative processes, the goal should always be to ensure that the patient receives timely and appropriate care. By mastering the specifics of insurance medical policies and understanding the depths of a patient's coverage, PA companies can play a pivotal role in streamlining the oncologic surgery journey. This not only ensures better patient outcomes but also strengthens the overall healthcare system by fostering trust, efficiency, and collaboration among its stakeholders. Challenges of Prior Authorization with Out-Of-Network Surgeons: Coverage Limitations: Even if a procedure is deemed medically necessary, it might not be covered or may be covered at a substantially lower rate when the surgeon is OON, presenting potential financial challenges for patients. Variability in PA Criteria: Different insurance companies maintain distinct criteria for granting PA, particularly for OON providers. This constant change makes it a challenge for OON surgeons to stay updated. Divergent Reimbursement Structures: OON surgeons might face uncertainties around how insurance companies will reimburse, leading to potential financial ambiguities for both providers and patients. Extended Wait Times: Without established protocols between OON providers and insurers, there might be delays in the PA process. Increased Scrutiny on Medical Necessity: OON requests might require more rigorous justification, including additional documentation or clinical evidence. Patient's Financial Dilemma: While a specific surgeon may be the best fit clinically, patients are often trapped between choosing the best care and potential financial repercussions. Strategies to Address the Challenges: Negotiated Fees: OON providers can negotiate fees directly with insurance companies. Such negotiations can result in an agreed-upon rate for services, which can mitigate some of the financial uncertainties for both the patient and the provider. Gap Exemptions: Some insurance plans offer a "gap exemption" if there's no available in-network provider with the required expertise. This means that an OON surgeon could be treated as in-network for reimbursement purposes, significantly reducing the patient's out-of-pocket expenses. Single Case Agreements: When a patient needs a specific procedure or expertise that only an OON surgeon can provide, single case agreements (SCA) can be utilized. SCAs are individually negotiated rates between the provider and the insurance company for a particular case, ensuring that both parties have clarity on costs and reimbursements. Proactive Patient Counseling: Engaging patients early and explaining the potential financial implications, while also discussing the avenues of negotiated fees, gap exemptions, or SCAs, can help in informed decision-making. Engage in Collaborative Communication: Direct communication lines with insurance companies can expedite the PA process and help address any queries or discrepancies in real-time. Transparency with Patients: Beyond medical details, ensure complete clarity about potential costs, the chances of obtaining a gap exemption, or the feasibility of a single case agreement. This transparency can empower patients in their healthcare journey. Navigating the terrain of prior authorization with out-of-network surgeons is undeniably complex. Yet, mechanisms like negotiated fees, gap exemptions, and single case agreements offer valuable pathways to bridge the gap between optimal patient care and the financial aspects of healthcare. By proactively harnessing these strategies and maintaining open communication, healthcare providers can offer patients both clinical excellence and financial clarity. Oncologic Surgeries that may Require Prior Authorization: Mastectomy and Breast Reconstruction: Procedures like radical mastectomy, modified radical mastectomy, and lumpectomy, followed by breast reconstruction surgeries, such as tissue expansion or flap reconstruction, often require prior authorization to ensure the patient is receiving the most appropriate care based on their specific diagnosis and health history. Lung Resection: Surgeries like lobectomy or pneumonectomy, performed to treat lung cancer, are significant operations that need prior verification to confirm the necessity of the procedure and ensure optimal patient outcomes. Prostatectomy: Radical prostatectomy, whether done via open surgery, laparoscopically, or using robotic assistance, is another procedure where PA might be mandated to validate the need for surgical intervention over other treatment options. Colectomy: Performed for colorectal cancers, surgeries like partial, total, or hemicolectomy can require PA due to the various surgical options available and the need to align the chosen method with evidence-based guidelines. Pancreatectomy: Whether it's a Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy) or a distal pancreatectomy, these surgeries for pancreatic cancer are intricate and often necessitate PA to ensure they're the best course of action for the patient. Cytoreductive Surgery with Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC): This is a specialized treatment for specific abdominal cancers. Given its complexity and the associated costs, PA is frequently required. Liver Resection: Partial hepatectomy or segmentectomy to address liver malignancies can necessitate PA to determine if the surgery aligns with the best practices for the specific type and stage of cancer. Radical Cystectomy: For invasive bladder cancer, a radical cystectomy, which involves removing the entire bladder and possibly surrounding organs, can require PA due to the procedure's invasiveness and potential for significant post-surgical complications. Bone Tumor Resections: Procedures like limb-sparing surgery or amputation for bone cancers like osteosarcoma or Ewing sarcoma might require PA to evaluate the necessity and potential outcomes of the surgery. Gynecologic Oncology Surgeries: Procedures like radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer, debulking surgery for ovarian cancer, or radical trachelectomy often need PA to ensure alignment with best-practice guidelines and individual patient needs. Glioma Resection: Surgery to remove tumors from the brain, such as for glioblastomas, demands intricate surgical skills and post-operative care. Given the risks associated with brain surgeries, PA is often required. Thyroidectomy: This procedure, which involves the partial or total removal of the thyroid gland, can be used to treat thyroid cancers. Different surgical approaches and their implications often make PA a necessity. Laryngectomy: Total or partial removal of the larynx due to laryngeal cancer can lead to significant changes in a patient's ability to speak or breathe normally, thus mandating PA. Esophagectomy: A procedure to remove part or all of the esophagus, typically for esophageal cancer. Given the procedure's potential impact on swallowing and digestion, PA is frequently required. Gastrectomy: Whether it's a partial or total removal of the stomach for gastric cancer, the implications for digestion and nutrition make PA crucial. Cholecystectomy: n the context of gallbladder cancer, this procedure involves the removal of the gallbladder and possibly parts of the liver and bile duct. Nephrectomy: This procedure involves the removal of a kidney, either partially or wholly, and is done in cases of renal cell carcinoma. Given the importance of the kidneys, PA is often a requisite. Oophorectomy: Removal of one or both ovaries due to ovarian cancer. Given the implications for fertility and hormone levels, PA is frequently required. Orchiectomy: Surgical removal of one or both testicles due to testicular cancer. The procedure can have ramifications for fertility and hormone production, making PA vital. Salpingectomy: This involves the removal of one or both fallopian tubes and is sometimes performed in cases of fallopian tube cancer or as a preventive measure for certain high-risk individuals. Resection of Sarcomas: Sarcomas, being rare and found in various locations like muscles, nerves, and bones, might require specialized surgical resections. Due to the variability and the potential impact on function, PA is often sought. Melanoma Excisions: Depending on the depth and location, melanomas might require wide excision surgeries, which often need PA, especially if skin grafting or other reconstructive procedures are anticipated. Tumor Debulking: In cases where removing an entire tumor isn't feasible, such as with certain ovarian or mesothelioma cases, debulking surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible might be conducted. The potential benefits versus risks often necessitate PA. Given the breadth of oncologic surgeries, it's crucial that PA processes are both rigorous and efficient. They play a pivotal role in ensuring patients receive surgeries that align with evidence-based guidelines, improving outcomes and ensuring the judicious use of healthcare resources. Insurance Payers websites:
To find prior authorization details for a specific insurer:
It's essential to note that prior authorization requirements and processes can vary within the same insurance company based on the specific plan, region, or state regulations. So, always ensure that you're referencing the correct resources for your particular scenario. For a comprehensive list tailored to your needs or for other insurance companies not mentioned here, it would be best to consult a directory or directly visit the website of the insurance payer in question. Third-party entities play a vital role in the prior authorization process for various insurance companies. Let's explore some of these entities, including Cohere, NIA (National Imaging Associates), and Carelone.
These entities offer tools and platforms to streamline the process of prior authorization, ensuring that patients receive timely, evidence-based care. Their collaborative frameworks often bridge the gap between healthcare providers and insurance payers, making the care journey smoother for all involved. Discover the Future of Prior Authorization with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions In the rapidly evolving realm of healthcare, finding a reliable partner for your prior authorization needs is paramount. Amid the myriad of options available, one company emerges as a trusted leader: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions. Why choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions? Here's what sets them apart: Expertise: With years of experience in the field, GoHealthcare has honed its skills to perfection. Their deep-rooted knowledge ensures that your prior authorization needs are addressed with precision and care. Integrity: Trust is non-negotiable in healthcare. GoHealthcare understands this, ensuring transparent, honest, and reliable services that you can depend on every step of the way. Efficiency: In the world of medical services, time is of the essence. GoHealthcare's efficient processes ensure swift turnarounds, minimizing wait times and streamlining operations. Customized Solutions: Recognizing that no two healthcare providers are the same, GoHealthcare offers tailored solutions, ensuring that the specific needs of each client are met. Advanced Technology: By leveraging cutting-edge technology, GoHealthcare ensures accuracy, speed, and a seamless experience, positioning themselves at the forefront of modern healthcare solutions. Dedicated Support: With a robust support team ready to assist, clients can be assured of constant guidance and prompt issue resolution. If you're in the market to outsource your prior authorization needs, don't leave it to chance. Opt for a company with a proven track record, unwavering commitment, and unparalleled expertise. Opt for GoHealthcare Practice Solutions – your trusted partner in navigating the intricacies of prior authorization. Patient-Centric Approach: At the heart of every service offered by GoHealthcare is the patient. By focusing on the patient's needs and ensuring timely and accurate prior authorizations, the company ensures that patients receive the care they deserve without unnecessary delays. Cost-Effective Solutions: With healthcare costs rising, GoHealthcare offers solutions that don't break the bank. Their efficient processes result in significant cost savings for healthcare providers, without compromising on the quality of service. End-to-End Services: Beyond just prior authorizations, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions provides an array of services, including billing, coding, and claim resolution. This holistic approach means clients can focus on patient care, leaving the administrative burdens to the experts. Industry Collaboration: Keeping pace with the dynamic healthcare landscape, GoHealthcare actively collaborates with industry experts, regulatory bodies, and insurance providers. This ensures they remain abreast of the latest changes and can swiftly adapt, offering their clients the most updated solutions. Data Security: In an age where data breaches are a growing concern, GoHealthcare makes no compromises. Employing state-of-the-art security measures, they ensure that every piece of information is guarded with the utmost care. Choosing the right outsourcing partner can make a world of difference in the healthcare ecosystem. Delays, inaccuracies, and inefficiencies not only impact the bottom line but, more critically, can affect patient care. Don't let your organization be bogged down by these challenges. Elevate your operations, enhance patient satisfaction, and streamline your administrative tasks. Partner with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions - a name synonymous with trust, efficiency, and excellence in the realm of prior authorization services. Scalability: One of GoHealthcare’s standout features is its ability to scale services according to the client’s needs. Whether you're a small clinic or a multi-specialty hospital, they can adjust their services to meet your demands. This flexibility ensures that as your practice grows, your prior authorization processes can evolve seamlessly alongside it. Proactive Approach: Unlike reactive services that only address issues as they arise, GoHealthcare adopts a proactive stance. Their team anticipates potential challenges and implements preemptive strategies, ensuring smoother workflows and reduced bottlenecks. Regulatory Compliance: In the ever-shifting landscape of healthcare regulations, staying compliant is imperative. GoHealthcare is steadfast in its commitment to regulatory adherence, ensuring that all processes align with current federal and state mandates. Transparent Reporting: Clients are never left in the dark. With GoHealthcare's transparent reporting system, healthcare providers receive regular updates, insights, and analyses, enabling them to make informed decisions and gain a clearer overview of their prior authorization status. Client-Centric Feedback Loop: GoHealthcare believes in the power of collaboration. They maintain an open channel of communication with clients, valuing feedback and using it as a tool for continuous improvement. Innovative Solutions: In a field that’s continually evolving, GoHealthcare doesn’t rest on its laurels. They're always on the lookout for innovative methods, tools, and best practices to enhance their service offerings and deliver unmatched value to their clients. Diverse Expertise: Their team is a blend of healthcare professionals, administrative experts, and technical specialists. This diversity ensures a well-rounded approach to prior authorization, merging the nuances of medical care with the precision of administrative processes. Sustainable Partnerships: GoHealthcare isn't just a service provider; they strive to be a partner in your growth. Their commitment extends beyond transactions, focusing on building long-term, sustainable relationships that support the overarching goals of their clients. In an industry where precision, timeliness, and patient welfare are paramount, there's no room for errors or inefficiencies. By choosing GoHealthcare Practice Solutions as your outsourcing partner, you're not just opting for a service – you're investing in a partnership that prioritizes excellence, innovation, and the highest standards of patient care. Join the ranks of numerous healthcare providers who have transformed their prior authorization processes with GoHealthcare, and experience the difference firsthand. Key Takeaways: Embracing Excellence with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions In the intricate dance of healthcare operations, prior authorization stands out as one of the most complex and critical steps. But with complexity comes the opportunity for innovation, and that's precisely where GoHealthcare Practice Solutions shines brightest. Here are some transformative takeaways from our deep dive into their services: Trust in Expertise: Decades of combined experience mean that GoHealthcare isn’t just performing tasks; they're crafting solutions tailored to each client's unique needs. The Power of Proactivity: In the fast-paced world of healthcare, being reactive just doesn't cut it anymore. GoHealthcare's proactive approach ensures potential issues are addressed long before they become problems. Innovation as a Standard: Stagnation is not in GoHealthcare's vocabulary. They’re perpetually at the cutting edge, integrating the latest tools and strategies to offer unparalleled service. A Partnership, Not Just a Service: With GoHealthcare, you're not just hiring an outsourcing company; you're gaining a partner genuinely invested in your growth, success, and the well-being of your patients. Comprehensive Care: From prior authorizations to billing, GoHealthcare offers an end-to-end service spectrum, ensuring healthcare providers can focus on what they do best: delivering exceptional patient care. The Assurance of Security: In a digitized age, the sanctity of data is paramount. With GoHealthcare, rest easy knowing that every fragment of information is shielded with state-of-the-art security measures. Transformative Scalability: Whether you're a budding clinic or a healthcare giant, GoHealthcare has the versatility to scale its solutions, ensuring you always get exactly what you need. Unwavering Commitment to Excellence: At its core, GoHealthcare's mission is unwavering dedication to excellence, ensuring each client receives the gold standard in service, every single time. In conclusion, while the challenges of healthcare are many, the solutions need not be complex or burdensome. With GoHealthcare Practice Solutions at your side, embrace a future where administrative excellence complements clinical expertise. Dive into a realm where patient care is unhindered by red tape, where every process is streamlined, and where your practice's potential is realized to the fullest. Embrace the GoHealthcare difference. Your patients, and your peace of mind, deserve nothing less. Why Prior Authorization Is Imperative in Orthopedic, Pain Management, and Hospital Care Discover the compelling reasons why prior authorization is imperative in the realms of orthopedic, pain management, and hospital care. Learn how it guarantees the highest level of care for patients and sustains healthcare providers' operations. The healthcare landscape in the United States has undergone significant transformations over the years, and with it, the complexities of healthcare administration have grown exponentially. One crucial aspect of this administrative puzzle is the process of prior authorization services, a critical component that directly impacts patient care, provider reimbursement, and the overall efficiency of healthcare delivery. In this article, we will delve into the importance of prior authorization services, with a special focus on its relevance in orthopedic, pain management, and hospital care settings. We will explore the process, challenges, and benefits associated with prior authorization services in these areas. Importance of Understanding Prior Authorization Process: Prior authorization services play a pivotal role in the healthcare ecosystem for several reasons:
The Process of Prior Authorization and why it matters: The process of prior authorization process is multifaceted and involves several key steps:
Challenges in Prior Authorization While prior authorization process serve critical purposes, they also come with challenges:
Benefits of Prior Authorization: Despite the challenges, prior authorization services offer several benefits:
Prior authorization services are an integral part of the modern healthcare system. They serve as a valuable tool for cost control, patient safety, and efficient resource allocation. While they come with administrative challenges, their benefits in terms of cost savings, quality control, and revenue protection cannot be overstated. In orthopedic, pain management, and hospital care settings, prior authorization plays a crucial role in ensuring that patients receive the right care at the right time while maintaining the financial health of healthcare providers and payers. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, finding ways to streamline and improve the prior authorization process will remain a priority to optimize patient care and resource utilization. Addressing Challenges and Enhancing Efficiency: To overcome the challenges associated with prior authorization, healthcare stakeholders should consider implementing strategies to enhance efficiency and reduce administrative burden:
Looking Ahead:
The importance of prior authorization process in orthopedic, pain management, and hospital care cannot be overstated. While the process comes with its share of challenges, it serves as a vital tool in maintaining the quality of care, controlling healthcare costs, and protecting the financial interests of healthcare providers. By addressing administrative inefficiencies and promoting transparency and standardization, the healthcare industry can work towards a future where prior authorization services are more efficient, less burdensome, and ultimately more patient-centered. Why Outsource your Prior Authorization of Procedures for Interventional Pain Management and Orthopedic Surgeries? Expertise and Experience: Specialized prior authorization companies, like GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, have a deep understanding of the intricate and evolving healthcare landscape. They possess the expertise required to navigate the complex requirements and guidelines specific to pain management services, ensuring a higher rate of successful approvals. Time Efficiency: Handling prior authorization in-house can be time-consuming, diverting valuable resources away from patient care. Outsourcing streamlines the process, reducing administrative burdens and allowing healthcare providers to focus on delivering quality pain management services. Increased Approval Rates: Outsourcing companies often have a proven track record of achieving higher approval rates. Their in-depth knowledge of medical necessity criteria, coding, and documentation requirements can significantly enhance the chances of successful authorizations. Cost Savings: Efficient prior authorization processes can lead to cost savings for the practice. Outsourcing eliminates the need for hiring and training additional staff, reduces administrative overhead, and minimizes potential revenue loss due to denied claims. Reduced Administrative Errors: Prior authorization entails meticulous documentation and adherence to stringent guidelines. Outsourcing companies are well-equipped to minimize errors and ensure that all necessary documentation is complete and accurate, reducing the likelihood of denials due to administrative issues. Streamlined Workflow: Outsourcing allows for a streamlined workflow, with dedicated experts managing the entire authorization process. This not only ensures a smoother process but also enables timely scheduling of patient appointments and procedures. Focus on Patient Care: By entrusting the prior authorization process to experts, healthcare providers can dedicate more time and attention to patient care, improving the overall patient experience and outcomes. Adaptation to Regulatory Changes: The healthcare industry is subject to frequent regulatory changes. Outsourcing companies stay updated with these changes and adapt quickly, ensuring compliance and minimizing the risk of denials due to regulatory non-compliance. Access to Technology: Outsourcing providers often have access to advanced technology and software that can further streamline the prior authorization process, making it more efficient and error-free. In summary, outsourcing pain management services' prior authorization is imperative because it combines expertise, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. It allows healthcare providers to focus on what they do best—delivering exceptional patient care—while ensuring that the necessary authorizations are obtained promptly and accurately. This not only benefits the practice's bottom line but also enhances the overall patient experience. Orthopedic Procedures that require Prior Authorization:
Pain Management Procedures that may require Prior Authorization:
Pain Management Procedures:
Spinal Procedures:
We need to understand that Prior authorization is not merely administrative work, it's a crucial bridge that connects our patients to the care they need while safeguarding the financial health of our practice. Your diligence in ensuring that every authorization request is thorough, accurate, and timely contributes directly to the quality of care our patients receive. We understand that the prior authorization process can be challenging and may sometimes feel like an administrative hurdle. However, it's important to remember that behind every authorization request is a patient seeking relief from pain, a chance for improved mobility, or a path to better health. Your dedication to this process directly impacts their lives, providing hope and healing. Let's remember that the prior authorization process is a critical link between exceptional patient care and the success of our practice as a business. Your dedication to this important task ensures that our patients receive the care they need, and our practice thrives. Thank you for your commitment and hard work in making a positive impact on both our patients' lives and our practice's future." The importance of prior authorization services in orthopedic, pain management, and hospital care settings cannot be overstated. As healthcare professionals and staff, your dedication to this process is a testament to your commitment to patient well-being and the success of our practice as a business. Remember that behind each authorization request lies a patient's hope for relief and a brighter future. By efficiently navigating this complex landscape, you ensure that our patients receive the care they need while safeguarding the financial health of our practice. Together, let's continue to streamline processes, leverage technology, and maintain open communication to make the prior. The prior authorization process stands as a cornerstone of your commitment to exceptional patient care and the profitability of your practice. Every prior authorization request represents an opportunity to enhance the lives of your patients, delivering them the relief and care they rightfully deserve. Moreover, it's a chance to ensure the financial well-being and continued growth of your practice as a business. As your endeavor to excel in both realms, we invite you to consider the exceptional support and expertise of GoHealthcare Practice Solutions. With an astounding track record boasting a remarkable 98% approval rate, they have consistently demonstrated their exceptional ability to assist your practice with prior authorization, resulting in significant time and financial savings. Their proficiency extends to eliminating the need for peer-to-peer consultations through meticulous review of medical necessity, aligned with utilization guidelines. Their extensive knowledge of clinical guidelines and policies, including frequency considerations, is unparalleled. By partnering with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, you open doors to a future where patients receive timely, necessary care without the hassle and uncertainty of prior authorization delays. It's an opportunity to streamline your operations, reduce administrative burdens, and focus on what you do best—providing exceptional care. Discover how GoHealthcare Practice Solutions can empower your practice's journey toward excellence. Explore their invaluable services and learn more about how they can transform the way you care for your patients and run your practice efficiently. Your choice to partner with them isn't just a decision; it's a commitment to a brighter, patient-centric future. Together, we can elevate your practice to new heights and ensure that every patient's path to healing is clear and uncompromised. Embrace the future of healthcare with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions. Learn more at https://www.gohealthcarellc.com Thank you for your unwavering dedication and the positive impact you make on both your patients' lives and your practice's future." Humana Files Lawsuit Over HHS's Recent Medicare Advantage Audit Rules
September 1st, 2023 Humana is contesting a newly imposed CMS regulation which aims to tighten audit procedures for Medicare Advantage (MA) plans. On September 1st, Humana, the second-largest MA insurer in the country, presented its case to the U.S District Court in the Northern District of Texas. The insurer requests that CMS reconsider and withdraw the newly finalized rule, emphasizing potential negative impacts on both Medicare Advantage providers and the senior citizens who rely on the MA program for their health services. At the start of the year, CMS announced its intention to omit the fee-for-service adjuster during the risk adjustment data validation audits. This adjuster previously served to determine acceptable payment error margins, ensuring that only errors surpassing this threshold would be pursued in recoveries. This rule modification is set to be implemented for contracts originating in 2018 and later. With the introduction of this revised audit process, CMS anticipates the possibility of recouping around $4.7 billion from MA plans over the next ten years due to overpayments. It's worth noting that various major insurance companies have, in the past, faced accusations related to Medicare Advantage discrepancies, though the industry has consistently refuted these claims. In their lawsuit, Humana argues that CMS's updated audit process infringes upon the stipulations of the Administrative Procedure Act. Humana has pointed out that, "The CMS failed to substantiate their newly introduced auditing procedures with either empirical evidence or actuarial assessments. Instead, they relied on legal arguments that don’t appear robust upon close examination." The broader insurance sector had reservations about this rule when CMS initially introduced it in 2018. Many insurers, Humana included, had expressed intentions of pursuing legal routes if the rule excluded the critical fee-for-service adjuster. Earlier this year, Bruce Broussard, CEO of Humana, articulated his concerns about CMS's decision to remove the fee-for-service adjuster from MA plan audits. A report from Bloomberg in January underscored Humana's potential vulnerability due to these clawbacks. The report suggested that up to 17% of Humana's earnings in 2023, equivalent to approximately $900 million, could be subjected to these new rules. As of June 30, Humana reported nearly 5.8 million members enrolled in Medicare Advantage, with aims of enrolling an additional 825,000 by year's end. A spokesperson from CMS has chosen not to comment, citing the ongoing litigation. Here's a prior authorization form for Aetna.
For more forms for Aetna, check out their website here - https://www.aetna.com/health-care-professionals/health-care-professional-forms.html
New CMS Edit Impacting Drug Testing Reimbursement CPT 80307 HCPCS G0480-G0483 - Effective July 1, 2023 I already saw this coming. For the past 5 years, I have made recommendation to my clients that these 2 tests should not be reported considering the timing of each test. It just simply doesn't happen on the same day and much more the result of these tests doesn't happen at the same time. Who's with me with this? Key Changes to NCCI PTP Edits for Medical Testing in 2023: The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) has made significant updates regarding the National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) Procedure to Procedure (PTP) edits. Here's a concise breakdown of these important changes affecting medical laboratories: 1. Implementation of NCCI PTP Edits: Starting from July 1, 2023, CMS introduced NCCI PTP edits which directly affect:
2. Limitation on Using NCCI Modifier: Currently, medical entities cannot override these edits using an NCCI modifier. However, this is about to change. 3. Introduction of the CCMI of 1: CMS announced a forthcoming modification. The edits will transition to a Correct Coding Modifier Indicator (CCMI) of 1. This significant shift means that providers can utilize a modifier to bypass the edits when the concurrent billing of these codes is deemed appropriate. 4. Determining Bypass Allowance: When can these codes be billed together using a modifier? This is primarily outlined by the Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) in their Local Coverage Determinations. 5. Retroactivity and Implementation: The acceptance of the modifier for bypassing will be retroactive, dating back to July 1, 2023. Come October 1, 2023, in their next quarterly update, the Medicare claims processing systems will reflect this change. 6. Guidance for Laboratories: During the transition period:
Laboratories also have the option to initiate the MAC appeals process if they prefer not to await the auto-adjustment. Alternatively, they can hold off on their claims submissions until CMS enforces the change. In essence, these modifications herald a more flexible approach to coding and billing, providing medical entities with more options and clearer pathways for claim submissions and adjustments. New Category III CPT Codes for Intra-Articular Minimally Invasive SI Joint Fusion Code X034T7/30/2023 New Category III CPT Codes for Intra-Articular Minimally Invasive SI Joint Fusion Code X034TExplore the newly introduced Category III CPT code for minimally invasive SI joint fusion. This comprehensive guide covers the clinical aspects of the procedure, implications for reimbursement, Medicare's guidelines, and what healthcare providers need to know. Stay updated on this significant development in spinal care and understand its impact on practice, coding, and patient care. This description captures key aspects of the article's content, including the introduction of a new CPT code, the clinical context, reimbursement considerations, and its relevance to healthcare providers. It's designed to give potential readers a clear idea of what they will find in the article and why it may be relevant to their interests and needs. A new Category III code was announced by the AMA CPT (American Medical Association Current Procedural Terminology) Editorial Panel for a specific medical procedure for minimally invasive insertion of a device into the intra-articular SI (sacroiliac) joint space. The code was proposed by ISASS (International Society for the Advancement of Spine Surgery) in May 2022 and will be released in July 2022, becoming effective from January 2023. All providers that are performing this procedure must be aware of this new code X034T. The Category III new code is defined as: X034T - Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous, with image guidance, includes placement of intra-articular implant(s) (e.g., bone allografts, synthetic devices) Since it's a Category III code, no RVU (Relative Value Units) are assigned, and providers are encouraged to provide estimated costs for reimbursement. Medical Necessity Aspects: 1. The Procedure (Arthrodesis of the Sacroiliac Joint): The described procedure involves fusing the sacroiliac joint, which connects the sacrum (base of the spine) to the ilium (pelvis), in a minimally invasive way. The insertion of intra-articular implants, such as bone allografts or synthetic devices, helps in stabilizing the joint and relieving pain. 2. Minimally Invasive Technique: This technique implies a smaller incision and less damage to surrounding tissues compared to traditional surgery. It often leads to faster recovery and less post-operative pain. 3. Image Guidance: The use of imaging technology ensures precision during the insertion of the implant, minimizing the risk of errors. 4. Indications for the Procedure: This could be used in cases of chronic pain, instability, or degenerative changes in the SI joint that have not responded to conservative treatments. Rationale: 1. Categorization as a Category III Code: This category is used for temporary coding for emerging technologies, services, and procedures. Since this is a specialized and new technique, it fits this category. 2. Reimbursement Process: By creating a specific code, the procedure can be more easily tracked and reimbursed. Since RVUs are not set, providers must determine their practice costs and bill accordingly. This can facilitate negotiation with payers and ensure appropriate compensation. 3. Recognition of the Procedure: Having a specific CPT code increases the recognition of this innovative procedure within the medical community and may promote its appropriate use. 4. Alignment with ISASS Goals: ISASS's involvement shows their commitment to advancing spinal procedures and ensuring proper coding and reimbursement for these specialized services. In summary, the creation of this new Category III code for intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion represents a step forward in recognizing and standardizing a specific medical procedure. It has implications for how the procedure is performed, reimbursed, and adopted within the broader healthcare system. How does this procedure going to be reimbursed by the insurance payers since it is a Category III code? The reimbursement of the intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion procedure by insurance payers will require some unique considerations since the newly created code is a Category III code, X034T - Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous, with image guidance, includes placement of intra-articular implant(s) (e.g., bone allografts, synthetic devices) Reimbursement Process: No Relative Value Units (RVUs): Unlike Category I codes, Category III codes do not have associated RVUs. RVUs are typically used to determine the amount of compensation for a medical procedure, so in this case, there is no standardized payment rate set. Provider-Estimated Costs: Since there are no RVUs set for this procedure, providers performing the service are expected to determine their practice costs for the service. They should consider factors such as the time involved, complexity of the procedure, overhead costs, and materials used (e.g., the implants themselves). Negotiation with Payers: Providers will then need to negotiate with insurance payers directly to agree on reimbursement rates. This might involve justifying the estimated costs and explaining the clinical value of the procedure. Potential Use of Gap Codes: Some insurance payers may have "gap codes" or other mechanisms to deal with procedures that do not fall under standard reimbursement categories. Providers might need to work with payers to understand the specific requirements for coding and reimbursement. Documentation and Authorization: It may be necessary for providers to offer robust clinical documentation and obtain prior authorization for the procedure. This would help demonstrate the medical necessity and ensure that the procedure aligns with the insurance payer's policies and guidelines. Possible Variability Among Payers: Different insurance payers may have different policies regarding Category III codes and emerging technologies. There might be variability in how receptive payers are to the procedure, and what evidence or justification they require. Tracking and Follow-up: Providers may need to carefully track these claims and follow up with payers to ensure proper reimbursement. Since this is a new and specialized code, there might be confusion or delays in processing the claims. Reimbursement for the intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion procedure under the new Category III code is likely to be a complex and individualized process. Providers will need to actively engage with payers, provide detailed cost estimates, and possibly navigate unique payer policies and procedures. Coordination, communication, and careful documentation will be key to securing appropriate reimbursement for this innovative procedure. How about the need for Prior Authorization from the insurance health payers? how is this going to be handled? Prior authorization (PA) is a requirement that a healthcare provider must obtain approval from a health insurance payer before delivering a specific medical service, medication, or medical device. In the context of the new Category III Code X034T - Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous, with image guidance, includes placement of intra-articular implant(s) (e.g., bone allografts, synthetic devices) for intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion, prior authorization would likely be an essential step. Here's how it might be handled: 1. Determination of Medical Necessity: Rationale: Providers would need to explain why this specific procedure is medically necessary for the patient, including a detailed clinical history, diagnosis, and why alternative treatments are not suitable. Documentation: This might require submitting records of previous treatments, imaging studies, consultation notes, or other relevant clinical evidence. 2. Submission of Request: Form: The provider would typically fill out a specific prior authorization request form, tailored to the individual payer's requirements. Procedure Details: Information regarding the new CPT code X034T - Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous, with image guidance, includes placement of intra-articular implant(s) (e.g., bone allografts, synthetic devices), expected costs, and a description of the procedure, including why it is being recommended, would be included. 3. Payer Review: Medical Review: Insurance payers would review the request, likely involving their medical review team to assess whether the procedure aligns with their clinical guidelines. Novelty Consideration: Since this is a new Category III code, payers might take additional time to review the procedure, especially if it's considered an emerging technology or if their policies around Category III codes are strict. 4. Communication of Decision: Approval or Denial: The payer will communicate the decision to the provider, either approving the request or denying it with an explanation. Timeline: Many payers are bound to respond within a certain timeframe, though this can vary depending on the jurisdiction and the urgency of the procedure. 5. Potential Appeals Process: If the request is denied, providers may have the option to appeal the decision, offering further justification or clarification. 6. Coordination with Patient: Keeping the patient informed of the status of the prior authorization request and what it means for their treatment plan is also an important step in the process. Conclusion: Prior authorization for this procedure would likely be a multi-step process involving detailed justification, careful documentation, and possibly navigating unique payer requirements. Given that the procedure involves a new Category III code and may be considered an emerging technology, providers should be prepared for additional scrutiny and potentially a more complex authorization process. They may also need to stay abreast of individual payer policies and guidelines related to Category III codes and minimally invasive joint procedures specifically. Coordination, communication, and perseverance might be essential to securing approval for this procedure. How long would this be a Category III X034T - Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous, with image guidance, includes placement of intra-articular implant(s) (e.g., bone allografts, synthetic devices)? Category III codes are temporary codes used for emerging technologies, services, and procedures that may have not yet met widespread acceptance criteria, or there may be limited published data and literature supporting their usage. A Category III code is essentially a placeholder allowing for data collection and assessment of new services and procedures. Here's how the transition from Category III might typically occur and the factors that could influence how long this particular procedure might remain in Category III: 1. Data Collection and Clinical Acceptance: Use of the Code: The procedure must be performed enough times to gather sufficient data about its efficacy, safety, and utilization. Clinical Trials and Research: Published studies and clinical trials showing the procedure's effectiveness and safety would bolster its case for moving to a permanent code. 2. Peer Review and Medical Community Acceptance: Guidelines and Recommendations: If professional organizations, such as the ISASS, endorse the procedure and include it in their guidelines, it may facilitate the transition. Peer Review: The procedure must be accepted by the broader medical community, especially those specializing in spine surgery. 3. Economic Considerations: Cost-Effectiveness: The procedure must demonstrate cost-effectiveness compared to existing alternatives. Reimbursement Patterns: Widespread acceptance by payers and consistent reimbursement practices might expedite the transition. 4. Regulatory Review and Decision: AMA Review: The AMA CPT Editorial Panel would review the collected data and determine whether the procedure should move to a Category I code. Timeline: This can be a lengthy process. It could take several years, depending on how quickly the required evidence is collected and accepted. : The transition from a Category III to a Category I code is not a fixed process and can vary widely based on many factors, including the rate of adoption of the procedure, the evidence supporting its efficacy, and the views of the medical community. In the case of the intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion, given that it's a specialized procedure, the process may be on the longer side, potentially taking several years. Collaboration between providers, researchers, professional organizations, and payers in gathering and disseminating evidence could expedite the process. However, without specific details about the current state of research and acceptance of this procedure, it's challenging to provide a more precise estimate. Who are the device manufacturing companies that might benefit from this new code X034T - Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous, with image guidance, includes placement of intra-articular implant(s) (e.g., bone allografts, synthetic devices)? The procedure in question involves the use of intra-articular implants, which could be bone allografts or synthetic devices. As such, companies specializing in the following areas may potentially benefit: Orthopedic Implants: Manufacturers that produce devices used in joint surgery, including specialized screws, plates, or other fixation devices. Spinal Devices: Companies that focus on products for spinal surgeries, including fusion devices, might find new opportunities with this code. Biologics and Synthetic Materials: Firms specializing in bone graft materials, both natural and synthetic, could benefit if these materials are used in the procedure. Medical Imaging: Given that the code specifies image guidance, companies providing imaging technologies used in minimally invasive surgeries might also see increased interest. Minimally Invasive Surgery Technology: Manufacturers of specialized tools and technologies for minimally invasive surgery could benefit from wider adoption of the procedure. Specific companies would depend on the exact nature of the devices used in this procedure, and it would require an up-to-date market analysis to identify them accurately. Companies might see the new code as an opportunity to innovate and develop new products tailored to this procedure, potentially driving growth in these specialized areas of medical technology. Existing players with relevant products might also find new marketing opportunities. However, it's also worth noting that as a Category III code, the procedure is still considered emerging, and there may be some uncertainty around reimbursement and broader adoption. Therefore, companies would need to carefully assess the market and consider both the opportunities and risks associated with this new code. Medical necessity is a critical consideration for many medical procedures, including the intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion. Medical necessity refers to the need for a service or procedure to diagnose or treat a disease, injury, condition, illness, or its symptoms, in accordance with accepted standards of medical practice. To support the medical necessity of this kind of procedure, a detailed and comprehensive set of medical documentation would typically be required. Here's a general outline of the types of medical documentation that may be needed: 1. Patient Medical History: Detailed patient history, including chronic conditions, previous treatments, surgeries, and family history of related conditions. Information about the specific complaint, such as chronic pain or instability in the SI joint, along with its duration and impact on daily life. 2. Physical Examination: Comprehensive physical examination records focusing on the affected joint, including mobility, pain, stability, and alignment. Specific tests or assessments used to evaluate the SI joint. 3. Diagnostic Studies and Imaging: Results of relevant diagnostic tests like X-rays, CT scans, MRI, or other imaging studies that visualize the joint and surrounding structures. Any specialized diagnostic procedures specific to the SI joint. 4. Treatment History: Documentation of conservative treatments that have been attempted, including physical therapy, medications, injections, or other non-surgical interventions. Detailed records of the outcomes of these treatments, including the patient's response and any ongoing symptoms or limitations. 5. Consultation Notes: Notes from specialists or other healthcare providers who have evaluated the patient. Their assessments, recommendations, and rationale for the procedure. 6. Operative Plan: A detailed surgical plan, including the specific procedure to be performed, the type of implant to be used, and the anticipated outcomes. Justification for why this specific procedure is considered the best option for the patient, considering their unique situation. 7. Patient Consent: Documentation of informed consent, where the patient has been explained the procedure, its risks, benefits, alternatives, and has agreed to proceed. 8. Follow-up Plans: Proposed follow-up care and rehabilitation plans, indicating how the procedure fits into the overall treatment strategy. Conclusion: The medical documentation needed to support the necessity of an intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion procedure must provide a comprehensive picture of the patient's condition, the rationale for the surgery, and why it is the appropriate medical intervention. This includes detailed information about the patient's medical history, the diagnosis and characterization of the joint condition, prior treatments, and specialist evaluations. It's essential that the documentation is thorough, clear, and consistent to provide evidence of the medical necessity for the procedure, particularly as it may be required for insurance reimbursement and prior authorization. How about ICD10 Medical Necessity Cross-over? In healthcare, the term "ICD-10 Medical Necessity Cross-over" often refers to the process of aligning ICD-10 diagnostic codes with specific medical procedures to demonstrate the medical necessity of those procedures. This alignment is essential for reimbursement purposes, as it helps payers understand why a particular procedure was performed. For the intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion procedure, the following steps might be involved in the ICD-10 Medical Necessity Cross-over process: 1. Identification of Relevant ICD-10 Codes: Identifying the specific ICD-10 codes that accurately describe the patient's diagnosis or condition requiring the procedure. This could include codes for SI joint dysfunction, pain, degenerative conditions, or trauma affecting the SI joint. 2. Linking the Diagnosis with the Procedure: Ensuring that the selected ICD-10 codes are consistent with the new Category III CPT code for the procedure. The documentation must clearly show how the diagnosis necessitates the procedure. 3. Reviewing Payer-Specific Guidelines: Different insurance payers may have specific guidelines about which ICD-10 codes they consider medically necessary for certain procedures. Providers would need to ensure that their selected ICD-10 codes align with the payer's requirements, policies, or Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs) where applicable. 4. Supporting Documentation: Including all relevant medical documentation, such as medical history, physical examinations, diagnostic studies, treatment history, and consultation notes, to support the selected ICD-10 codes and the need for the procedure. 5. Prior Authorization and Communication with Payers: If required, the provider may need to obtain prior authorization, ensuring that the payer agrees with the medical necessity as demonstrated by the ICD-10 codes. Clear communication with payers might be necessary to clarify or justify the codes and the procedure's necessity. The ICD-10 Medical Necessity Cross-over process for the intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion would involve carefully selecting and linking appropriate ICD-10 diagnostic codes with the procedure. This process requires a detailed understanding of the patient's condition, the procedure itself, and the specific guidelines and requirements of the insurance payer. What Diagnosis Code is indicated with this procedure? The specific ICD-10 diagnosis codes that might be associated with the procedure of intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion will depend on the exact condition being treated. Without more specific information about the patient's condition, it's challenging to identify the precise ICD-10 code. CPT Code Category III X034T - Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous, with image guidance, includes placement of intra-articular implant(s) (e.g., bone allografts, synthetic devices) mostly crosses over with the following diagnosis based on medical necessity: Sacroiliac Joint Pain or Dysfunction: M53.3 – Sacrococcygeal disorders, not elsewhere classified M47.817 – Spondylosis without myelopathy or radiculopathy, lumbosacral region Traumatic Injury to the Sacroiliac Joint: S33.7XXA – Sprain of sacroiliac joint, initial encounter S33.7XXD – Sprain of sacroiliac joint, subsequent encounter Degenerative or Inflammatory Conditions: M46.1 – Ankylosing hyperostosis [Forestier] M13.8 – Other specified arthritis Post-Laminectomy Syndrome: M96.1 – Postlaminectomy syndrome, not elsewhere classified Other Pain or Disorder in the Lumbar Region: M54.59 – Low back pain These codes are examples, and the specific code chosen would depend on the detailed assessment of the patient's condition, including any underlying causes or related symptoms. Medical coding must be highly accurate, reflecting the patient's specific situation, and it requires deep expertise in both the clinical aspects of care and the coding guidelines. The choice of ICD-10 code could also based on the payer's clinical policies or guidelines that define when the procedure is considered medically necessary. Coordination between the clinical team performing the procedure and the coding and billing professionals is crucial to ensure that the correct codes are used and that they accurately represent the medical necessity for the procedure. It's worth noting that coverage for a specific procedure like intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion can vary widely between different insurance payers and even between different plans within the same payer. The coverage may also be influenced by the specific patient's condition, the medical necessity of the procedure, and other factors such as location and provider network. Here's a general list of types of insurance payers that might cover this kind of procedure, depending on their specific policies and guidelines: Private Insurance Payers:
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) may cover the procedure, but coverage details would depend on various factors including medical necessity, provider qualifications, and the specific Medicare Administrative Contractor (MAC) in your region. Medicaid: Medicaid coverage can vary widely by state, as each state administers its Medicaid program with its own rules and guidelines. Some states may cover the procedure, while others may not, or there may be specific requirements or limitations. Workers' Compensation and Other Specialty Payers: Some workers' compensation insurance plans or other specialized payers may cover the procedure if it's related to a workplace injury or other specific circumstances. It's essential to consult with the specific insurance payer to understand the exact coverage details, any prior authorization requirements, and other considerations that might apply to this procedure. Patients considering this procedure should also discuss with their healthcare provider and contact their insurance company to verify coverage and understand any potential out-of-pocket costs. Where is this procedure normally performed? The procedure of intra-articular minimally invasive sacroiliac (SI) joint fusion is typically performed in a surgical setting where proper imaging, sterility, and anesthesia can be administered. Here's where this procedure might be normally performed: Hospitals: Many hospitals have specialized orthopedic or spinal surgery units with state-of-the-art facilities and skilled surgical teams. This would be a common setting for such a procedure. Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs): ASCs are healthcare facilities that specialize in providing surgery, pain management, and certain diagnostic services outside the hospital setting. Many ASCs have the necessary technology and expertise to perform this type of minimally invasive procedure. Specialized Orthopedic or Spine Clinics: Some orthopedic or spine-focused medical centers might have the facilities to perform this type of surgery. They would be staffed with orthopedic surgeons and other specialists experienced in spinal procedures. University or Teaching Hospitals: Academic medical centers often have cutting-edge technology and leading experts in the field. These facilities might perform this kind of procedure, possibly as part of ongoing research or clinical trials related to new surgical techniques or devices. The choice of setting may depend on various factors, including the patient's overall health, the complexity of the procedure, the surgeon's preferences and experience, and the availability of necessary technology and equipment. Minimally invasive procedures like this generally require specialized imaging equipment to guide the surgery, sterile surgical facilities to prevent infection, and a skilled surgical team with experience in this particular procedure. Anesthesia services are also generally required, either general or regional, depending on the specifics of the surgery and patient needs. So, the setting must be equipped to provide these essential services. What's Medicare's guideline and utilization policy on this procedure? Generally, Medicare coverage decisions for a specific procedure are based on the following criteria: Medical Necessity: Medicare typically covers procedures that are considered reasonable and necessary for the diagnosis or treatment of an illness or injury. Detailed medical documentation would be needed to demonstrate the medical necessity of the SI joint fusion. Clinical Evidence and Guidelines: Medicare often considers professional guidelines, clinical studies, and other evidence to evaluate the effectiveness and appropriateness of a procedure. Since this is a Category III code, it may represent a procedure that is still under evaluation or considered experimental in some cases. Provider Qualifications: The surgeon performing the procedure must generally meet specific qualifications and be licensed and credentialed to perform the surgery. Facility Requirements: The procedure would need to be performed in an appropriate setting, such as a hospital or ambulatory surgery center, meeting Medicare's standards for safety and quality. Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs): Specific coverage policies might be issued by individual MACs, providing detailed guidelines for when the procedure would be covered in their region. Prior Authorization: Depending on the specifics of the procedure and the Medicare policy, prior authorization might be required. This process would involve submitting detailed information about the patient's condition, the planned procedure, and the medical necessity to Medicare for review before the procedure is performed. Since Medicare policies can change and may vary by region and over time, it would be essential for providers to consult the specific MAC in their region or the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) for the most accurate and up-to-date information on the coverage and utilization guidelines for this procedure. The newly announced Category III status and other factors could influence Medicare's policy for this specific procedure, so direct consultation with the relevant authorities would be advisable. Take away from this Category III New Code X034T - Arthrodesis, sacroiliac joint, percutaneous, with image guidance, includes placement of intra-articular implant(s) (e.g., bone allografts, synthetic devices). Here's some additional valuable information that could be relevant to the topic of intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion, especially considering the newly announced Category III CPT code: Understanding Category III Codes: Category III codes are often used for emerging technologies, procedures, or services that may still be under review or considered experimental. These codes can help track utilization and outcomes, which may eventually lead to a transition to Category I if the procedure gains widespread acceptance and has a proven benefit. Reimbursement Challenges: Since no Relative Value Units (RVUs) are set for Category III codes, providers might face challenges in determining appropriate reimbursement rates and negotiating payment with payers. Collaboration with payers and a clear understanding of the procedure's costs will be essential. Prior Authorization: Even if a procedure is covered by insurance, it may still require prior authorization. Providers will need to be proactive in understanding the documentation and criteria required to obtain authorization and should anticipate potential delays in the process. Patient Communication: Given the potential complexities around coverage and reimbursement for a Category III procedure, clear communication with patients about potential out-of-pocket costs, risks, benefits, and alternatives is vital. Monitoring Regulatory Changes: As this is a newly categorized procedure, it will be essential to monitor ongoing regulatory changes, updates to payer policies, and potential shifts from Category III to Category I status as more evidence and acceptance emerge. Continued Education and Training: Surgeons and healthcare teams may benefit from ongoing education and training specific to this procedure, especially if it involves new or specialized techniques or devices. Evidence-Based Practice: Continual review of the latest research, clinical guidelines, and best practices related to SI joint fusion will be necessary to ensure that the procedure is being utilized appropriately and that patients are receiving the most effective care. Coordination with Device Manufacturers: Since the new code mentions intra-articular implant(s), working closely with device manufacturers may provide insights into the specific technologies, techniques, and support available for this procedure. Multidisciplinary Approach: Managing conditions related to the SI joint may require a multidisciplinary approach involving orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, pain management specialists, and other healthcare professionals. Coordinated care can enhance patient outcomes and satisfaction. Clinical Trials and Research: Participation in clinical trials or research related to this procedure might provide valuable insights into its effectiveness, safety, and best practices. In conclusion, the introduction of a new Category III CPT code for intra-articular minimally invasive SI joint fusion represents a notable development in the healthcare coding and reimbursement landscape. It will require close attention from providers, payers, and other stakeholders to navigate the unique challenges and opportunities presented by this categorization. Staying abreast of evolving guidelines, actively engaging with payers, and prioritizing patient-centered care will be key factors in successfully implementing this procedure in clinical practice. American Medical Association (AMA): Information about the new CPT code and Category III codes can be obtained directly from the AMA's CPT Editorial Panel. Website: AMA CPT Editorial Panel ISASS (International Society for the Advancement of Spine Surgery): Since ISASS sponsored the code change proposal, their official website or direct contacts may provide additional insights. Website: ISASS Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): CMS provides guidelines and policies for Medicare-covered procedures, including potentially this specific procedure. Website: CMS Medicare Coverage FDA (Food and Drug Administration): Information about the devices used in this procedure may be found on the FDA's website, specifically in the section on medical devices. Website: FDA Medical Devices National Institutes of Health (NIH) or PubMed: For clinical evidence, guidelines, and research studies related to SI joint fusion, these databases may provide peer-reviewed articles. Website: PubMed Local Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs): Each MAC may have specific guidelines related to this procedure for their region, and their websites would be the primary source of that information. Specialized Orthopedic or Spine Journals: Peer-reviewed journals focusing on spinal surgery may have published research or reviews related to this procedure. Some examples include: The Spine Journal Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research So how can we help?
GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Prior Authorization for Spinal Fusion Services **1. Expertise in Spinal Fusion Procedures: Our team at GoHealthcare Practice Solutions possesses specialized knowledge in spinal fusion procedures. We understand the clinical guidelines, medical necessity criteria, and specific documentation required to obtain authorization for spinal fusion surgeries. **2. Personalized Case Management: Each spinal fusion case is unique, and our dedicated case managers provide personalized attention to ensure all necessary clinical information is gathered, properly documented, and submitted to insurance companies for prior authorization. **3. Integration with EHR and Imaging Systems: Our system seamlessly integrates with providers' existing EHR and imaging platforms, allowing for efficient retrieval of medical records, radiological images, and other vital information necessary for prior authorization. **4. Continuous Collaboration with Medical Professionals: We work closely with surgeons, specialists, and other healthcare providers to ensure that the medical justification for spinal fusion is clearly articulated and supported by evidence, thereby increasing the likelihood of approval. **5. Real-Time Status Tracking and Notifications: Our platform offers real-time tracking of the prior authorization status, and both providers and patients are notified at key milestones. This transparency helps in better planning and reduces uncertainty. **6. Appeals and Denial Management: Should a denial occur, our specialized appeals team, well-versed in spinal fusion procedures, will actively engage with the insurance company, providing additional information and arguments to advocate for authorization. **7. Educational Support and Training: We offer comprehensive training and educational resources to healthcare providers, ensuring they are up to date with the changing landscape of spinal fusion coverage policies and prior authorization requirements. **8. Patient Engagement: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions understands the importance of patient-centered care. We actively engage with patients, keeping them informed about the authorization process and addressing their concerns, which ultimately enhances the overall patient experience. **9. Compliance and Quality Assurance: Our processes adhere to regulatory compliance standards, ensuring that all actions taken within the prior authorization process meet legal and ethical guidelines. Our quality assurance measures further guarantee accuracy and timeliness. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions' specialized prior authorization services for spinal fusion procedures reflect our commitment to excellence and patient-centered care. By leveraging our expertise, technology, and collaboration, we facilitate a smooth and efficient prior authorization process, enabling healthcare providers to focus on delivering quality care. Our tailored approach ensures that the unique complexities of spinal fusion services are expertly handled, resulting in higher approval rates, better provider satisfaction, and improved patient outcomes. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Claims Appeals Services for Spinal Fusion Services **1. Understanding of Complex Spinal Fusion Procedures: At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we recognize that spinal fusion services encompass complex and often intricate procedures. We are deeply familiar with the nuances of spinal surgery, the varying techniques involved, and the medical necessity criteria that must be met. **2. Expert Analysis of Denials: When a spinal fusion claim is denied, our expert team conducts a thorough review of the denial reasons. By understanding the specific medical, coding, and policy issues at hand, we can identify the best course of action for an appeal. **3. Detailed Medical Documentation: Spinal fusion claims require robust and precise medical documentation. Our team works closely with medical professionals to gather all relevant records, operative reports, diagnostic information, and evidence of medical necessity. We ensure that the appeal is supported by solid clinical evidence. **4. Coding Expertise: Our specialized coders are proficient in the coding requirements for spinal fusion services, including the latest updates in ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes. Their expertise ensures that coding errors, a common reason for denials, are promptly identified and corrected. **5. Appeal Strategy and Submission: We develop a tailored appeal strategy for each denied spinal fusion claim, considering the unique circumstances and insurance payer’s guidelines. Our team then submits the appeal, accompanied by persuasive arguments and supporting evidence, directly to the insurance payer. **6. Continuous Monitoring and Communication: We continuously monitor the appeal's progress, promptly responding to any requests for additional information and keeping the healthcare provider informed of any developments. This consistent communication ensures that everyone involved is aligned and informed. **7. Legal Support (if required): Should an appeal require legal intervention, our network of healthcare attorneys can provide legal support and representation. This includes pursuing cases in court if necessary. **8. Outcome Analysis and Process Improvement: We analyze the outcomes of the appeals, identifying trends and insights that can help in future claim submissions. By understanding the common reasons for denials and applying learned lessons, we help providers improve their claims submission processes. Conclusion: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions offers specialized Claims Appeals Services for Spinal Fusion Services. Our understanding of spinal surgery, coupled with our expertise in medical documentation, coding, and appeals strategy, positions us as a valuable partner for healthcare providers dealing with denied claims. We are committed to working tirelessly to overturn denials and ensure appropriate reimbursement for the vital spinal fusion services provided. Our collaborative approach, ongoing communication, and focus on continuous improvement set us apart in the field of healthcare claims appeals. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Surgical Coordination for Spinal Fusion Services 1. Pre-Surgical Assessment & Coordination: GoHealthcare's team of experienced professionals works closely with surgeons, specialists, and referring physicians to ensure a comprehensive pre-surgical assessment. This includes a detailed review of medical history, diagnostic tests, and coordination of pre-operative consultations. 2. Insurance Verification & Prior Authorization Handling: Navigating insurance requirements can be complex, particularly for specialized procedures like spinal fusion. We verify insurance coverage, manage the prior authorization process, and ensure that all required documentation is submitted, reducing delays and denials. 3. Scheduling & Facility Coordination: Our surgical coordination includes scheduling the procedure at an appropriate facility, ensuring that both the surgical team and the necessary equipment are available. We coordinate with hospitals, surgical centers, and other stakeholders to ensure smooth logistics. 4. Patient Communication & Education: Understanding a spinal fusion procedure can be overwhelming for patients. We provide personalized education and support, explaining the process, risks, and expectations. Our dedicated patient liaison ensures that all questions are answered, contributing to patient comfort and preparedness. 5. Post-Surgical Follow-Up & Care Coordination: Recovery from spinal fusion requires careful follow-up and coordinated care. We help in scheduling follow-up appointments, therapy sessions, and coordinating with home care services if needed. Our team stays connected with patients, providing support throughout the recovery process. 6. Billing & Financial Coordination: Spinal fusion surgeries involve multiple billing components. We provide transparent billing services and coordinate with insurers to ensure accurate reimbursement. Our financial team is available to address any billing or insurance-related concerns. 7. Quality Assurance & Compliance: Compliance with healthcare regulations and quality standards is at the forefront of our services. We maintain rigorous quality assurance protocols to ensure that all aspects of surgical coordination adhere to industry standards. 8. Collaboration with Multidisciplinary Teams: Spinal fusion procedures often require collaboration across various medical disciplines. We facilitate communication and collaboration among neurosurgeons, orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, pain management specialists, and other involved professionals. 9. Technology-Driven Solutions: Our state-of-the-art technology platform enables efficient coordination, real-time updates, and provides all stakeholders with access to relevant information. This technology-driven approach enhances accuracy and efficiency. 10. Customized Solutions: Understanding that each spinal fusion case is unique, we offer customized coordination plans that align with the specific needs and preferences of the surgeon, patient, and healthcare facility involved. Conclusion: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions offers a comprehensive, patient-centric approach to surgical coordination for spinal fusion services. By handling everything from pre-surgical assessments to post-surgical follow-up, we provide a seamless experience for both healthcare providers and patients. Our specialized focus on spinal fusion surgeries, combined with our commitment to quality and personalized care, makes us a trusted partner for this complex and vital medical procedure. Our aim is to enhance the efficiency, quality, and overall success of spinal fusion surgeries, contributing to improved patient outcomes. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Patient Access Services for Spinal Fusion Services 1. Patient Education and Consultation: Our Patient Access team offers comprehensive education and consultation services for patients considering spinal fusion surgery. We explain the procedure, potential risks, benefits, and alternative treatments, ensuring patients are well-informed and comfortable with their decision. 2. Insurance Verification and Prior Authorization: Understanding the complexities of insurance coverage for spinal fusion, our specialists verify insurance benefits and manage the prior authorization process. We liaise with insurance providers, ensuring that all requirements are met, and approvals are obtained in a timely manner. 3. Financial Counseling and Payment Options: Spinal fusion surgery can be expensive. Our financial counseling service helps patients understand their financial responsibility, available payment options, and potential assistance programs. We work with patients to create feasible payment plans that align with their financial situation. 4. Coordination of Care: We act as a liaison between surgeons, hospitals, physical therapists, and other healthcare providers involved in spinal fusion care. This ensures seamless communication and coordination, enhancing the overall quality of care. 5. Scheduling and Logistics: From scheduling consultations and preoperative assessments to planning the surgery itself, our team takes care of all logistical aspects. We coordinate with healthcare providers and patients to create a schedule that minimizes disruption and meets the specific needs of each patient. 6. Post-Surgical Support and Follow-up: Spinal fusion requires ongoing care and support post-surgery. We arrange follow-up appointments, physical therapy sessions, and provide resources to assist in recovery. Our team remains accessible to patients, addressing concerns, and providing guidance as needed. 7. Utilization of Cutting-Edge Technology: Our Patient Access services incorporate advanced technology, including patient portals and telemedicine, to enhance accessibility, streamline processes, and maintain ongoing communication with patients and healthcare providers. 8. Compliance and Quality Assurance: We adhere to stringent compliance standards and maintain a commitment to quality assurance. Our practices align with healthcare regulations, and our continuous monitoring ensures a high standard of service delivery. 9. Personalized Approach: Understanding that each patient's needs and circumstances are unique, we provide personalized services, tailoring our approach to align with individual preferences, medical history, and financial considerations. Conclusion: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions' Patient Access services for Spinal Fusion Services offer a holistic and patient-centered approach, aimed at simplifying the complexities of spinal fusion care. From education and insurance handling to post-surgical support, our team provides a comprehensive solution that prioritizes patient needs, enhances collaboration among providers, and ensures a seamless care pathway. Our commitment to excellence, transparency, and individualized care makes us a trusted partner for patients undergoing spinal fusion surgery. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Who We Are 1. Dedicated Professionals: At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we are a team of dedicated professionals committed to supporting healthcare providers in delivering the best possible patient care. With diverse backgrounds in healthcare management, clinical practice, finance, technology, and patient support, we bring a holistic perspective to our work. 2. Patient-Centered Approach: Our team believes in putting patients at the heart of everything we do. We work closely with healthcare providers to understand their unique needs and tailor our solutions to enhance patient satisfaction, accessibility, and outcomes. 3. Experts in Healthcare Solutions: With specialized knowledge in various aspects of healthcare practice management, our team offers comprehensive solutions ranging from prior authorization to patient access services for complex procedures like spinal fusion. Our expertise allows us to navigate the intricacies of healthcare systems, regulations, and insurance policies with ease. 4. Innovative Thinkers: In a rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, our team strives to stay ahead of the curve through innovation and technology adoption. We leverage cutting-edge tools and methodologies to deliver efficient, streamlined services that meet the contemporary needs of healthcare providers and patients. 5. Collaborative and Supportive Culture: We foster a collaborative and supportive work environment where each team member's contribution is valued and encouraged. We believe in working together, sharing ideas, and supporting one another to achieve our common goals. 6. Ethical and Transparent: Our team operates with integrity, transparency, and adherence to the highest ethical standards. We believe in building trust with our clients and patients through open communication and responsible practices. 7. Focused on Continuous Improvement: We are committed to continuous improvement and professional development. Our team regularly participates in training, workshops, and industry events to stay informed about the latest trends, regulations, and best practices in healthcare management. 8. Community-Oriented: At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we recognize our responsibility to the wider community. We actively engage in community outreach, support charitable causes, and strive to make a positive impact on the communities we serve. 9. Flexible and Adaptable: Understanding that healthcare needs vary widely, our team demonstrates flexibility and adaptability to meet the specific needs of different practices, healthcare systems, and patient populations. Conclusion: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions is more than just a team; we are a community of like-minded professionals united by a passion for enhancing healthcare delivery. Our combined expertise, commitment to excellence, patient-centered approach, and innovative thinking position us as a leading partner for healthcare providers seeking to navigate the complex world of modern healthcare. Whether it's simplifying prior authorization, enhancing patient access, or providing financial counseling, our team is here to support healthcare providers in achieving their goals and delivering exceptional patient care. Prior Authorization Required by Medicare for Facet Joint Interventions for Pain Management Effective July 1, 2023 Prior Authorization for Certain Hospital Outpatient Department (OPD) Services General Documentation Requirements for Facet Joint Interventions - Intraarticular (IA) Facet Joint Interventions, Medial Branch Blocks (MBB), and Radiofrequency Ablations
Therapeutic Facet Joint Procedures (IA)
For each covered spinal region, no more than four (4) therapeutic facet joint injection (IA) sessions will be reimbursed per rolling 12 months. Facet Joint Denervation (RFA)
For each covered spinal region, no more than two (2) radiofrequency sessions will be reimbursed per rolling 12 months. Procedure CPT Codes: 64490 Injection(s), diagnostic or therapeutic agent, paravertebral facet (zygapophyseal) joint (or nerves innervating that joint) with image guidance (fluoroscopy or CT), cervical or thoracic, single level 64491 Injection(s), diagnostic or therapeutic agent, paravertebral facet (zygapophyseal) joint (or nerves innervating that joint) with image guidance (fluoroscopy or CT), cervical or thoracic, second level (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) 64492 Injection(s), diagnostic or therapeutic agent, paravertebral facet (zygapophyseal) joint (or nerves innervating that joint) with image guidance (fluoroscopy or CT), cervical or thoracic; third and any additional level(s). 64493 Injection(s), diagnostic or therapeutic agent, paravertebral facet (zygapophyseal) joint (or nerves innervating that joint) with image guidance (fluoroscopy or CT), lumbar or sacral; single level 64494 Injection(s), diagnostic or therapeutic agent, paravertebral facet (zygapophyseal) joint (or nerves innervating that joint) with image guidance (fluoroscopy or CT), lumbar or sacral; second level (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) 64495 Injection(s), diagnostic or therapeutic agent, paravertebral facet (zygapophyseal) joint (or nerves innervating that joint) with image guidance (fluoroscopy or CT), lumbar or sacral; third and any additional level(s) (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) 64633 Destruction by neurolytic agent, paravertebral facet joint nerve(s), with imaging guidance (fluoroscopy or CT); cervical or thoracic, single facet joint 64634 Destruction by neurolytic agent, paravertebral facet joint nerve(s), with imaging guidance (fluoroscopy or CT); cervical or thoracic, each additional facet joint (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) 64635 Destruction by neurolytic agent, paravertebral facet joint nerve(s), with imaging guidance (fluoroscopy or CT); lumbar or sacral, single facet joint 64636 Destruction by neurolytic agent, paravertebral facet joint nerve(s), with imaging guidance (fluoroscopy or CT); lumbar or sacral, each additional facet joint (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Note: 64492 or 64495 describes a third and additional levels and should be listed separately in addition to the code for the primary procedure and the second level procedure and cannot be reported more than once per day. 64492 should be reported in conjunction with 64490/64491 and 64495 should be reported in conjunction with 64493/64494. Codes 64492 and 64495 will only be covered upon appeal if sufficient documentation of medical necessity is present. References: Noridian Medicare Contractor Attachment:
So can we help? GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Prior Authorization for Spinal Services **1. Expertise in Spinal Services Procedures: Our team at GoHealthcare Practice Solutions possesses specialized knowledge in Spinal Services procedures. We understand the clinical guidelines, medical necessity criteria, and specific documentation required to obtain authorization for spinal fusion surgeries. **2. Personalized Case Management: Each Spinal Services case is unique, and our dedicated case managers provide personalized attention to ensure all necessary clinical information is gathered, properly documented, and submitted to insurance companies for prior authorization. **3. Integration with EHR and Imaging Systems: Our system seamlessly integrates with providers' existing EHR and imaging platforms, allowing for efficient retrieval of medical records, radiological images, and other vital information necessary for prior authorization. **4. Continuous Collaboration with Medical Professionals: We work closely with surgeons, specialists, and other healthcare providers to ensure that the medical justification for spinal fusion is clearly articulated and supported by evidence, thereby increasing the likelihood of approval. **5. Real-Time Status Tracking and Notifications: Our platform offers real-time tracking of the prior authorization status, and both providers and patients are notified at key milestones. This transparency helps in better planning and reduces uncertainty. **6. Appeals and Denial Management: Should a denial occur, our specialized appeals team, well-versed in Spinal Services procedures, will actively engage with the insurance company, providing additional information and arguments to advocate for authorization. **7. Educational Support and Training: We offer comprehensive training and educational resources to healthcare providers, ensuring they are up to date with the changing landscape of spinal fusion coverage policies and prior authorization requirements. **8. Patient Engagement: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions understands the importance of patient-centered care. We actively engage with patients, keeping them informed about the authorization process and addressing their concerns, which ultimately enhances the overall patient experience. **9. Compliance and Quality Assurance: Our processes adhere to regulatory compliance standards, ensuring that all actions taken within the prior authorization process meet legal and ethical guidelines. Our quality assurance measures further guarantee accuracy and timeliness. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions' specialized prior authorization services for Spinal Services procedures reflect our commitment to excellence and patient-centered care. By leveraging our expertise, technology, and collaboration, we facilitate a smooth and efficient prior authorization process, enabling healthcare providers to focus on delivering quality care. Our tailored approach ensures that the unique complexities of spinal fusion services are expertly handled, resulting in higher approval rates, better provider satisfaction, and improved patient outcomes. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Claims Appeals Services for Spinal Services **1. Understanding of Complex Spinal Services Procedures: At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we recognize that spinal fusion services encompass complex and often intricate procedures. We are deeply familiar with the nuances of spinal surgery, the varying techniques involved, and the medical necessity criteria that must be met. **2. Expert Analysis of Denials: When a spinal fusion claim is denied, our expert team conducts a thorough review of the denial reasons. By understanding the specific medical, coding, and policy issues at hand, we can identify the best course of action for an appeal. **3. Detailed Medical Documentation: Spinal Services claims require robust and precise medical documentation. Our team works closely with medical professionals to gather all relevant records, operative reports, diagnostic information, and evidence of medical necessity. We ensure that the appeal is supported by solid clinical evidence. **4. Coding Expertise: Our specialized coders are proficient in the coding requirements for Spinal Services, including the latest updates in ICD-10, CPT, and HCPCS codes. Their expertise ensures that coding errors, a common reason for denials, are promptly identified and corrected. **5. Appeal Strategy and Submission: We develop a tailored appeal strategy for each denied spinal fusion claim, considering the unique circumstances and insurance payer’s guidelines. Our team then submits the appeal, accompanied by persuasive arguments and supporting evidence, directly to the insurance payer. **6. Continuous Monitoring and Communication: We continuously monitor the appeal's progress, promptly responding to any requests for additional information and keeping the healthcare provider informed of any developments. This consistent communication ensures that everyone involved is aligned and informed. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions offers specialized Claims Appeals Services. Our understanding of spinal surgery, coupled with our expertise in medical documentation, coding, and appeals strategy, positions us as a valuable partner for healthcare providers dealing with denied claims. We are committed to working tirelessly to overturn denials and ensure appropriate reimbursement for the vital spinal fusion services provided. Our collaborative approach, ongoing communication, and focus on continuous improvement set us apart in the field of healthcare claims appeals. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Surgical Coordination for Spinal Services 1. Pre-Surgical Assessment & Coordination: GoHealthcare's team of experienced professionals works closely with surgeons, specialists, and referring physicians to ensure a comprehensive pre-surgical assessment. This includes a detailed review of medical history, diagnostic tests, and coordination of pre-operative consultations. 2. Insurance Verification & Prior Authorization Handling: Navigating insurance requirements can be complex, particularly for specialized procedures like spinal fusion. We verify insurance coverage, manage the prior authorization process, and ensure that all required documentation is submitted, reducing delays and denials. 3. Scheduling & Facility Coordination: Our surgical coordination includes scheduling the procedure at an appropriate facility, ensuring that both the surgical team and the necessary equipment are available. We coordinate with hospitals, surgical centers, and other stakeholders to ensure smooth logistics. 4. Patient Communication & Education: Understanding a spinal fusion procedure can be overwhelming for patients. We provide personalized education and support, explaining the process, risks, and expectations. Our dedicated patient liaison ensures that all questions are answered, contributing to patient comfort and preparedness. 5. Post-Surgical Follow-Up & Care Coordination: Recovery from spinal fusion requires careful follow-up and coordinated care. We help in scheduling follow-up appointments, therapy sessions, and coordinating with home care services if needed. Our team stays connected with patients, providing support throughout the recovery process. 6. Billing & Financial Coordination: Spinal fusion surgeries involve multiple billing components. We provide transparent billing services and coordinate with insurers to ensure accurate reimbursement. Our financial team is available to address any billing or insurance-related concerns. 7. Quality Assurance & Compliance: Compliance with healthcare regulations and quality standards is at the forefront of our services. We maintain rigorous quality assurance protocols to ensure that all aspects of surgical coordination adhere to industry standards. 8. Collaboration with Multidisciplinary Teams: Spinal fusion procedures often require collaboration across various medical disciplines. We facilitate communication and collaboration among neurosurgeons, orthopedic surgeons, physical therapists, pain management specialists, and other involved professionals. 9. Technology-Driven Solutions: Our state-of-the-art technology platform enables efficient coordination, real-time updates, and provides all stakeholders with access to relevant information. This technology-driven approach enhances accuracy and efficiency. 10. Customized Solutions: Understanding that each Spinal Services is unique, we offer customized coordination plans that align with the specific needs and preferences of the surgeon, patient, and healthcare facility involved. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions offers a comprehensive, patient-centric approach to surgical coordination for spinal fusion services. By handling everything from pre-surgical assessments to post-surgical follow-up, we provide a seamless experience for both healthcare providers and patients. Our specialized focus on spinal fusion surgeries, combined with our commitment to quality and personalized care, makes us a trusted partner for this complex and vital medical procedure. Our aim is to enhance the efficiency, quality, and overall success of spinal fusion surgeries, contributing to improved patient outcomes. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Patient Access Services. 1. Patient Education and Consultation: Our Patient Access team offers comprehensive education and consultation services for patients considering spinal fusion surgery. We explain the procedure, potential risks, benefits, and alternative treatments, ensuring patients are well-informed and comfortable with their decision. 2. Insurance Verification and Prior Authorization: Understanding the complexities of insurance coverage for spinal fusion, our specialists verify insurance benefits and manage the prior authorization process. We liaise with insurance providers, ensuring that all requirements are met, and approvals are obtained in a timely manner. 3. Financial Counseling and Payment Options: Spinal fusion surgery can be expensive. Our financial counseling service helps patients understand their financial responsibility, available payment options, and potential assistance programs. We work with patients to create feasible payment plans that align with their financial situation. 4. Coordination of Care: We act as a liaison between surgeons, hospitals, physical therapists, and other healthcare providers involved in spinal fusion care. This ensures seamless communication and coordination, enhancing the overall quality of care. 5. Scheduling and Logistics: From scheduling consultations and preoperative assessments to planning the surgery itself, our team takes care of all logistical aspects. We coordinate with healthcare providers and patients to create a schedule that minimizes disruption and meets the specific needs of each patient. 6. Post-Surgical Support and Follow-up: Spinal fusion requires ongoing care and support post-surgery. We arrange follow-up appointments, physical therapy sessions, and provide resources to assist in recovery. Our team remains accessible to patients, addressing concerns, and providing guidance as needed. 7. Utilization of Cutting-Edge Technology: Our Patient Access services incorporate advanced technology, including patient portals and telemedicine, to enhance accessibility, streamline processes, and maintain ongoing communication with patients and healthcare providers. 8. Compliance and Quality Assurance: We adhere to stringent compliance standards and maintain a commitment to quality assurance. Our practices align with healthcare regulations, and our continuous monitoring ensures a high standard of service delivery. 9. Personalized Approach: Understanding that each patient's needs and circumstances are unique, we provide personalized services, tailoring our approach to align with individual preferences, medical history, and financial considerations. Conclusion: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions' Patient Access services for Spinal Services offer a holistic and patient-centered approach, aimed at simplifying the complexities of spinal fusion care. From education and insurance handling to post-surgical support, our team provides a comprehensive solution that prioritizes patient needs, enhances collaboration among providers, and ensures a seamless care pathway. Our commitment to excellence, transparency, and individualized care makes us a trusted partner for patients undergoing spinal fusion surgery. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions: Who We Are 1. Dedicated Professionals: At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we are a team of dedicated professionals committed to supporting healthcare providers in delivering the best possible patient care. With diverse backgrounds in healthcare management, clinical practice, finance, technology, and patient support, we bring a holistic perspective to our work. 2. Patient-Centered Approach: Our team believes in putting patients at the heart of everything we do. We work closely with healthcare providers to understand their unique needs and tailor our solutions to enhance patient satisfaction, accessibility, and outcomes. 3. Experts in Healthcare Solutions: With specialized knowledge in various aspects of healthcare practice management, our team offers comprehensive solutions ranging from prior authorization to patient access services for complex procedures like spinal fusion. Our expertise allows us to navigate the intricacies of healthcare systems, regulations, and insurance policies with ease. 4. Innovative Thinkers: In a rapidly evolving healthcare landscape, our team strives to stay ahead of the curve through innovation and technology adoption. We leverage cutting-edge tools and methodologies to deliver efficient, streamlined services that meet the contemporary needs of healthcare providers and patients. 5. Collaborative and Supportive Culture: We foster a collaborative and supportive work environment where each team member's contribution is valued and encouraged. We believe in working together, sharing ideas, and supporting one another to achieve our common goals. 6. Ethical and Transparent: Our team operates with integrity, transparency, and adherence to the highest ethical standards. We believe in building trust with our clients and patients through open communication and responsible practices. 7. Focused on Continuous Improvement: We are committed to continuous improvement and professional development. Our team regularly participates in training, workshops, and industry events to stay informed about the latest trends, regulations, and best practices in healthcare management. 8. Community-Oriented: At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we recognize our responsibility to the wider community. We actively engage in community outreach, support charitable causes, and strive to make a positive impact on the communities we serve. 9. Flexible and Adaptable: Understanding that healthcare needs vary widely, our team demonstrates flexibility and adaptability to meet the specific needs of different practices, healthcare systems, and patient populations. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions is more than just a team; we are a community of like-minded professionals united by a passion for enhancing healthcare delivery. Our combined expertise, commitment to excellence, patient-centered approach, and innovative thinking position us as a leading partner for healthcare providers seeking to navigate the complex world of modern healthcare. Whether it's simplifying prior authorization, enhancing patient access, or providing financial counseling, our team is here to support healthcare providers in achieving their goals and delivering exceptional patient care. Need Immediate Assistance? Call us at 1 (800) 267-8752CLAIMS DENIALS: SOLUTIONS TO MAXIMIZING REVENUE AND MINIMIZING LOSSES Healthcare organizations are facing significant financial pressure due to various factors such as wage inflation, rising costs, declining patient and service volume, and the lingering uncertainty caused by the pandemic. These challenges are further compounded by the prevalence of unresolved claims denials, which lead to substantial annual losses for hospitals and healthcare facilities. In order to alleviate this financial burden, it is essential for organizations to adopt a strategic approach that focuses on preventing denials and effectively managing the claims process. The Rising Denial Rates: Over the past five years, denial rates have been on the rise, with an average increase of over 20 percent. Currently, the average claims denial rate exceeds 10 percent. A recent survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association (MGMA) reveals that medical practices experienced an average increase in denials of 17 percent in 2021 alone. Industry data indicates that nearly 20 percent of all claims are denied, and a significant portion of returned claims are never resubmitted. The cost of reworking or appealing denials further exacerbates the financial impact, with practices spending an average of $25 per claim, and hospitals facing a staggering $181 per claim. Identifying the Common Causes: Preventing denied claims begins with understanding the most common reasons for claim rejections.
Effective Denial Management and Prevention:To mitigate the financial impact of denied claims, healthcare organizations should prioritize prevention efforts while also implementing effective denial management strategies. This involves:
Best Practices to Combat Denials: Implementing the following best practices can significantly enhance denials management and improve overall outcomes:
Leveraging Technology Solutions: Implementing the right technology resources can significantly enhance denial management efforts. Claim editor or "claim scrubber" software can help identify coding errors, medical necessity issues, and technical errors before claims are submitted. Medical claim scrubber solutions automate the matching of diagnosis and procedure codes, ensuring compliance with coding guidelines. Code check software and encoders validate and improve coding accuracy, saving time and improving efficiency. Mitigating Losses and Protecting the Bottom Line: While it may not be possible to eliminate denials entirely, a strategic and proactive approach, backed by data analysis, automation, and technology tools, can mitigate their impact on the financial bottom line. By continuously monitoring, identifying trends, collaborating with payers, and adhering to best practices, healthcare organizations can reduce write-offs and safeguard their revenues. Efficient denial management requires a comprehensive approach that includes prevention, understanding denial codes, effective correction and appeals, continuous improvement, collaboration with payers, and leveraging technology solutions. By implementing these strategies and practices, healthcare organizations can minimize the financial impact of denied claims, optimize revenue generation, and maintain a stable bottom line while providing quality care to patients. The Role of Staff Training: Investing in staff training is crucial for effective denial management. By equipping employees with the necessary knowledge and skills, organizations can reduce errors and improve the accuracy of claims submissions. Training should cover topics such as coding guidelines, payer requirements, documentation best practices, and effective communication with payers. Continuous Monitoring and Analysis: To stay ahead of denials, it's essential to continuously monitor and analyze denial data. Regularly running reports to identify denial patterns and trends can provide valuable insights into the root causes of denials. By identifying these patterns, organizations can take proactive measures to prevent future denials, implement process improvements, and enhance overall revenue cycle management. Utilizing Outsourced Services: For healthcare organizations that lack the resources or expertise to handle denial management internally, outsourcing services can be a viable solution. Outsourced medical billing and coding companies specialize in managing denials, ensuring efficient claims processing, and optimizing revenue collection. By leveraging the expertise of these external partners, organizations can alleviate the burden on their internal teams and achieve better denial management outcomes. Our company, the GoHealthcare Practice Solutions can easily help you with this! Denial management is a critical component of revenue cycle management in healthcare organizations. By focusing on prevention, utilizing effective denial management strategies, leveraging technology solutions, and investing in staff training, organizations can mitigate the financial impact of denied claims and protect their bottom line. Continuous monitoring, analysis of denial patterns, and collaboration with payers are essential to identify opportunities for improvement and implement proactive measures. By adopting these best practices, healthcare organizations can optimize revenue generation, enhance operational efficiency, and provide quality care to their patients. Reading Sources and References:
Contact us today!Prior Authorizations: Benefits Using Outsourcing Services Discover how outsourcing prior authorization can improve revenue cycle management, ensure medical necessity, and streamline healthcare services. Prior Authorization: A Key to Successful Revenue Cycle Management Prior Authorization is a pre-approval or precertification process, where healthcare providers must obtain approval from a patient's insurance company for coverage of a specific medication, procedure, or service. It is a cost containment measure that ensures medical necessity, avoiding unnecessary or potentially harmful treatments. Moreover, it’s a crucial part of the revenue cycle management, impacting the bottom-line profitability of a healthcare provider and facilities. Incorrect or incomplete Prior Authorization can lead to claim denials, increasing the financial burden on healthcare providers. However, by outsourcing Prior Authorization services, healthcare organizations can eliminate these risks, enhance revenue, and streamline their operations. Outsourcing Prior Authorization: Why it Matters Outsourcing Prior Authorization comes with several benefits. It can expedite the approval process, improve billing accuracy, and reduce administrative workload, freeing up valuable time and resources for patient care. This is where eliminating 'peer to peer' time becomes crucial. By outsourcing the process to professionals who understand the medical necessity, utilization, and frequency management, providers can eliminate unnecessary peer-to-peer discussions, improving efficiency and productivity. Furthermore, outsourcing provides access to skilled professionals who understand complex Prior Authorization requirements, ensuring compliance and reducing the risk of denials. They work closely with healthcare providers to gather necessary medical records, submit requests, follow up with insurance companies, and manage the entire process efficiently. Understanding the Importance of Prior Authorization in Different Healthcare Services Certain services and specialties may have stricter Prior Authorization requirements. Here's why it becomes indispensable in these situations:
Outsourcing the prior authorization process work in the healthcare industry, including medical practices, providers, hospitals, and surgery centers, can offer several benefits. Here are some key advantages:
Why Choose GoHealthcare Practice Solutions for Your Prior Authorization Needs? Among the plethora of companies offering Prior Authorization outsourcing, GoHealthcare Practice Solutions stands out as a trusted and efficient partner. Our organization is rooted in the belief that healthcare providers should focus on what they do best – providing quality patient care – while we handle the intricacies of Prior Authorization. We have a deep understanding of the healthcare industry and the challenges it faces. This understanding allows us to tailor our services to suit your unique needs, creating customized solutions that deliver measurable results. Here are some reasons why GoHealthcare Practice Solutions is the ideal choice for your Prior Authorization outsourcing needs: Expertise and Experience: GoHealthcare Practice Solutions brings a wealth of experience and expertise to the table. Our team of professionals is well-versed in handling Prior Authorization for a wide range of services, ensuring a high accuracy rate and minimal denials. Compliance and Accuracy: We prioritize compliance and accuracy, staying updated with the latest regulations and changes in insurer policies. This proactive approach reduces the risk of non-compliance and ensures that your Prior Authorization process is always in line with the latest requirements. Customized Solutions: We understand that each healthcare provider is unique, with specific needs and challenges. That's why we offer tailored solutions to suit your specific requirements, processes, and objectives. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we believe in building partnerships, not just business relationships. We are committed to helping you navigate the complexities of Prior Authorization, freeing your team to focus on patient care and clinical services. By choosing us as your Prior Authorization outsourcing partner, you're not just choosing a service provider; you're choosing a strategic ally who will work with you to drive growth, improve efficiency, and shape a sustainable future for your healthcare organization. Trust GoHealthcare Practice Solutions to transform your Prior Authorization process and see the difference it makes to your bottom line. In the ever-evolving healthcare landscape, we stand by you as your reliable partner, powering your journey towards excellence with our comprehensive, efficient, and innovative Prior Authorization solutions. Leveraging Patient Access Services for Optimized Healthcare Workflow and Revenue Cycle Management6/13/2023 LEVERAGING PATIENT ACCESS SERVICES FOR OPTIMIZED HEALTHCARE WORKFLOW AND REVENUE CYCLE MANAGEMENT Discover the pivotal role of Patient Access Services in streamlining healthcare operations and revenue cycle management. Learn how these services significantly influence patient satisfaction, operational efficiency, and overall revenue generation for healthcare facilities.
In today's complex healthcare landscape, patient access services are emerging as a cornerstone of effective healthcare delivery, dramatically reshaping the traditional workflow. This article provides an in-depth exploration of patient access services, examining its advantages, workflow, importance, and its critical role in successful revenue cycle management for healthcare facilities such as hospitals, surgery centers, and physician offices. Understanding Patient Access Services Patient access services are an integral part of healthcare facilities, representing the front-end operations that guide a patient's healthcare journey, from the first point of contact to the completion of care delivery. These services encompass various functions, including appointment scheduling, patient registration, insurance verification, preauthorization, financial counseling, and ensuring patient rights and responsibilities. In essence, patient access services work as the welcoming committee and navigation guide for patients, simplifying their interactions with the complex machinery of the healthcare system. It plays a pivotal role in influencing a patient’s perception about the quality of care received, impacting patient satisfaction and loyalty. Advantages of Patient Access Services The benefits of effective patient access services are manifold, affecting all stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem – patients, providers, and payers.
A typical patient access workflow begins with patient registration. This involves capturing demographic and medical history data, along with verifying patient identity and insurance coverage. After this, the financial obligations, including deductibles, co-pays, and co-insurance, are discussed with the patient. Next, necessary authorizations and referrals are obtained. This is followed by scheduling appointments and coordinating with the concerned medical department. The workflow concludes with informing patients about their rights and responsibilities, confidentiality practices, and any advance directives. Throughout this workflow, there's a continual emphasis on patient education and communication, helping patients understand and navigate their healthcare journey with ease. Importance of Patient Access Services Patient access services are not only the patient’s first point of contact with the healthcare facility, but they also have a lasting impact on the patient's overall experience and the facility's operational efficiency and revenue generation. By reducing administrative burdens and removing obstacles in the care delivery process, these services enhance patient satisfaction, care quality, and revenue outcomes. Furthermore, these services contribute to healthcare's triple aim: improving the patient experience, improving population health, and reducing healthcare costs. By facilitating early intervention, better coordination, and more effective management of health conditions, patient access services can lead to better health outcomes at a lower cost. Patient Access Services: The Backbone of Revenue Cycle Management The significance of patient access services extends beyond patient satisfaction and operational efficiency. The services are a driving force behind the success of revenue cycle management. Errors in patient registration, insurance verification, or preauthorization can lead to claim denials or payment delays, which are detrimental to the facility's On the other hand, a streamlined patient access workflow can help ensure accurate data collection, timely and correct billing, fewer denials, and quicker reimbursements. From the perspective of hospitals, surgery centers, and physician offices, having robust patient access services is invaluable. When healthcare facilities fail to manage patient access effectively, it can lead to significant revenue leakage. This can undermine the financial stability of the healthcare organization and compromise its ability to provide quality care. Patient access services, therefore, are the first line of defense in revenue cycle management. They play a critical role in securing payments for services rendered by identifying coverage, obtaining necessary authorizations, providing financial counseling, and communicating with patients about their financial responsibilities. Envisioning the Future of Healthcare with Patient Access Services In the age of value-based care and patient-centered care models, the significance of patient access services is more pronounced than ever. These services bridge the gap between patients and providers, fostering relationships built on trust and transparency. Patient access services can transform the healthcare landscape by driving improvements in patient satisfaction, operational efficiency, and revenue cycle management. By recognizing the critical role of these services, healthcare organizations can position themselves for success in today's competitive environment. Indeed, patient access services are no longer optional. They are a critical component of the modern healthcare ecosystem, serving as the backbone of effective and efficient care delivery. Therefore, investing in patient access services should be a strategic priority for healthcare organizations seeking to enhance their service delivery and safeguard their financial health. With the escalating demand for patient-centric care and the simultaneous pressure to optimize costs, healthcare providers need to embrace and invest in patient access services. They are, after all, the first point of contact in the patient's journey and play a crucial role in setting the tone for the entire healthcare experience. The future of healthcare is inextricably linked with the quality and effectiveness of patient access services. As the healthcare industry continues to evolve and adapt to the new normal, patient access services will undoubtedly remain at the forefront, paving the way for a seamless, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare delivery model. Technology and Patient Access Services In the digital era, technology is playing a transformative role in enhancing the effectiveness of patient access services. Advanced solutions like Electronic Health Records (EHRs), Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and sophisticated scheduling software are streamlining the patient access workflow, leading to a significant reduction in manual errors and an enhancement in operational efficiency. For instance, integrated EHRs allow for seamless data sharing, enabling real-time updates of patient information across all departments. This not only facilitates quicker decision-making but also ensures that all stakeholders have the latest information at their fingertips. In addition, healthcare facilities are leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) to predict patient behavior, such as no-show probabilities, enabling them to optimize appointment scheduling and resource allocation. Similarly, AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants are enhancing patient interaction, providing round-the-clock support and instantly resolving patient queries. Such technological advancements are making patient access services more responsive, accurate, and efficient, leading to better patient experiences and improved healthcare outcomes. Patient Access Services: An Instrument of Change in Healthcare The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the critical role of patient access services in managing healthcare delivery during crises. With the unprecedented influx of patients, these services were central to organizing care, providing critical information, and ensuring seamless healthcare delivery. Moreover, patient access services have been pivotal in the widespread adoption of telehealth services. By coordinating virtual visits, managing online appointment scheduling, and providing technical support, these services have made healthcare more accessible to patients, particularly those in remote areas or those unable to visit healthcare facilities due to the pandemic. In this sense, patient access services are not just a mechanism for healthcare delivery but a catalyst for change, driving the evolution of the healthcare industry in the face of challenges and opportunities. Cultivating a Culture of Patient-Centricity with Patient Access Services Finally, it's important to note that patient access services have a profound impact on the overall culture of healthcare organizations. By placing the patient at the center of all operations, these services foster a culture of patient-centricity. This culture is crucial in today's healthcare environment, where patient satisfaction is a key determinant of a healthcare facility's reputation and success. It influences everything from patient loyalty and referral rates to reimbursement under value-based payment models. By prioritizing patient needs and experiences, patient access services cultivate a culture where every interaction is guided by the principles of empathy, respect, and understanding. This not only enhances patient experiences but also motivates healthcare professionals, creating a positive work environment characterized by collaboration, transparency, and mutual respect. Summing Up Patient access services, while often overlooked, form the lifeblood of modern healthcare systems. They are the bridge that connects patients with providers, ensuring that every interaction is seamless, efficient, and patient-centered. At the same time, these services are critical for the financial health of healthcare organizations. They facilitate accurate data collection, streamline billing and collection processes, and play a crucial role in preventing revenue leakage. With the rise of digital technologies and the increasing focus on patient-centric care, the role of patient access services is set to grow even further. Healthcare facilities that recognize and invest in these services are likely to enjoy higher patient satisfaction, improved operational efficiency, and robust financial health. In essence, patient access services are not just a pathway to healthcare but the very foundation upon which the future of healthcare rests. They are shaping the healthcare landscape of tomorrow, driving improvements in care delivery and transforming patient experiences. Patient access services, therefore, warrant recognition, investment, and continual improvement. By doing so, healthcare organizations can navigate the complexities of the healthcare environment, delivering high-quality care while staying financially viable. Let's delve into the complete workflow of Patient Access in the healthcare industry: 1. Initial Contact and Appointment Scheduling The Patient Access workflow begins when a patient reaches out to a healthcare provider to seek medical attention. This initial point of contact can be through various channels, such as phone calls, online portals, or even walk-ins. During this phase, Patient Access representatives collect preliminary information, including the reason for the appointment, preferred time and date, and any specific physician requests. Using this information, they schedule an appointment for the patient. 2. Pre-Registration This is the step where the patient's demographic details and insurance information are collected. It includes acquiring personal information, emergency contact information, and details about their insurance coverage. Pre-registration can be done over the phone, through a web portal, or in person. It is during this stage that the consent for treatment and agreement to pay are obtained from the patient. 3. Insurance Verification The next step is to verify the patient's insurance details. This includes checking the patient's eligibility for the claimed insurance benefits, understanding the details of coverage, and identifying any limitations or exclusions. This stage is critical as it determines the financial responsibilities of the patient and the healthcare provider. 4. Pre-Authorization Certain procedures or treatments require authorization from the insurance provider before they can be carried out. In the pre-authorization step, Patient Access representatives obtain this necessary approval, ensuring that the services rendered will be covered by the insurance company. This process typically involves submitting a detailed request outlining the need for the specific procedure or treatment. 5. Financial Counseling Financial counseling is an essential part of the Patient Access workflow. During this phase, patients are informed about their financial responsibilities, such as co-pays, deductibles, and out-of-pocket maximums. If the patient is uninsured or underinsured, various payment options, including financial aid, are discussed. 6. Registration Registration is the official admittance of the patient into the healthcare facility. All the information gathered in the pre-registration phase is verified, and any additional necessary information is collected. It also includes educating patients about their rights and responsibilities. 7. Point-of-Service Collections Patient Access services also play a crucial role in revenue collection. In the point-of-service collections phase, any upfront payments such as co-pays or deductibles are collected from the patient. 8. Coordination of Care This is the actual delivery of care, where the patient meets with the healthcare provider. Patient Access representatives ensure a seamless transition of the patient from the front desk to the care delivery team, coordinating with various departments as necessary. 9. Post-Visit Follow-ups After the patient's visit, there may be post-visit follow-ups scheduled, based on the healthcare provider's recommendations. These could include additional tests, procedures, or simple check-ups. Patient Access services manage these follow-ups, ensuring that patients are informed and reminded of their subsequent appointments. 10. Feedback and Resolution Finally, patient feedback is collected, and any complaints or issues raised by the patient are addressed. This step is crucial for improving the patient experience and for quality improvement initiatives. Throughout this workflow, communication is key. Patient Access services ensure that patients are informed and comfortable at every step, promoting transparency and trust. They also facilitate effective communication between different departments within the healthcare facility, ensuring a smooth, efficient care delivery process. In essence, the Patient Access workflow is a comprehensive and patient-centric process that ensures patients receive timely, efficient, and satisfactory healthcare services, while also safeguarding the financial health of the healthcare facility. 11. Data Management and Integrity A crucial part of the Patient Access workflow is maintaining the accuracy and completeness of patient data. Patient Access teams are responsible for updating patient records with the most recent information, verifying existing data for accuracy, and rectifying errors when identified. The quality of data directly impacts the accuracy of billing, the effectiveness of care coordination, and ultimately, patient satisfaction. 12. Compliance and Confidentiality Adhering to regulations and maintaining patient confidentiality are paramount in the Patient Access workflow. This involves complying with HIPAA rules, protecting patient information from unauthorized access, and ensuring that the sharing of patient information for care coordination or billing purposes is done in a manner that respects privacy laws and regulations. 13. Revenue Cycle Management Patient Access teams play a key role in Revenue Cycle Management. This starts with collecting co-pays, deductibles, and other payments due at the point of service. After the patient visit, these teams are also involved in the claim submission process, ensuring that claims are submitted accurately and promptly to minimize denials and payment delays. 14. Patient Education and Engagement Patient Access services are responsible for educating patients about their care, including explaining complex insurance benefits, discussing treatment costs, and clarifying the responsibilities of the patient. By ensuring patients understand their care journey, Patient Access services enhance patient engagement, which can lead to better health outcomes. 15. Continuous Improvement Patient Access teams regularly review their processes for opportunities for improvement. This could involve analyzing patient feedback to identify areas of dissatisfaction, reviewing denial data to pinpoint common causes, or examining operational metrics to find inefficiencies. The teams then use this information to improve the Patient Access workflow, enhance patient satisfaction, and boost revenue collection. Outsourcing Patient Access services can be beneficial for several reasons, primarily revolving around improving efficiency, enhancing patient experience, and achieving better outcomes. Let's delve into these aspects in detail: 1. Cost-Effective Operations: Outsourcing can be a cost-effective solution for healthcare facilities. It eliminates the need to hire, train, and maintain an in-house team, thus reducing operational costs. Moreover, outsourcing providers have the advantage of scale, being able to spread their costs over many clients, which can lead to cost savings. 2. Access to Specialized Expertise: By outsourcing Patient Access services, healthcare organizations gain access to a team of specialists with a specific focus on this area. These teams are trained in the latest best practices, regulatory guidelines, and technological advancements. This specialized expertise can lead to increased efficiency and accuracy, ultimately resulting in improved patient satisfaction and financial outcomes. 3. Focus on Core Competencies: Outsourcing allows healthcare providers to focus on their core competencies, such as delivering high-quality medical care. By leaving the administrative tasks to experts, physicians and clinical staff can devote more time and attention to patient care, leading to better health outcomes. 4. Enhanced Patient Experience: Outsourcing companies often have the resources and technology to provide superior patient experiences. For instance, they may offer multilingual support, 24/7 availability, and advanced digital tools for appointment scheduling, pre-registration, and more. These features can improve patient access, making it easier for patients to navigate their healthcare journey. 5. Scalability: Outsourced Patient Access services offer scalability, allowing healthcare organizations to quickly adjust to changing patient volumes. This flexibility is particularly advantageous during unexpected events such as public health emergencies or seasonal fluctuations. 6. Technology Adoption: Outsourcing partners often have access to state-of-the-art technology that may be too expensive or complex for individual healthcare organizations to implement. These advanced tools can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and enhance patient communication, leading to better overall outcomes. 7. Revenue Cycle Management: Outsourcing providers specialize in handling the intricacies of insurance verification, pre-authorization, and billing, thereby reducing the risk of claim denials and payment delays. This expertise can significantly enhance the revenue cycle, ensuring that healthcare organizations receive timely and accurate payments for services rendered. 8. Regulatory Compliance: Keeping up with the continuously evolving healthcare regulations can be challenging. Outsourcing partners are adept at staying current with these changes, ensuring that Patient Access processes remain compliant with all relevant laws and guidelines. In summary, while not all healthcare organizations will find outsourcing to be the right fit for their needs, many can benefit significantly from this approach. With its potential to enhance patient access, streamline operations, and improve financial outcomes, outsourcing Patient Access services can be a strategic move towards more efficient and patient-centric healthcare delivery. 9. Data Security: Outsourcing companies that specialize in healthcare services often have robust data security measures in place, including firewalls, encryption, and secure data centers. These measures, coupled with regular security audits and adherence to HIPAA and other regulations, can ensure the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive patient data. 10. Quality Control: Patient Access service providers typically have well-established quality control processes. They consistently monitor and review their work to maintain high standards of accuracy and efficiency. This continual focus on quality assurance can lead to superior results in patient interactions, data management, and revenue cycle management. 11. Continuous Improvement: Outsourcing partners often have dedicated teams for process improvement. They regularly analyze their operations, identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, and implement improvements. This culture of continuous improvement can drive consistent enhancements in the quality and efficiency of Patient Access services. 12. Disaster Recovery: Outsourcing can provide an added layer of security in case of emergencies or disasters. Many outsourcing companies have comprehensive disaster recovery and business continuity plans to ensure uninterrupted service. This reliability can be crucial for maintaining patient access and satisfaction during unforeseen circumstances. 13. Patient Satisfaction Tracking: Patient Access service providers often have systems in place for tracking and analyzing patient satisfaction. By measuring key performance indicators (KPIs) and gathering patient feedback, they can help healthcare organizations identify areas for improvement and implement changes to enhance patient experience. 14. Streamlining Communication: Outsourcing companies can provide a single point of contact for patients, simplifying communication. They can handle everything from appointment scheduling to billing queries, providing consistent, reliable information and reducing the likelihood of miscommunication. 15. Reducing Administrative Burden: Healthcare staff often juggle multiple responsibilities, and administrative tasks can detract from their primary roles. By outsourcing Patient Access services, administrative burdens are reduced, freeing up staff to focus more on patient care. In conclusion, outsourcing Patient Access services can offer a wealth of benefits. From improving patient satisfaction to enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs, outsourcing can be a strategic move for healthcare organizations aiming to navigate the complexities of today's healthcare landscape. However, it's essential for each organization to thoroughly evaluate their specific needs, capabilities, and goals before deciding whether to outsource these services. 16. Efficiency and Productivity: Outsourcing partners usually bring industry best practices, efficient processes, and high-quality standards to the table. They operate with a high level of efficiency and have key performance metrics that their teams adhere to. This can result in improved productivity, quicker turnaround times, and ultimately, increased patient satisfaction. 17. Innovation: Outsourcing providers often invest heavily in research and development to stay ahead in the competitive market. They continually innovate their processes, tools, and technologies. Healthcare organizations can take advantage of these advancements to offer their patients the latest and best in services and care. 18. Mitigate Risks: Outsourcing can help mitigate risks associated with regulatory compliance, data security, and changing market conditions. Outsourcing providers have expertise in these areas and take the onus of managing these risks, reducing the burden on the healthcare organization. 19. Staff Training and Development: Outsourcing companies invest in their staff's ongoing training and development. They ensure that their team is up-to-date with the latest industry knowledge, regulations, and technologies. This consistent level of training can lead to high-quality service delivery. 20. Business Transformation: Outsourcing is not just about cost savings; it can also be a strategic move towards business transformation. By outsourcing Patient Access services, healthcare organizations can re-engineer their processes, adopt innovative technologies, and re-focus their internal resources towards strategic goals. 21. Access to Global Talent Pool: Outsourcing opens the door to a global talent pool. Healthcare providers can benefit from the experience, expertise, and cultural diversity of professionals from around the world. This diversity can lead to innovative solutions and better problem-solving capabilities. While the benefits of outsourcing Patient Access services are numerous, it's not a decision to be taken lightly. Healthcare organizations should carefully consider their operational needs, patient demographics, and strategic goals. It's important to partner with a reputable and experienced service provider who can align with the organization's vision and deliver services that add value to patients' experience. 22. Round-the-Clock Service: An outsourcing partner can provide 24/7 support to cater to patients across different time zones or those who prefer contacting the healthcare facility after regular working hours. This non-stop service can enhance patient satisfaction and lead to higher patient engagement. 23. Multilingual Support: In our increasingly globalized world, providing support in multiple languages is a significant advantage. An outsourcing provider may offer multilingual support, thus enhancing the patient experience by communicating in the language they are most comfortable with. 24. Proactive Approach: Many outsourcing partners take a proactive approach to manage Patient Access services, anticipating issues and resolving them before they become problems. This can reduce delays, minimize mistakes, and lead to smoother operations. 25. Technological Advancement: Outsourcing partners usually have access to advanced technology platforms and tools that may not be feasible for individual healthcare organizations to acquire. They leverage these technologies to provide streamlined services, reduce errors, automate manual processes, and generate actionable insights for improvement. 26. End-to-End Service: Outsourcing partners can manage all aspects of Patient Access services, from the first point of contact to post-visit follow-ups. This end-to-end service ensures a seamless patient journey and reduces the risk of communication gaps or errors. 27. Benchmarking: Outsourcing companies often provide benchmarking data, comparing performance against industry standards. This data can be valuable for healthcare organizations to identify areas of improvement and track progress over time. 28. Flexibility and Customization: Outsourcing partners usually offer flexible and customizable service models. They can tailor their services to meet the specific needs and goals of the healthcare organization. This flexibility allows for a service delivery model that aligns with the healthcare provider's objectives, patient demographics, and organizational culture. In summary, outsourcing Patient Access services can have far-reaching benefits for healthcare organizations. These advantages range from operational and financial to strategic and patient-centric. However, the decision to outsource these services should be taken with careful consideration, thorough analysis, and due diligence to ensure a successful partnership that adds value to the healthcare organization and enhances the patient experience. By partnering with a competent and experienced outsourcing provider, healthcare organizations can transform their Patient Access services into a strategic asset that contributes to enhanced patient satisfaction, improved revenue cycle management, and overall organizational success. Understand the necessity of Prior Authorization (PA) in healthcare delivery, especially in orthopedics, pain management, and hospital settings. Unpack the detailed PA process and discover the best PA services for surgeons, providers, and hospitals. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we specialize in providing an essential service to the healthcare sector – Prior Authorization (PA) services. As a trusted partner for surgeons, providers, and hospitals, we are committed to delivering timely, accurate, and comprehensive PA approvals, reducing the administrative burden on medical professionals, and ensuring the uninterrupted flow of patient care. Our goal is to facilitate seamless healthcare experiences, particularly within orthopedic, pain management, and hospital contexts, by managing the often complicated and time-consuming PA process. Understanding the IMPORTANCE AND PROCESS OF PRIOR AUTHORIZATION SERVICES: FOCUSING ON ORTHOPEDIC, PAIN MANAGEMENT, AND HOSPITAL CARE Prior Authorization (PA), also known as pre-approval, is an essential component of healthcare delivery, serving as a gatekeeper between patients, providers, and insurance companies. The process aims to validate the necessity of certain treatments or medications before they are administered, ensuring patient safety, preventing unnecessary procedures, and controlling healthcare costs. When applied correctly, PA services can be a significant force for good in healthcare. However, the process can be complex and challenging. Therefore, it is imperative to understand why PA approvals are so important and the procedures required for a successful application. The Importance of Prior Authorization Approvals. The importance of PA cannot be overstated. Firstly, it helps in maintaining the quality of healthcare services. By requiring prior authorization for orthopedic surgeries, pain management therapies, and other hospital treatments, insurance companies can ensure that the recommended procedures align with evidence-based medicine. It acts as a protective measure, screening out potentially harmful or unnecessary treatments and medications. For instance, in pain management, it may prevent the over-prescription of opioids, mitigating the risk of addiction. Secondly, PA also assists in controlling healthcare costs. It can deter the excessive use of costly treatments when more cost-effective alternatives can provide equivalent outcomes. By mitigating overutilization, PA helps manage healthcare expenditures, potentially translating into lower insurance premiums. Lastly, PA plays a crucial role in promoting transparency. It obliges providers to justify their treatment plans, which fosters open communication between all stakeholders—patients, providers, and payers. The Prior Authorization Process The PA process typically starts when a healthcare provider identifies a service or medication that requires pre-approval from the patient's health insurance company. The steps involved are:
Despite its benefits, the PA process can be time-consuming and complex, often leading to delays in patient care. This is where dedicated PA services, like those offered by XYZ Healthcare Solutions, come into We act as intermediaries between healthcare providers and insurance companies, managing all aspects of the PA process. This includes identifying the need for PA, completing and submitting the necessary paperwork, tracking PA requests, and facilitating communication between the provider and insurer. Our specialized PA service spans across various medical specialties. We provide prior authorization for orthopedic surgeries, handling the intricate approval processes associated with various orthopedic procedures such as joint replacements, spinal surgeries, and arthroscopic procedures. We also provide prior authorization for pain management, helping ensure that patients have access to necessary treatments like nerve blocks, epidurals, and opioid medications while minimizing potential misuse. Our team of experts understands the specific requirements for these authorizations and works diligently to expedite approvals. In the broader context of hospital care, we manage PAs for an extensive range of treatments and procedures. This can significantly reduce the administrative burden on hospital staff, allowing them to focus on patient care. With our expert knowledge and experience, we can help streamline the PA process, minimize delays, and ensure that patients receive their treatments in a timely manner. Our goal is to make the PA process as efficient and hassle-free as possible for both providers and patients. Prior authorization is a critical aspect of healthcare delivery. It serves as a quality control measure, ensures cost-effectiveness, and promotes transparency. However, navigating the PA process can be a challenge for many providers. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we're dedicated to making this process easier. Our prior authorization services for surgeons, providers, and hospitals ensure that medical professionals can focus on what they do best – providing excellent patient care – while we handle the administrative complexities of the PA process. We're committed to offering the best PA services, particularly in orthopedics, pain management, and hospital settings. We understand that the sooner a PA is approved, the sooner a patient can receive the necessary care. Together, let's make healthcare more efficient, effective, and patient-centric. Prior Authorization Services: A Necessity Not Just an Option While PA services are indispensable for any healthcare setting, they become crucial when specialized care is involved. The unique challenges in these fields demand a more nuanced understanding of the intricacies involved in the PA process. For instance, the prior authorization for orthopedic procedures involves understanding a wide array of surgeries, each with its own set of considerations. Joint replacements may require justifications for why less invasive methods are not applicable, while spinal surgeries may necessitate a detailed history of conservative treatments before the insurance company approves the procedure. Our PA service in the orthopedic field is equipped to handle these complexities, allowing for a smoother process and more effective outcomes. Similarly, in pain management, the need for PA services becomes more acute due to the ongoing opioid crisis. Ensuring that the treatment is medically necessary, safe, and effective for the patient becomes crucial, requiring careful handling of the PA process. Streamlining the Prior Authorization Process: We have developed a systematic, clinical and physician-patient centric approach to managing the prior authorization process. Accurate Documentation: We ensure that all patient information, diagnosis details, proposed treatment plans, and supporting medical literature is accurately documented and submitted in a timely manner. This not only speeds up the process but also reduces the likelihood of denials due to incomplete or incorrect information. Persistent Follow-ups: We actively follow up on every PA request with the insurance company. Regular follow-ups prevent delays and keep the process moving forward. Managing Denials and Appeals: In case of a denial, we don't just stop there. We work closely with the healthcare provider to understand the reason for denial and collect additional information that can be used for an appeal. Communication: We keep everyone in the loop - patients, providers, and insurance companies. This ensures transparency and builds trust among all parties involved. Prior Authorization for Hospitals: A Special Focus Hospitals face unique challenges when it comes to prior authorization. They deal with a high volume of patients, diverse medical conditions, and a wide array of procedures and treatments. Additionally, hospitals also have to manage administrative work, patient care, and regulatory compliance, which can make the PA process quite overwhelming. Our dedicated prior authorization services for hospitals are designed to handle these challenges efficiently. We have a team of experts who understand hospital operations and the specific PA requirements associated with various hospital treatments. Our aim is to reduce the administrative burden on hospitals, improve operational efficiency, and ultimately enhance patient satisfaction. The Takeaway: Prior Authorization Services as a Valuable Ally In the dynamic and often demanding world of healthcare, services like ours can play an instrumental role in smoothing processes and enhancing outcomes. While the benefits of prior authorization are manifold, the complexities involved in securing approvals can act as hurdles. By leveraging our specialized prior authorization services for orthopedic surgeries, pain management, and hospital care, these obstacles can be effectively addressed. As we continue to evolve, innovate, and refine our offerings at GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we remain committed to our core mission - facilitating better healthcare experiences by simplifying the PA process. We invite you to partner with us in this mission, and together, let’s create a healthcare environment that is efficient, patient-centric, and transparent. Building Partnerships: A Collaborative Approach to Prior Authorization ServicesIn the healthcare ecosystem, collaboration is key. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we pride ourselves on being more than just a service provider. We aim to be a partner to all our clients - be they surgeons, pain management specialists, or hospitals. By understanding the unique challenges each medical professional faces, we are able to tailor our PA services to meet their specific needs. In our partnership, we work closely with your team, aligning ourselves with your operational workflow, understanding your patient demographics, and acquainting ourselves with your insurance scenarios. This collaboration allows us to provide you with a seamless, integrated prior authorization process. Proactive Problem-Solving: The Future of Prior Authorization Services Looking forward, we at GoHealthcare Practice Solutions believe in a proactive rather than reactive approach to the prior authorization process. Using advanced analytics and predictive modeling, we aim to identify potential roadblocks in the PA process ahead of time and resolve them before they cause delays. By predicting which treatments or medications might require more extensive documentation or may be more likely to be denied, we can preemptively prepare the necessary information, resulting in faster PA approvals. Our Commitment to Continuous Improvement The world of healthcare is constantly evolving, and so are we. We continually invest in our technology and our people to stay ahead of the curve. Regular training and education sessions keep our team up-to-date on the latest trends and changes in the prior authorization landscape. This ensures that we can offer our clients the most efficient and effective PA services, regardless of changes in insurance policies or regulatory requirements. In addition, we are dedicated to refining our processes based on feedback from our clients and their patients. Patient care is at the heart of everything we do. By continually improving our PA services, we can help ensure that patients receive the care they need, when they need it. From understanding the importance of prior authorization approvals to examining the detailed process for securing these approvals, it's clear that prior authorization services play an integral role in the healthcare landscape. Whether you're a surgeon, a provider of pain management services, or a hospital, engaging a specialist in the PA process can help you navigate the often complex approval process, ensuring your patients get timely access to the treatments they need. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we're proud to offer industry-leading prior authorization services. With a particular focus on orthopedics, pain management, and hospital care, we're dedicated to helping you deliver the best possible care to your patients. Reach out to us today to learn more about how we can simplify the PA process for you, freeing you up to focus on what you do best - providing top-notch patient care. The Crucial Connection Between Prior Authorization and Claims Payments Denials: One aspect that truly underscores the importance of a well-managed prior authorization process is the direct impact it has on claims approval. Claims denial due to the lack of or incorrect prior authorization is a common issue plaguing the healthcare industry. Let's delve deeper into this connection. Prior Authorization: A Prerequisite for Claims Approval Insurance companies necessitate prior authorization for certain procedures or treatments to ensure they are medically necessary, align with coverage policies, and prevent misuse of healthcare services. It becomes especially crucial for high-cost procedures like surgeries, advanced diagnostic tests, and specialized treatments in orthopedics and pain management. When a claim is submitted to the insurance company without appropriate prior authorization, it is very likely to be denied. This not only results in non-payment for the provider but also leads to financial stress for patients, administrative hassles, and delays in care delivery. The Impact of Claims Denial Claims denial can have far-reaching consequences. For providers and hospitals, it directly impacts revenue, disrupts cash flow, and adds to administrative costs. The effort required to correct and resubmit denied claims or manage appeals is time-consuming and diverts staff from patient care responsibilities. For patients, claim denials can mean unexpected out-of-pocket costs, leading to financial stress. It also creates dissatisfaction and mistrust, potentially damaging the provider-patient relationship. Navigating the Challenge with Effective Prior Authorization Services At Gohealthcare Practice Solutions, our goal is to minimize claim denials related to prior authorization issues. Our team of experts navigates the intricacies of the prior authorization process to ensure a higher approval rate. Thorough Documentation: We ensure that every PA request is supported by thorough and accurate documentation, presenting a compelling case for the medical necessity of the procedure. Timely Submissions: We adhere to strict timelines for submitting PA requests, ensuring that there are no delays that might lead to procedural postponements and subsequent claims denial. Appeals and Resubmissions: In case of PA denial, we promptly manage the appeal or resubmission process, furnishing additional supporting information as needed. Regular Updates and Follow-ups: We regularly follow up on the status of PA requests and update healthcare providers, ensuring they are informed at every stage of the process. A Preventive Approach: Minimizing Claims Denial Our preventive approach at XYZ Healthcare Solutions is designed to tackle potential issues before they arise. Our specialized prior authorization services not only facilitate prompt PA approvals but also significantly minimize the risk of claims denial. Our experts understand the PA requirements of various insurance companies and are well-versed in the specific prerequisites of different treatments, be it orthopedic surgeries or pain management therapies. Navigating the complex landscape of prior authorization is no easy task, but it's a crucial step in ensuring claims are approved, and timely care is delivered to patients. The role of expert prior authorization services like those offered by GoHealthcare Practice Solutions in mitigating claims denial cannot be overstated. We are committed to providing the best in prior authorization services, allowing healthcare providers to concentrate on their core objective - patient care. With our specialized services, let's together ensure a smoother, more efficient, and patient-centric healthcare delivery system. Eliminating the Need for Peer-to-Peer Reviews: Enhancing Efficiency and Cost-SavingsIn the healthcare landscape, a peer-to-peer review, also known as a physician-to-physician review, often becomes necessary when a prior authorization request is denied by the insurance company. This process involves a conversation between the requesting provider and a doctor representing the insurer, aiming to discuss the case and provide an opportunity for the provider to justify the medical necessity of the requested service. While peer-to-peer reviews can sometimes overturn an initial denial, they require significant investment of time and resources. The need for detailed preparation, scheduling, and follow-ups can detract from a provider’s time that could have otherwise been devoted to patient care. For hospitals and healthcare providers, this can translate into substantial costs, adding to the financial burden. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we understand these challenges and strive to minimize the need for peer-to-peer reviews, ultimately contributing to cost savings for our clients. Mitigating the Need for Peer-to-Peer ReviewsOur strategy revolves around proactive and comprehensive management of the prior authorization process, which significantly reduces the likelihood of initial denials that lead to peer-to-peer reviews. Robust Documentation: We prioritize providing thorough and accurate documentation right from the first PA request. By furnishing comprehensive medical histories, supporting literature, and a clear demonstration of the treatment's necessity, we minimize questions or concerns from the insurer's side. Clear Communication: We maintain open lines of communication with insurance companies, proactively addressing queries and providing clarifications. This reduces misinterpretations or misunderstandings that might lead to a denial. Staying Updated: Our team stays abreast of the ever-evolving insurance policies and guidelines, ensuring that all PA requests comply with the latest insurer requirements. Streamlining the Peer-to-Peer ProcessIn cases where a peer-to-peer review becomes unavoidable, we work closely with providers to streamline the process. We help prepare for the review by gathering all necessary information, scheduling the review at a time convenient for the provider, and assisting in follow-up steps. Prior Authorization Services: Enhancing Profitability and Patient CareBy mitigating the need for time-consuming peer-to-peer reviews, our prior authorization services not only bring about direct cost savings but also allow healthcare professionals to focus on their core task - patient care. This contributes to enhanced patient satisfaction, improved health outcomes, and overall profitability. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, our objective extends beyond managing the prior authorization process. We aim to be a partner in your growth, helping streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance the quality of care. Together, let's create a healthcare system that's efficient, cost-effective, and patient-centric. Our success rate is at 98% and it's a faster turnaround time. We can get started in less than 48 hours. It's a very easy process. We do not have a binding contract. The GoHealthcare Practice Solutions Advantage: High Success Rates, Rapid Turnaround, and MoreOur commitment to delivering excellence in prior authorization services is reflected in our performance metrics. With a success rate of 98%, we pride ourselves on our ability to secure PA approvals quickly and efficiently. Our team's expertise and dedication translate into faster turnaround times, ensuring patients can access needed treatments without unnecessary delays. Swift Implementation, No Binding Contracts. Getting started with us is a breeze. We can have our services up and running for your practice in less than 48 hours. Plus, we believe in our services and the value they provide, so we don't tie you down with a binding contract. Our goal is to make the transition as smooth and hassle-free as possible. Your Return on Investment with GoHealthcare Practice Solutions Choosing GoHealthcare Practice Solutions as your partner in the prior authorization process yields tangible results. Here are the key returns on investment you can anticipate: Cost-Effectiveness: Our services, by mitigating the need for in-house teams to handle prior authorization, help you save on operational costs. Elimination of Unnecessary Peer-to-Peer Process: We minimize the need for time-consuming and resource-intensive peer-to-peer reviews, adding to your bottom line. Solution to Staffing Shortages: By taking over the prior authorization tasks, we help eliminate staffing shortages, ensuring your team can focus on their primary responsibilities. Increased Revenue: Our efficient management of the PA process, combined with a reduction in claim denials, can increase your revenue by up to 35%. Boosted Physician Productivity: With less time spent on administrative tasks, physicians can concentrate more on patient care, boosting their productivity by up to 30%. Don't forget and keep in mind claims denials. This might help you decide why you seriously need help with your prior authorization and utilization management. Understanding Claim Denials: Common Reasons and Mitigation Strategies Claim denials pose significant challenges to healthcare providers, interrupting revenue cycles and adding to administrative burdens. Understanding the common reasons behind denials can help providers better navigate the prior authorization process and enhance their chances of approval. 1. Lack of Prior Authorization: One of the most common reasons for claim denials is the absence of proper prior authorization for the services rendered. Certain procedures, medications, and treatments require pre-approval from the insurance company to ensure their medical necessity and appropriateness. 2. Incorrect Patient Information: Errors in patient demographic details, such as name, date of birth, policy number, or insurance ID, can lead to claim denials. These mistakes can occur due to typographical errors or outdated information. 3. Invalid or Incorrect Procedure or Diagnosis Codes: Every claim submitted needs to include accurate procedure codes (CPT codes) and diagnosis codes (ICD-10 codes). If the codes are incorrect, incomplete, or do not match, the claim can be denied. 4. Service Not Covered by the Plan: Each insurance plan has specific coverage limitations. If the service rendered is not covered under the patient's insurance plan, the claim will be denied. 5. Time Limit for Claim Submission Exceeded: Insurance companies have a specific timeframe within which a claim must be submitted. If the claim is submitted after this period, it is likely to be denied. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, our prior authorization services are designed to proactively address these common issues, significantly reducing the risk of claim denials. Our team meticulously ensures each PA request is accompanied by correct patient information, accurate procedure and diagnosis codes, and compelling evidence of medical necessity. We also maintain strict timelines for PA requests and claim submissions, ensuring they are sent within the stipulated periods. By effectively managing these common causes of claim denials, we can help increase your claims approval rate, enhance your revenue, and reduce the administrative burden on your team. With our expert services, claim denials become less of a hurdle and more of a stepping stone towards a streamlined and efficient healthcare practice. Senate Demands Transparency in Medicare Advantage Denials. And what's with the Algorithms?5/18/2023 Senate Subcommittee Probes Medicare Advantage Insurers Over Coverage Denials and Profits: Demanding Transparency and Better Patient Care Explore the Senate subcommittee's deep dive into Medicare Advantage insurers' practices, their profit motives, and the impact on beneficiaries. Learn about the concerns over the use of algorithms for coverage decisions and the calls for transparency and patient-focused reform in the healthcare industry. 05/18/2023 Wednesday: On Wednesday, a Senate subcommittee asked top Medicare Advantage insurers to disclose internal documents that reveal their decision-making process for healthcare coverage. The request was made during a hearing on healthcare delays and denials under the Medicare Advantage program. The committee is concerned about the detrimental effects of these decisions on patients needing skilled nursing care. The chairman, Richard Blumenthal, said there's increasing evidence that insurers are using algorithms, instead of medical professionals, to make care denial decisions. These decisions often affect seriously ill patients who require specialized or rehabilitation care before going home. Blumenthal said that while these algorithms are described as mere tools by insurers, the repeated denials they cause cannot be ignored. He emphasized the need for transparency around these algorithms, which the insurers often label as proprietary. Blumenthal also linked the continual need for prior authorizations or premature ending of certain healthcare coverages to insurers' profit motives. He shared data indicating that Medicare Advantage plans have higher profit margins per insured person compared to other insurance markets. Letters have been sent to CVS-Aetna, United Heath, and Humana—companies that collectively cover more than half of all Medicare Advantage beneficiaries—requesting more details on their operational practices. The Department of Health and Human Services’ Office of Inspector General testified that Medicare Advantage plans' criteria should align with original Medicare. However, she pointed out the potential incentive for insurers to deny services due to the fixed payment system in Medicare Advantage. A report from last year highlighted the frequent denial of skilled nursing stays by Medicare Advantage plans, causing a decrease in stays and the length of such stays for skilled nursing providers. Witnesses discussed the issues surrounding denial of skilled nursing care, highlighting that Medicare Advantage plan holders often face a complicated process to appeal their denied coverage. Patients caught in this system often have to choose between paying out of pocket or leaving the facility against medical advice. Appeals that are eventually approved can take up to a year to be reimbursed. The hearing also examined the difficulty in controlling insurers' practices that help them manage risk. Changing these practices could lead to higher costs for the government. However, the focus of the subcommittee members seemed to be on the personal hardships caused by coverage concerns. Personal stories shared included that of a widow from Connecticut, who detailed her struggles to secure intensive therapy for her husband following the removal of a brain lesion. The emotional and financial strain of navigating the healthcare system added to the distress of dealing with her husband's health crisis. The committee's examination of Medicare Advantage's internal workings underscores the larger concerns about private insurance companies' role in managing public health benefits. It also draws attention to the long-debated issue of transparency in how these companies operate, particularly in their decision-making process for providing coverage. Given the fixed payment system in Medicare Advantage, insurance companies may have financial incentives to limit services provided to beneficiaries, leading to a conflict of interest between ensuring quality care and maintaining profitability. Testimonies and personal stories shared during the hearing highlighted this concern. They also underscored the need for reform, particularly in areas such as skilled nursing care and rehabilitation services. While these services are often crucial in recovery, they are also costly, leading to frequent denials that can delay or impede necessary treatment. The committee expressed interest in potentially legislating to improve the situation if necessary. However, the potential for increased governmental costs presents a significant obstacle, suggesting the need for a balanced approach that ensures both adequate patient care and sustainable cost management. An additional point of concern is the use of artificial intelligence and algorithms in decision-making. There's growing evidence that these tools may be contributing to systematic denials of care. While they may increase efficiency, there's a risk that they could lead to arbitrary or inappropriate denial of services, particularly if they are not overseen or understood adequately. The shift to more transparency in the Medicare Advantage plans, which now cover more than half of all Medicare beneficiaries, could result in significant changes to how these plans operate and provide coverage. However, the details of these potential changes and their impact on beneficiaries, insurance companies, and overall healthcare costs remain to be seen. As of now, the committee has put the major insurance companies on notice, seeking more information on their practices and signaling their intent to improve the system for patients who depend on Medicare Advantage for their healthcare needs. More on this news. Read here - https://www.mcknights.com/news/impossible-medicare-advantage-denials-decried-during-senate-hearing/
Medicare denial codes, also known as Remittance Advice Remark Codes (RARCs) and Claim Adjustment Reason Codes (CARCs), communicate why a claim was paid differently than it was billed. These codes are universal among all insurance companies. Most of the commercial insurance companies the same or similar denial codes. Pay attention to action that you need to make in order for the claims to get paid. Here are some common Medicare denial codes:
searched keywords: Medicare Denial Codes, Medicare Claims, Claims Denial, Claims Adjustment, Healthcare Providers and Medicare, Understanding Medicare Denial Codes, Medicare Claims Processing, Medicare Coverage, Responding to Medicare Denials, Medicare Claims Adjudication, Medicare Billing, Medicare Coverage Rules, Denial Codes Guide, Medicare Benefits, Medical Billing and Coding Mastering Medical Prior Authorization Appeals: A Step-by-Step Guide to Overturning Denials5/16/2023 Mastering Medical Prior Authorization Appeals: A Step-by-Step Guide to Overturning Denials Learn how to effectively appeal a medical prior authorization denial with our comprehensive guide, including tips, templates, and resources to navigate the process with ease. Are you struggling with a medical prior authorization denial? You're not alone. Many healthcare providers and patients find themselves in this frustrating situation. But don't lose hope! Our step-by-step guide will help you effectively appeal the denial and improve your chances of getting the necessary treatment or service authorized. At GoHealthcare Practice Solutions, we specialize in simplifying the complex world of medical billing and prior authorizations. Visit our website at https://www.gohealthcarellc.com for more information on our services. Step 1: Understand the Denial Reason Before you can appeal a denial, you need to understand why it was denied. The denial letter should clearly state the reason, which may include lack of medical necessity, incorrect or incomplete information, or procedural errors. If the reason is unclear, contact the insurance company for clarification. Step 2: Gather Supporting Documentation To build a strong appeal, gather all relevant medical records, clinical notes, and any additional supporting documents. This may include:
Step 3: Write a Clear and Concise Appeal Letter Compose an appeal letter that clearly explains the reason for the appeal, why the service or treatment is medically necessary, and how it aligns with the patient's health plan benefits. Use persuasive language and be sure to reference any supporting documentation. Step 4: Submit the Appeal Follow the insurance company's guidelines for submitting the appeal, which should be detailed in the denial letter. This may include submission via mail, fax, or an online portal. Make sure to keep copies of all documents and confirm receipt of your appeal. Step 5: Follow Up Regularly follow up with the insurance company to check on the status of your appeal. Be prepared to provide additional information or clarification if requested. Step 6: Escalate if Necessary If the initial appeal is denied, consider escalating the case to an external review, if applicable. This process may involve an independent third-party reviewer who will examine the case and make a determination. Step 7: Seek Professional Assistance If you're still having difficulty with the appeal process or simply need guidance, consider seeking professional assistance from a medical billing specialist or a healthcare advocate. GoHealthcare Practice Solutions offers expert services to help healthcare providers navigate the complex world of medical billing and prior authorizations. While appealing a medical prior authorization denial can be challenging, following this step-by-step guide can improve your chances of success. Always remember to be persistent, keep accurate records, and don't hesitate to seek professional help if needed. Top 10 Medical Practice Management Software to Transform Your Healthcare Facility in 2023 Discover the best medical practice management software in 2023 that can help streamline your healthcare facility's operations and improve patient care with advanced features and user-friendly interfaces. As medical practices continue to embrace technology to improve their operations and patient care, the demand for effective medical practice management software (MPM) has skyrocketed. In this blog post, we'll explore the top 10 MPM software solutions that are transforming healthcare facilities in 2023. Kareo(https://www.kareo.com) Kareo is a comprehensive and user-friendly MPM software designed for independent practices. With features such as billing, scheduling, and electronic health records (EHR) integration, Kareo streamlines your administrative tasks and enhances patient care. AdvancedMD (https://www.advancedmd.com) AdvancedMD is an all-in-one MPM software that offers robust EHR and practice management solutions. Its automation and reporting features simplify administrative tasks, allowing healthcare providers to focus on patient care. athenahealth (https://www.athenahealth.com)athenahealth is a cloud-based MPM software that offers a full suite of services, including EHR, billing, and patient engagement. Its intuitive interface and data-driven insights make it a top choice for healthcare facilities of all sizes. DrChrono (https://www.drchrono.com) DrChrono is an innovative MPM software that offers flexible, customizable solutions for EHR, medical billing, and practice management. With its mobile-first approach, DrChrono allows providers to manage their practice on the go. CareCloud (https://www.carecloud.com) CareCloud offers a user-friendly, cloud-based MPM software that helps practices improve efficiency, increase revenue, and enhance the patient experience. Its advanced analytics and reporting tools provide valuable insights for practice growth. Greenway Health (https://www.greenwayhealth.com) Greenway Health is a comprehensive MPM software that offers an integrated EHR, billing, and practice management solution. Its user-friendly interface and customizable features make it suitable for practices of all sizes. eClinicalWorks (https://www.eclinicalworks.com) eClinicalWorks provides a robust MPM software that offers EHR, practice management, and billing solutions. Its cutting-edge technology and telehealth capabilities make it a popular choice for modern healthcare practices. NextGen Healthcare (https://www.nextgen.com) NextGen Healthcare offers a powerful MPM software with integrated EHR, practice management, and billing solutions. Its wide range of features and scalable options cater to practices of all sizes and specialties. Practice Fusion (https://www.practicefusion.com)Practice Fusion is a cloud-based MPM software that provides EHR, practice management, and billing solutions in one platform. Its intuitive design and affordable pricing make it an excellent option for small to medium-sized practices. PrognoCIS (https://www.prognocis.com) PrognoCIS is a customizable MPM software that offers EHR, billing, and practice management solutions. Its seamless integration and advanced features make it a reliable choice for healthcare facilities looking to improve their operations. In conclusion, medical practice management software has become an essential tool for healthcare facilities looking to streamline their operations and improve patient care. By exploring the top 10 MPM software solutions mentioned above, you can find the perfect fit for your practice and take your facility to new heights. 10 Proven Tips for Streamlining the Medical Prior Authorization Process for Healthcare Providers5/15/2023 10 Proven Tips for Streamlining the Medical Prior Authorization Process for Healthcare Providers Learn the top 10 tips to expedite the medical prior authorization process for healthcare providers, boosting efficiency and patient satisfaction. Medical prior authorization can be a time-consuming and challenging process for healthcare providers. To help you expedite this process and improve your practice's efficiency, we've compiled a list of 10 actionable tips. Implement these strategies to streamline your medical prior authorization process and provide better care to your patients.
By implementing these tips, healthcare providers can expedite the medical prior authorization process, improve patient satisfaction, and boost practice efficiency. Healthcare Data Analytics: Unlocking Insights to Improve Patient Care Discover how healthcare data analytics can help medical professionals make informed decisions and improve patient care. Learn the benefits and best practices of data analysis in the healthcare industry. Healthcare data analytics is a growing field that uses data analysis and insights to improve patient care and medical practice management. In today's data-driven world, it's more important than ever for healthcare providers to leverage data to make informed decisions and improve patient outcomes. In this article, we will explore the benefits and best practices of healthcare data analytics. Benefits of Healthcare Data Analytics
Enhanced Risk Management: Data analytics can help identify and mitigate risks, such as medical errors, adverse events, and fraud, leading to improved patient safety. Best Practices for Healthcare Data Analytics
Healthcare data analytics has the potential to transform the healthcare industry by improving patient care, reducing costs, and enhancing resource utilization. By following best practices and using the right tools, healthcare providers can unlock insights from their data and make informed decisions. |

ABOUT THE AUTHOR:
Ms. Pinky Maniri-Pescasio is the Founder of GoHealthcare Consulting. She is a National Speaker on Practice Reimbursement and a Physician Advocate. She has served the Medical Practice Industry for more than 25 years as a Professional Medical Practice Consultant. search hereArchives
July 2024
Categories
All
BROWSE HERE
All
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- About
- Leadership
- Contact Us
- Testimonials
- READ OUR BLOG
-
Let's Meet in Person
- 2023 ORTHOPEDIC VALUE BASED CARE CONFERENCE
- 2023 AAOS Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- 2023 ASIPP 25th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Interventional Pain Management
- 2023 Becker's 20th Annual Spine, Orthopedic & Pain Management-Driven ASC Conference
- 2023 FSIPP Annual Conference by FSIPP FSPMR Florida Society Of Interventional Pain Physicians
- 2023 New York and New Jersey Pain Medicine Symposium
- Frequently Asked Questions and Answers - GoHealthcare Practice Solutions
- Readers Questions
Photos from shixart1985 (CC BY 2.0), www.ilmicrofono.it, shixart1985
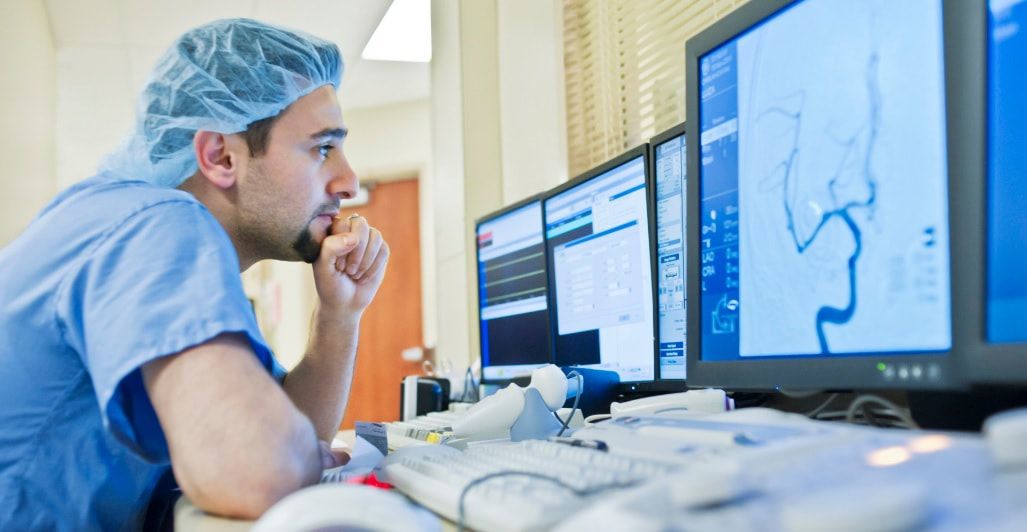























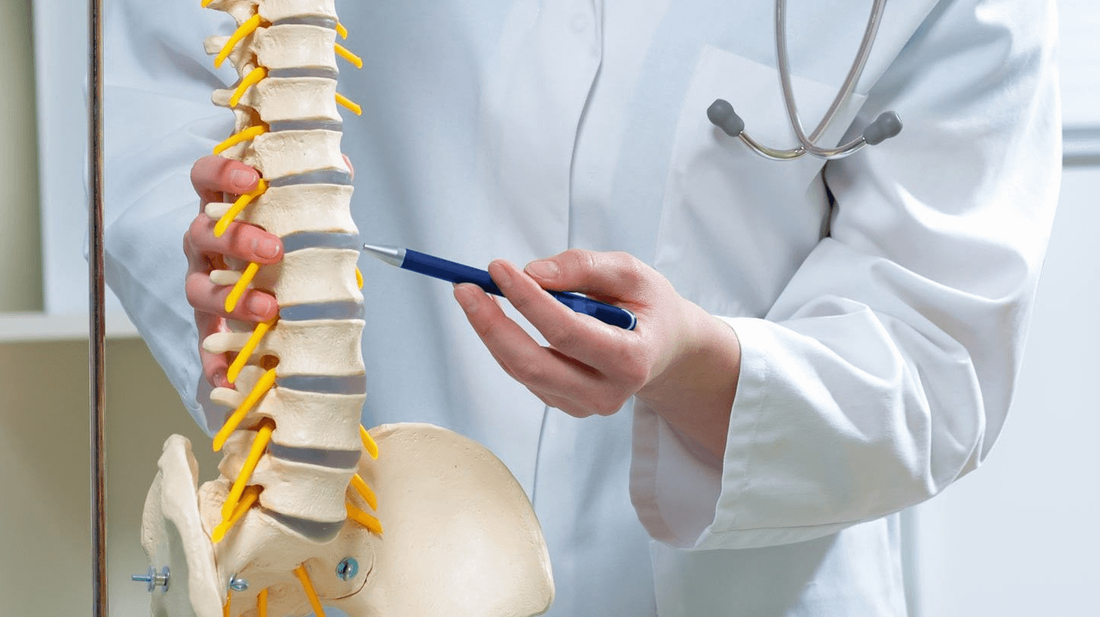


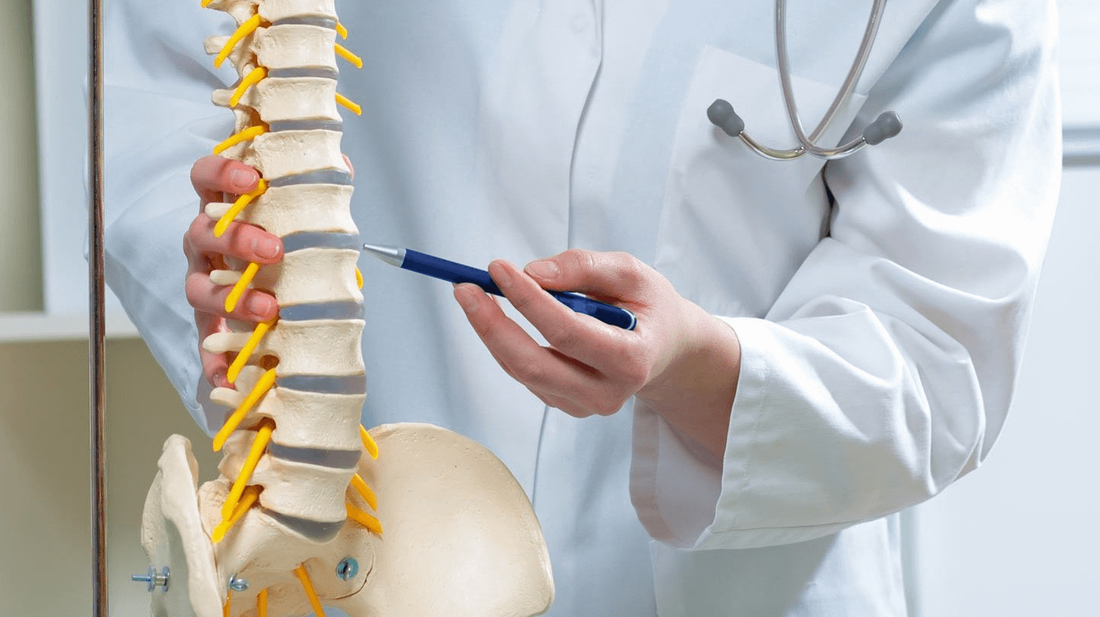









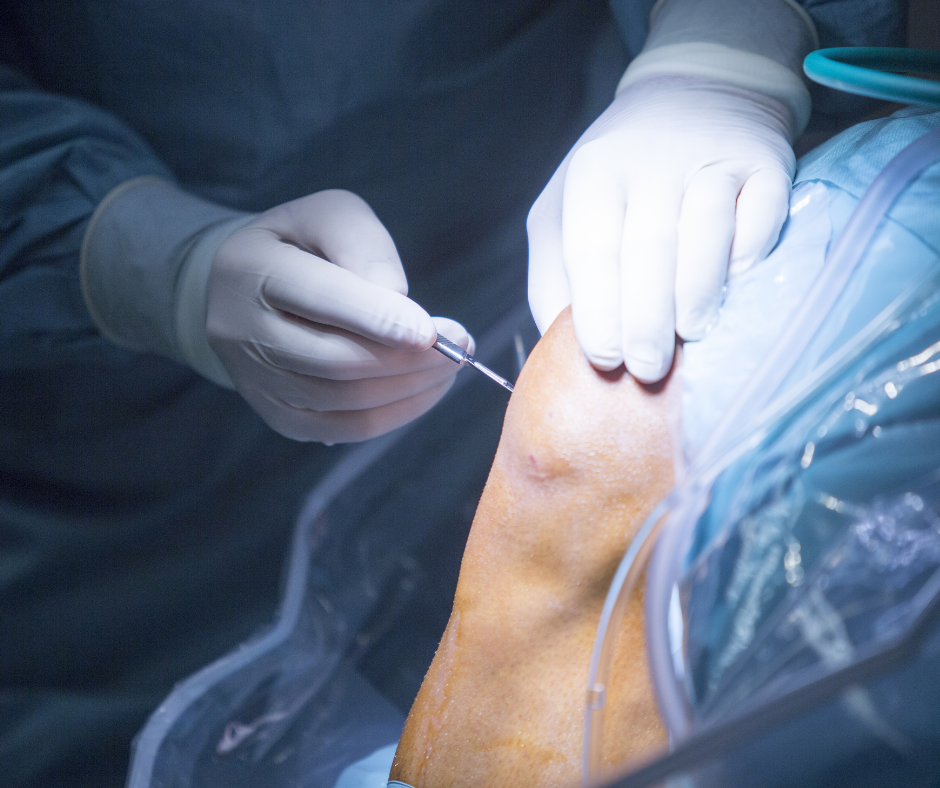






















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed