Billing and Coding for Orthopedic Spinal Fusion Let's begin with some terminology to remember;
Understanding the Posterior Lumbar Interbody Spinal Fusion 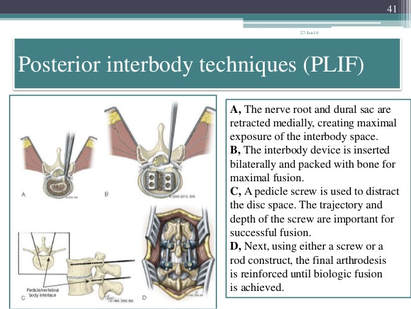 Techniques:
Image Source: https://www.slideshare.net/drpraveenktripathi/lumbar-interbody-fusion-indications-techniques-and-complications
Your CPT® Codes for PLIF and TLIF Spinal Fusion Coding: CPT Code 22630, +22632 22630 Arthrodesis, posterior interbody technique, including laminectomy and/or discectomy to prepare interspace (other than for decompression), single interspace; lumbar +22632 Each Additional interspace (list separately in addition to code for primary procedure code) Here's what occurs when 22630 is performed: The provider performs an arthrodesis, also known as spinal fusion, in the lumbar spine, or lower back, to permanently join two vertebrae, the interlocking bones of the spine. He excises the lamina and disk material and applies bone graft between the disks to fuse them. The procedure helps to alleviate persistent pain caused by various spinal conditions, including herniated intervertebral disks, stenosis, or spinal injuries. Then, in 2012 Code 22633 was introduced to to represent the combination of 22630 and 22612 Arthrodesis, posterior or posterolateral technique, single level; lumbar (with lateral transverse technique, when performed) at the same level. The Anterior Interbody Fusion Approach
Videos to watch for Procedure PLIF and TLIF Your CPT® Codes for ALIF, DLIF and OLIF Spinal Fusion Coding: CPT Code 22558, +22585 22558 Arthrodesis, anterior interbody technique, including minimal discectomy to prepare interspace (other than for decompression); lumbar Remember: (For arthrodesis using pre-sacral interbody technique, see 22586, 0195T) +22585 Arthrodesis, anterior interbody technique, including minimal discectomy to prepare interspace (other than for decompression); each additional interspace (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Remember: (Use 22585 in conjunction with 22554, 22556, 22558) (Do not report 22585 in conjunction with 63075, even if performed by a separate individual. To report anterior cervical discectomy and interbody fusion at the same level during the same session, use 22552) Here's what occurs when 22558 is being performed: The provider performs arthrodesis, also known as spinal fusion, in the lower back, to permanently join two vertebrae, the interlocking bones of the spine, to alleviate persistent pain caused by a herniated, or bulging, disk, or other spinal condition. He makes an incision in the abdomen to access the spine and remove disk material. Instrumentation may be required to stabilize the Spinal Fusion POSTERIOR INSTRUMENTATION: Add-Code +22840 Posterior non-segmental instrumentation (eg, Harrington rod technique, pedicle fixation across 1 interspace, atlantoaxial transarticular screw fixation, sublaminar wiring at C1, facet screw fixation) (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use 22840 in conjunction with 22100-22102, 22110-22114, 22206, 22207, 22210-22214, 22220-22224, 22310-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040-63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081, 63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290, 63300-63307) Add-On Code +22841 Internal spinal fixation by wiring of spinous processes (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Add-On Code +22842 Posterior segmental instrumentation (eg, pedicle fixation, dual rods with multiple hooks and sublaminar wires); 3 to 6 vertebral segments (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Use 22842 in conjunction with 22100- 22102, 22110- 22114, 22206, 22207, 22210- 22214, 22220-22224, 22305-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040-63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081, 63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290, 63300- 63307)Text has been updated Add-On Code +22843 7 to 12 vertebral segments (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use 22843 in conjunction with 22100- 22102, 22110-22114, 22206, 22207, 22210- 22214, 22220-22224, 22305-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040-63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081,63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290,63300- 63307)Text has been updated Add-On Code +22844 13 or more vertebral segments (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use 22844 in conjunction with 22100- 22102, 22110-22114, 22206, 22207, 22210- 22214, 22220-22224, 22305-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040-63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081, 63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290, 63300- 63307) ANTERIOR INSTRUMENTATION Add-On Code +22845 Anterior instrumentation; 2 to 3 vertebral segments (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use 22845 in conjunction with 22100- 22102, 22110-22114, 22206, 22207, 22210- 22214, 22220-22224, 22305-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040-63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081,63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290,63300- 63307)Text has been updated Add-On Code +22846 4 to 7 vertebral segments (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Use 22846 in conjunction with 22100- 22102, 22110-22114, 22206, 22207, 22210- 22214, 22220-22224, 22305-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040-63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081, 63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290, 63300- 63307)Text has been updated Add-On Code +22847 8 or more vertebral segments (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use 22847 in conjunction with 22100-22102, 22110-22114, 22206, 22207, 22210-22214, 22220-22224, 22305-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040- 63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081, 63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290,63300-63307)Text has been updated Add-On Code +22848 Pelvic fixation (attachment of caudal end of instrumentation to pelvic bony structures) other than sacrum (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) (Use 22848 in conjunction with 22100- 22102, 22110-22114, 22206, 22207, 22210- 22214, 22220-22224, 22305-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040-63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081, 63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290, 63300- 63307)  Co-Surgeon Modifier 62 may not be appended with your Instrumentation Codes! Spinal Prosthetic Devices may also be required to be reported CPT Code 22853 22853 Insertion of interbody biomechanical device(s) (eg, synthetic cage, mesh) with integral anterior instrumentation for device anchoring (eg, screws, flanges), when performed, to intervertebral disc space in conjunction with interbody arthrodesis, each interspace (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Notes: (Use 22853 in conjunction with 22100-22102, 22110-22114, 22206, 22207, 22210-22214, 22220-22224, 22310-22327, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812, 63001-63030, 63040-63042, 63045-63047, 63050-63056, 63064, 63075, 63077, 63081, 63085, 63087, 63090, 63101, 63102, 63170-63290, 63300-63307) (Report 22853 for each treated intervertebral disc space) Code +22853 is one of several new codes within the spine section for the insertion of biomechanical devices that replace deleted code +22851 (Application of intervertebral biomechanical device[s] ...). The new add-on codes are more specific regarding the type and location of the biomechanical devices. CPT® guidelines direct you to report +22853 for each treated intervertebral disc space. Report +22853 in addition to the definitive procedure(s) since it is an add-on code. Do not append modifier 62 (Two surgeons) to 22853. The provider inserts a metallic cage or mesh device between two vertebrae and may use screws or flanges to attach it to the front part of the vertebrae; the device maintains the disc space, provides spinal stability, and yet preserves some range of motion, which helps relieve persistent pain caused by a herniated, or bulging, disk or other spinal condition. The provider performs this procedure during a spinal interbody arthrodesis procedure, which is fusion, or permanent joining, of vertebrae over the joint space. Remember! Code +22853 is an add–on code and must be reported with an appropriate primary procedure, such as 22548–22586 (Anterior or anterolateral approach technique arthrodesis procedures on the spine [vertebral column]), but there are many other codes that can be reported as a primary code. Report one unit of this code for each interspace treated, not for the number of devices inserted. For example, if the provider inserts two cages into a single interspace, you report this code only once. If the provider inserts a device at two separate interspaces, e.g., between C3–4 and C5–6, then you would report this code twice. This code is for the application of a device to expand or maintain an intervertebral disc space. For a similar procedure to cover a defect created by removal of a vertebral body, report 22854 (Insertion of intervertebral biomechanical device(s) [e.g., synthetic cage, mesh] with integral anterior instrumentation for device anchoring [e.g., screws, flanges], when performed, to vertebral corpectomy[ies] [vertebral body resection, partial or complete] defect, in conjunction with interbody arthrodesis, each contiguous defect [List separately in addition to code for primary procedure]). For insertion of a similar device to treat an intervertebral disc space or vertebral body removal defect but without interbody fusion (arthrodesis), report 22859 (Insertion of intervertebral biomechanical device[s] [e.g., synthetic cage, mesh, methylmethacrylate] to intervertebral disc space or vertebral body defect without interbody arthrodesis, each contiguous defect [List separately in addition to code for primary procedure]). Report Bone Grafting if allowable, CPT Code 20930 20930 Allograft, morselized, or placement of osteopromotive material, for spine surgery only (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Notes: (Use 20930 in conjunction with 22319, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812) Here's what occurs when 20930 is being performed; The provider applies small pieces of donor or synthetic bone graft material during a spinal surgery to encourage bone growth during the healing period. Coding Tip! Code 20930 is an add on code and used for specified spinal procedures only. Check with your payer to determine if 20930 can be billed separately or if the application of the bone graft material is included in the code for the primary surgical procedure. Do not append modifier 62 to bone graft codes 20900-20938. (For spinal surgery bone graft[s] see codes 20930-20938) Check with your payer if you can separately report this code; +20931 Allograft, structural, for spine surgery only (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Notes: (Use 20931 in conjunction with 22319, 22532-22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812) A provider uses a structural allograft, a type of donor bone, to fill in bony defects as she performs a spinal surgery procedure. Coding Tips: Code 20931 is an add on code describing application of structural allograft to spinal defects and must be reported with an allowable primary spinal procedure code. Report 20930, Allograft, morselized, or placement of osteopromotive material, for spine surgery only, together with 20931 only in the case of a human donor who is a different person from the recipient. You should never append modifier 50, Bilateral procedure, to 20931. The CMS Physician Fee Schedule Database includes a 9 indictor in the BILAT SURG column for this code. According to further CMS instructions, a 9 indicator in this column means that the concept of a bilateral surgery with spinal grafting does not apply. +20936 Autograft for spine surgery only (includes harvesting the graft); local (eg, ribs, spinous process, or laminar fragments) obtained from same incision (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Notes: (Use 20936 in conjunction with 22319, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812) A provider uses an autograft, a type of donor bone, to fill in bony defects as she performs a spinal surgery procedure. She extracts the autograft from the patient’s own bone, taken from the same surgical incision. Coding Tips: Code 20936 is an add on code describing grafting from a donor area using the same incision during a major operative procedure and must be reported with an allowable primary spinal procedure code. You should never append modifier 50, Bilateral procedure, to 20936. The CMS Physician Fee Schedule Database includes a 9 indictor in the BILAT SURG column for this code. According to further CMS instructions, a 9 indicator in this column means that the concept of a bilateral surgery with spinal grafting does not apply. +20937 Autograft for spine surgery only (includes harvesting the graft); morselized (through separate skin or fascial incision) (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Notes: (Use 20937 in conjunction with 22319, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812) The provider uses an autograft, a type of donor bone, to fill in bony defects as she performs a spinal surgery procedure. She extracts the autograft from the patient’s own body during the surgical procedure, through a separate incision. Coding Tips: Code 20937 is an add on code describing preparation and application of a morselized autograft through a separate skin incision and must be reported with an allowable primary spinal procedure code. *** A vertebral segment describes the basic constituent part into which the spine may be divided. It represents a single complete vertebral bone with its associated articular processes and laminae. A vertebral interspace is the non-bony compartment between two adjacent vertebral bodies which contains the intervertebral disc, and includes the nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus, and two cartilaginous endplates. Autograft for spine surgery only (includes harvesting the graft); structural, bicortical or tricortical (through separate skin or fascial incision) (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure) Notes: (Use 20938 in conjunction with 22319, 22532, 22533, 22548-22558, 22590-22612, 22630, 22633, 22634, 22800-22812) (For aspiration of bone marrow for bone grafting, spine surgery only, use 20939) The provider uses an autograft, a type of donor bone, to fill in bony defects as she performs a spinal surgery procedure. She extracts the autograft from the patient's own body during the surgical procedure, through a separate incision. Reporting Cosurgeries Source: CPT® Assistant July 1996 page 7 Coding Tip Reporting Cosurgeries "We receive many questions concerning how to report surgeries performed by more than one physician. To help you understand the proper coding we present the following information." The General Question "I am a general surgeon who sometimes performs surgeries with other surgeons (cosurgeries), such as orthopedic or neurosurgeons. I open the surgical site, the other surgeon does the definitive portion of the procedure, and then I close. What CPT codes should I report for my services? I have heard from some sources that I should bill for a thoracotomy and wound repair. But other sources have told me to report the same CPT codes as the other surgeon. Which is correct? CPT® ASSISTANT'S REPLY: Here's How to Code: "For situations in which one surgeon performs the opening and closing of a surgery and another physician performs the definitive portion of the procedure, both physicians should report the same CPT codes, and appropriately append either modifier -62 or modifier -66." Illustration A patient's surgery includes arthrodesis of two interspaces of the thoracic spine by anterior interbody technique, with anterior instrumentation of three vertebral segments. Physician "A" performs a thoracotomy at the start of the surgical session, and Physician "B" performs the arthrodesis and spinal instrumentation. Upon completion of the arthrodesis and spinal instrumentation, Physician A closes the operative site. Coding the Illustration (The physicians in the illustration would report the codes indicated below.) Physician A 22556-62 Physician B 22556-62 22558-62 22558-62 22845-62 22845-62 When performing these cosurgeries, it is important to communicate with the other surgeon's office to be certain that you submit the claims properly  CPT® Guideline September 1997 page 8 Coding Communication How to Code Prosthetic Devices It is not often that we devote an entire article to a single code, but sometimes this is the only way to fully explain the use of certain codes-22851, application of prosthetic device (eg, metal cages, methylmethacrylate) to vertebral defect or interspace, is such a code. But before we review how to report this code, it is probably a good idea to first do a brief anatomical review of the vertebral column. The vertebral column (spine) consists of a series of bones known as vertebrae. An adult human possesses 33 vertebrae divided into the following five types: 7 cervical vertebrae; 12 thoracic vertebrae; 5 lumbar vertebrae; 5 sacral vertebrae; and 4 coccygeal vertebrae. The sacral vertebrae are typically fused into a single bone known as the sacrum. The coccygeal vertebrae are sometimes fused into a single bone known as the coccyx. Therefore, the actual number of bones in the vertebral column may be 26-29, depending on if the coccygeal vertebrae are fused. Vertebrae are commonly named by a letter that corresponds to the region of the vertebral column to which the vertebrae belongs, followed by a number that indicates where in the region the vertebrae is located. For example, the most superior cervical vertebra is called C1, with the next cervical vertebrae down designated C2. The most superior thoracic vertebrae is T1, with the next one down designated T2. Fig. 1 - Spinal Prosthetic Devices Between each pair of vertebrae is a disc that cushions the spinal column. If one of the discs degenerates or if one of the 26-29 vertebrae are injured (as in the case of a fracture, degenerative disease, or secondary to tumor destruction) the physician may need to place a prosthetic device (eg, metal cages or methyl-methacrylate) in the vertebral defect or interspace. (Fig. 1) In these instances, a segment of vertebral level may be drilled and metal cages packed with porous implants of bone graft may be inserted or methylmethacrylate may be placed between the affected vertebrae. Proper Reporting of code 22851 It is important to note that CPT® code 22851 is not intended to be reported per cage. CPT® code 22851 should only be reported one time, regardless if one or more metal cages are placed in the intervertebral space at the same level. However, if metal cages are placed at two different levels, (eg, metal cage placed at L3-4 interspace and L5-S1 interspace), then 22851 may be reported more than once to indicate that one or more cages were placed at two or more different levels. It is important to note that a single cage or methylmethacrylate can cover a defect of several vertebral segments (eg, a single cage may replace three entire vertebrae), wherein code 22851 would still only be reported one time. Within the spine section, instrumentation procedure codes (22840-22855) are reported in addition to the definitive procedure(s) without appending the modifier -51. Therefore, if arthrodesis is performed in addition to the placement of the metal cages, then it would be appropriate to report code 22851 in addition to the appropriate arthrodesis code, 22548-22632. In this instance, the modifier -51 would not be appended to code 22851. If metal cages are placed through an anterior approach and pedicle screws are placed through a posterior approach, it would be appropriate to report both code 22851 and one of the codes from the posterior instrumentation series, 22840, 22842-22844. However, if different instrumentation is used in addition to the metal cages or methylmethacrylate through the same approach (eg, an anterior plating system) or pedicle screws and posterior lumbar interbody fusion utilizing cages), then the appropriate instrumentation code would be reported in addition to code 22851. However, 22851 and 22845 should not both be reported if only the metal cage is inserted. If fracture treatment, dislocation, or arthrodesis is performed in addition to spinal instrumentation, then the appropriate fracture treatment, dislocation or arthrodesis code (22325, 22326, 22327, 22548-22812) would be reported separately in addition to code 22851. In this instance, CPT® code 22851 would be reported in addition to the definitive procedure(s) without the modifier -51 appended. If bone grafting is performed in addition to code 22851, then the appropriate bone grafting code, 20930-20938, would be reported additionally. Clinical Sample: CPT® Code 22851 A 50-year-old man undergoes an anterior fusion of L5-S1 for degenerative disease. A retroperitoneal incision is made and an arthrodesis performed using a BAK cage. A distracter is placed in the interspace, a hole is drilled in the interspace, and the BAK cage is placed in the hole. The spacer is removed and replaced with another BAK cage. Both cages are filled with bone graft. (Report arthrodesis and/or bone grafting separately using the appropriate CPT code[s]). The exposed disk space and adjacent vertebrae are prepared with bone-cutting instruments for acceptance of the prosthetic device. Preparation of the recipient site is made according to the protocol of the particular device. If methylmethacrylate is to be used, a screw or pin may be inserted into the adjacent vertebral surfaces to anchor the methylmethacrylate. Provision is made for cooling of adjacent tissues and protection of heat sensitive tissue from the exothermic reaction of the curing of the methylmethacrylate. For cages, the recipient site is prepared by bone dissection, a trial fit with the device or a spacer or template as indicated by the protocol is inserted and removed for any final modifications of the recipient site. The prosthetic device is then screwed, impacted, or injected into place according to protocol for this particular device. (Additional fixation, other provision for arthrodesis, or bone grafting are coordinated with the placement of the prosthetic device and are coded separately.) For devices that incorporate graft material, that material is appropriately placed into the device prior to its final insertion. CPT® ASSISTANT September 2000 page 10 Coding Consultation Musculoskeletal System, Surgery, 22548-22585, 22899 (Q&A) Question "Should I use the anterior or anterolateral approach technique arthrodesis series of codes (22548-22585) to report intra-abdominal laparoscopic, video assisted anterior interbody fusion?" AMA CPT® Comment "The anterior or anterolateral approach technique arthrodesis series of codes (22548-22585) are intended to describe arthrodesis performed via an open surgical approach. There is not a specific CPT code that accurately describes laparoscopic anterior interbody fusion. Therefore, code 22899, Unlisted procedure, spine should be reported. When reporting an unlisted code to describe a procedure or service, it will be necessary to submit supporting documentation (eg, procedure report) along with the claim to provide an adequate description of the nature, extent, need for the procedure, and the time limit, effort, and equipment necessary to provide the service." CPT® ASSISTANT March 2015 page 9 Frequently Asked Questions:Surgery: Musculoskeletal System Question: "Are CPT codes 22851 and 22845 appropriate to report when modular implants, such as the RSB (RSB LLC; Cleveland, OH) InterPlate® (a modular interbody platform technology), are implanted for spinal fusion procedures?" Answer: "No. The RSB InterPlate® describes a stand-alone interbody fusion device that consists of an interbody spacer with screw fixation or other mechanisms, which engage adjacent vertebrae. Such devices should be reported with code 22558, Arthrodesis, anterior interbody technique, including minimal discectomy to prepare interspace (other than for decompression); lumbar, and 22851, Application of intervertebral biomechanical device(s) (eg, synthetic cage(s), methylmethacrylate) to vertebral defect or interspace (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure). An additional anterior instrumentation code (22845) is not applicable because there is no separate construct placed across the vertebral segment." Question: "Would it be appropriate to separately report any of the following with the hammertoe correction code 28285 (2nd digit), if adequately documented? (1) Resection of hypertrophied base of proximal phalanx (28126), if performed through a separate incision at the metatarsophalangeal (MTP joint); (2) flexor tenotomy (28232) performed through a separate incision at the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint; (3) an additional unit of 28285 if K-wire is inserted through the DIP, MTP, or proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joint." Answer: "No. Code 28126, Resection, partial or complete, phalangeal base, each toe; code 28232, Tenotomy, open, tendon flexor; toe, single tendon (separate procedure); and the insertion of K-wire through DIP, PIP, and MTP joints are all inclusive components of the procedure described by code 28285, Correction, hammertoe (eg, interphalangeal fusion, partial or total phalangectomy), and should not be reported separately." References: 2020 AMA's CPT® Guidelines 2019 AMA's CPT® Guidelines 2018 AMA's CPT® Guidelines 2017 AMA's CPT® Guidelines CPT® Assistant Archives Websites: NASS Spine-Health Medtronic Ahima AAPC CMS All other commercial payers clinical guidelines from the public domains on the internet Read more blog posts:
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |

ABOUT THE AUTHOR:
Ms. Pinky Maniri-Pescasio is the Founder of GoHealthcare Consulting. She is a National Speaker on Practice Reimbursement and a Physician Advocate. She has served the Medical Practice Industry for more than 25 years as a Professional Medical Practice Consultant. search hereArchives
July 2024
Categories
All
BROWSE HERE
All
|
- About
- Leadership
- Contact Us
- Testimonials
- READ OUR BLOG
-
Let's Meet in Person
- 2023 ORTHOPEDIC VALUE BASED CARE CONFERENCE
- 2023 AAOS Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- 2023 ASIPP 25th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Interventional Pain Management
- 2023 Becker's 20th Annual Spine, Orthopedic & Pain Management-Driven ASC Conference
- 2023 FSIPP Annual Conference by FSIPP FSPMR Florida Society Of Interventional Pain Physicians
- 2023 New York and New Jersey Pain Medicine Symposium
- Frequently Asked Questions and Answers - GoHealthcare Practice Solutions
- Readers Questions
Photos from shixart1985 (CC BY 2.0), www.ilmicrofono.it, shixart1985



 RSS Feed
RSS Feed